Symptoms of lichen plan
Lichen planus is a dermatosis that can affect the skin, mucous membranes and integuments (hair, nails)
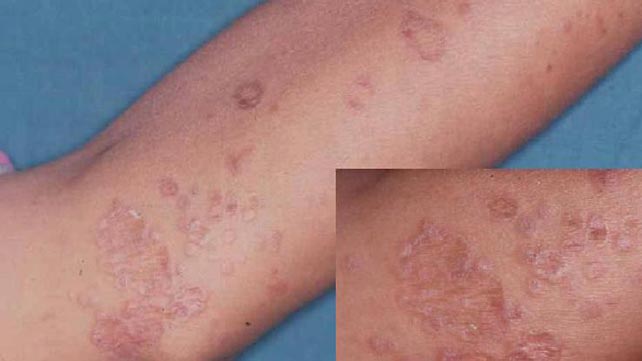
1 / Lichen cutané plan
Lichen planus is characterized by the appearance of papules (skin rises) of pinkish red then purple in color, crossed on the surface by fine grayish streaks features called Wickham’s streaks. They can be observed on all parts of the body, but they are preferentially found on the anterior sides of the wrists and ankles.
benefits linear lesions may appear along scratch marks or on scars, realizing the Koebner phenomenon.
Lichen planus papules itch almost constantly.
Then the purple papules collapse and give way to a residual pigmentation whose color varies from light brown to blue, even black. We are talking about pigmentogenic lichen planus
2 / Mucous lichen planus
It is estimated that about half of patients with cutaneous lichen planus have mucosal involvement associated. Lichen planus can also affect only the mucous membranes without skin involvement in ¼ of cases. The women are more often affected mucosally than men. The oral mucosa is most often affected, but all mucous membranes can be affected: the genital area, the anus, the larynx, the esophagus, etc.
2.A/ Lichen plan buccal
Oral lichen planus includes the following clinical forms: reticulate, erosive, and atrophic. Preferred locations are the jugal mucosa or tongue.
2.Aa / Reticulated buccal lichen planus
Reticulate lesions are typically without symptoms (without burning, itching …) and bilateral on both internal sides of the cheeks. They create a whitish network in ” fern leaf ».
2.A.b/ Lichen plan buccal érosif
Erosive lichen planus is characterized by eroded and painful mucous areas with sharp boundaries, covered with pseudomembranes, on a red background, whether or not associated with a reticulated lichenian network. It sits preferentially on the inner side of cheeks, tongue and gums.
2.A.c/ Lichen plan atrophique
Atrophic forms (the mucous membrane is thinner on areas of lichen) are more readily observed on gums that become irritated when brushing the teeth and the back of the tongue, causing depapillation, making the tongue more sensitive to spicy foods.
2.B / Genital lichen planus
Lichen planus involvement of the genitalia is very rarer than oral involvement. It affects both men and women and the affected areas are the inner surface of the labia majora and labia minora in women, the glans in men. The genital lesions are comparable to those of oral lichen planus (reticulated, erosive or atrophic forms). In women, we describe a vulvo-vagino-gingival syndrome, teaming up :
• erosive vulvitis, and sometimes a reticulate network around the lesions;
• erosive vaginitis;
• erosive sheet gingivitis, whether or not associated with other oral lichen lesions.
3. Phanereal involvement (hair, nails, hair)
3.A / Hair lichen planus: follicular lichen planus
Hair damage may appear during a typical outbreak of cutaneous lichen planus, in the form of small acuminate crusty points centered by the hairs, we speak of spinulosic lichen.
3.B / Lichen planus of the hair: lichen planus pilaris
On the scalp, lichen planus is characterized by areas of alopecia (areas without hair) scarring (the scalp is whitish and atrophic).
The syndrome Lassueur-Graham-Little associates an attack of the scalp, a spinulosic lichen, as well as a fall of the axillary and pubic hair.
A particular form of lichen planus pilaris has been identified in postmenopausal women over the age of 60:alopecia postmenopausal fibrous frontal, characterized by frontotemporal cicatricial alopecia in a crown at the edge of the scalp and eyebrow depilation.
3.C / Lichen planus of the nails: nail lichen planus
The nails are most often affected during severe and diffuse planar lichen. There is usually a thinning of the nail tablet preferentially affecting the big toes. Nail lichen planus can progress to destructive and irreversible pterygium-like lesions (the nail is destroyed and replaced by skin).