Contents
Tapeworm
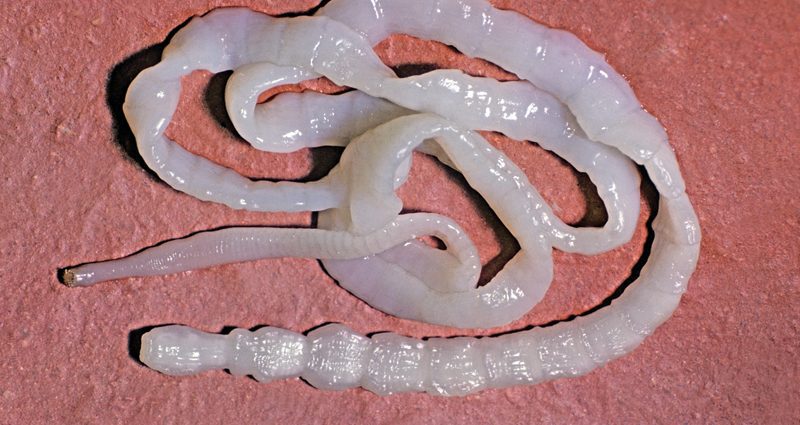
Tapeworm, also called tapeworm or taenia, designates a see parasite, of the Cestodes class, which develops in the intestine human hail where it can live for 30 to 40 years, sometimes causing disturbances. Flat and segmented in shape, with the appearance of a ribbon, the tapeworm is hermaphroditic and can measure up to 10 meters in length at adult size.
Causes of tapeworm
These parasitic worms are transmitted via eating meat infected with live larvae : beef or pork, usually raw or undercooked. For humans, these infesting forms are called cysticerci. They are present in the muscles of animals and therefore in their meat.
Two species of tapeworm can affect humans:
- le Taenia saginata (soft tapeworm), transmitted by beef, which is thought to be present in 0,5% of the French population.
- le The bathtub tape (armed tapeworm), which is transmitted to it via the pig (there are no longer cases described in France, even if it persists in certain countries of the European Union such as Poland).
Mode of infection and symptoms of tapeworm
Once ingested, the tapeworm larva attaches itself through its head to the wall of the small intestine. It develops there gradually thanks to the food ingested by the host and reaches its adult size in three months. The worm is then able to reproduce: it develops by making rings (segments) provided with a reproductive system.
Regularly, rings containing the eggs break free and are expelled through the anus. Tapeworm rings are flat, rectangular in shape and can measure up to 2 cm long by 6 to 8 mm wide. They are often described as resembling pasta.
The discovery of these rings in underwear, stools, sheets, or in the shower is often the first sign of the presence of the tapeworm in the body. The rings are often actively expelled because they are mobile, which is why they can be found outside the stool.
This is because the infection goes unnoticed in most cases and it is quite possible to harbor the parasite for years without realizing it.
However, several symptoms can be observed in certain subjects: abdominal pain, nausea, appetite disturbances, skin rashes, fatigue, headaches, etc.
Abnormal and rapid weight loss can also be a sign of the infection.
Tapeworm: treatment and complications
An antiparasitic drug (or dewormer) is usually prescribed to kill the tapeworm.
Two molecules are particularly effective and used:
- le praziquantel (BiltricideÒin single dose at 10 mg / kg),
- la niclosamide (TremedineÒ, 2 tab in the morning, then 2 tab 2 hours later; the latter is not available in all countries).
Once destroyed, the tapeworm is expelled with the stool by natural means.
Tapeworm: are there any complications?
The tapeworm is a relatively benign condition and complications linked to the parasite (appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, etc.) are very rare.
In the case of The bathtub tape; however, humans can themselves become an intermediate host through the accidental consumption of parasite eggs, which are present in the stools of other humans. The eggs ingested pass into the blood vessels and attach themselves to various muscle tissues, even in the brain, in the most severe cases, to form cysticerci (or larvae). We then speak of human cysticercosis, a serious pathology that leads to eye and neurological disorders.
How to prevent tapeworm?
The most important thing is to ensure prolonged freezing (- 10 ° C for 10 days minimum) or sufficient cooking of beef or pork, in order to destroy tapeworm larvae.
Consuming raw beef (steak tartare) is risky. Food hygiene measures must be observed in particular in regions of the world where health and veterinary controls are less developed.
Less commonly, other meats can transmit tapeworm saginata:
- sheep,
- caribou,
- the lamp
- the antelope,
- the wildebeest,
- the GIRAFE,
- the lemur,
- the gazelle,
- the camel…
It is important for humans not to place their stool within reach of animals such as cattle. This gesture could transmit the tapeworm saginata to them …
It is also important not to consume vegetables that may have been soiled by human excreta, because of the risk of human cysticercosis.
That is why human fertilizer is prohibited.
Complementary approaches to treat tapeworm
In herbal medicine, it is proposed to fight against tapeworm by proceeding as follows:
- Make a cure by consuming, during a day, only one or two liters of fruit juice (grape juice is suitable), possibly diluted with one or two liters of spring water.
- The next day, use the squash seeds (about 200 g for an adult man). Reduce the seeds to a powder and mix them with the same weight of liquid honey.
Take this preparation in the morning on an empty stomach, upon getting up. Repeat the operation after half an hour and then another 30 minutes later (i.e. three doses on the same day).
- Prepare in parallel a decoction (infusion time: 5 minutes) of a tablespoon of buckthorn bark for a cup of water, followed by two hours of infusion. Once the infusion is finished, you can drink it.
The tapeworm should disappear permanently 3 months later. If only the rings have been removed and not the head, it will be necessary to start again, this time by dividing the doses by 2 but by spreading the treatment over 3 days. The cure will be maintained during this period of time. The decoction does not take place until the third day.
You can also :
- for 2 days, make a monodiet of a seasonal fruit (preferably from organic farming and maximum 1 kg per day), the ideal remaining the grape. You can also opt for plums, figs or apples or do a complete fast.
- On the same two days, drink at will (in large quantities) a decoction of male fern root.