Contents
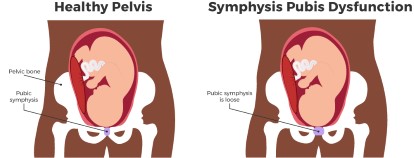
Symphysitis is a divergence of the pubic articulation during pregnancy, which can be manifested by pain and gait disturbance.
During pregnancy, a woman’s body is constantly changing. The hormonal background changes, the bones diverge, the uterus enlarges, and so on. This leads to increased pressure on the pelvic bones and tension in the pubic region. This is how symphysis occurs.
Symphysitis during pregnancy is a disease that is difficult to foresee. To identify it, a woman needs to regularly undergo medical examinations, monitor the level of vitamins and trace elements in the blood, and carefully study the symptoms of the disease.
About the disease
The difference between symphysitis (symphysiopathy) and the norm is determined by the distance between the right and left pubic bones of the small pelvis. With a normal pregnancy, the width of the pubic symphysis is up to 4-6 mm. If this distance increases, then the pregnant woman develops pubic-lumbar pain and lameness. These signs testify in favor of symphysitis, which is more correctly called symphysiopathy.
The fact is that one of the first hypotheses of pubic pain was an inflammatory theory. However, as it turned out later, the cause of this pathology is not associated with inflammation, but with metabolic disorders. In particular, this applies to deficiency of vitamin D, calcium and magnesium, which predispose to disruption of the structure of connective and cartilage tissue.
Symphysite classification
Traumatologists distinguish 3 degrees of symphysitis in pregnant women:
- The first degree, or stable damage, when the pubic bones have diverged from each other at a distance of no more than 20 mm.
- The second degree, or conditionally stable damage, when the interpubic distance is from 20 to 50 mm.
- Third degree, or unstable damage, when the discrepancy is more than 50 mm.
Clinical symptoms of symphysitis
Clinical signs of symphysitis depend on the severity of metabolic disorders. The main symptoms are:
- pain in the pubic region, which in severe cases also extends to the lower limbs and lower back;
- gait disturbance – from slight limping to complete immobility with a pronounced divergence of the pubic bones.
In addition, patients with symphysiopathy may have the following symptoms:
- “Crawling crawling” on the skin of the legs;
- muscle twitches;
- spasms of the muscles of the lower extremities.
Typically, these symptoms begin to appear after the 20th week of gestation. This is due to the fact that from about the second half of pregnancy, especially a lot of relaxin is synthesized. The formation of this hormone occurs first in the corpus luteum, and then in the uterine mucosa. Its main task is to prepare the birth canal for the upcoming birth. Under the influence of relaxin, the cervix softens and its “ripening”, which determines the readiness of the female body for the birth of a child. A “side effect” of relaxin may be its effect on the connective tissue of the pubic symphysis. If a pregnant woman has a vitamin-mineral imbalance, then excessive symphysis fibrillation may occur, which will lead to divergence of the bones and the appearance of appropriate symptoms.
In what trimester can symphysitis appear?
Symptoms of symphysitis appear as childbirth approaches. Most often by the end of the second and beginning of the third trimester. In some women, the pain syndrome persists even after childbirth for several months. The main cause of symphysitis after childbirth is a hereditary predisposition. The second is a deficiency of vitamins and calcium.
Symphysitis symptoms
Symphysis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain of varying severity and localization;
- swelling in the area of the pubic joint;
- gait changes;
- constant feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area;
- inability to perform certain movements.
As a rule, painful sensations are aggravated during physical exertion: when changing the position of the body, when walking, when climbing stairs (1).
Pain sensations
The main manifestation of the disease is pain. It can be weak and intensify only during sudden movements, or it can be acute and appear even at rest. Usually pain syndrome occurs locally in the pelvis or lower extremities. But sometimes a woman experiences shooting or pulling pains in the lower back, coccyx, hips or lower extremities. Soreness with symphysitis can be aggravated at night, during physical activities, when performing certain movements.
Puffiness
With symphysitis, swelling may occur in the area of the pubic joint. At first, it is insignificant, but with the progression of the disease, the edema can become stronger.
Gait changes
Painful sensations can also affect a woman’s gait. With severe symphysitis, a change in gait or even lameness is possible. Sometimes while walking, crackling, clicking and grinding can be heard.
Constant feeling of heaviness in the pelvis
The feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area refers to the subjective symptoms of symphysitis. It is impossible to make a diagnosis on this basis alone.
Limited movement
The inability to perform various movements, for example, to raise straight legs in a prone position, is another symptom of the disease. If, due to sharp pain, a woman cannot perform her usual actions, this is a serious reason to see a doctor.
Diagnosis of symphysis
You can diagnose symphysitis with the help of a gynecological examination, ultrasound of the pubic joint, x-ray of the pelvic bones and a biochemical blood test. Ultrasound will help to identify not only the disease itself, but also its stage (2).
Obstetrician-gynecologist Natalia Osokina explains:
– There are several degrees of symphysitis:
- 1 degree – a discrepancy of 5-9 mm: there are usually no complaints;
- Grade 2 – discrepancy 10-20 mm: mostly complaints of pain in the sacrum;
- Grade 3 – a discrepancy of more than 20 mm: women complain of severe pain, in which it is difficult to walk, move their legs, roll over.
Symphysitis treatment
Calcium preparations are often prescribed for the treatment of symphysitis. But only if a blood test shows its deficiency. In other situations, this is not recommended, since in the last months of pregnancy, calcium can do more harm than good.
A real salvation for symphysitis is a bandage. It supports muscles and relieves pain. Currently, there are also special corsets on sale that are designed to hold the pelvic bones.
For severe pain, the doctor may prescribe bed rest or hospitalization. The hospital usually prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs and physical therapy to help relieve pain.
Types of treatment for symphysitis
The program for the treatment of symphysitis in pregnant women is an orthopedic traumatologist. The choice of therapeutic tactics is determined by the degree of divergence of the pubic bones. So, with the first and second degree, conservative measures are sufficient, with the third, minimally invasive methods are shown.
Conservative treatment
Conservative therapy for pubic diastasis, which does not exceed 50 mm, includes wearing a fixing pelvic girdle. The bandage will be effective if it captures the skewers of the femur. Physiotherapy exercises, selected by a specialist, are also recommended. With severe violations of the function of the pubic symphysis, bed rest may be indicated. In the complex treatment of symphysitis, physiotherapy is widely used – magnetotherapy, calcium and phosphorus electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation.
To reduce the severity of pain are recommended:
- analgesics that are not contraindicated during pregnancy (in particular, Paracetamol, the dose of which is calculated by the doctor);
- applying cold;
- massage and taping of the pubic area, thighs and legs.
For the pathogenetic treatment of symphysiopathy of pregnant women, vitamin D, calcium and magnesium preparations are indicated. The optimal dose is selected by the doctor based on the results of laboratory tests.
Surgery
At the third degree, when the diastasis exceeds 50 mm, external fixation of the pubic bones is indicated. It helps to fully restore the musculoskeletal anatomy and provide an early load on the legs.
Causes
It is currently believed that the occurrence of symphysitis in pregnant women is associated with the action of 2 main factors. Thus, the hormones relaxin and progesterone, produced during pregnancy, predispose to defibration of the connective tissue. If a pregnant woman has a vitamin D deficiency in combination with a calcium-magnesium imbalance, then the situation is even more aggravated. These vitamin and mineral disorders underlie an even greater decrease in the strength of the connective tissue fibers that make up the pubic symphysis. As a result, the pubic bones move away from each other, which leads to compression of the nerve endings and the appearance of pain. The more the bones are separated, the more pronounced the gait disturbance.
The following factors increase the likelihood of developing symphysitis:
- young age – up to 25 years, when the formation of the extracellular matrix is higher than the rate of mineralization;
- nutritional features when a woman does not consume dairy products (the main source of calcium);
- excessive coffee consumption, which can disrupt the absorption of calcium and magnesium in the intestines;
- hypodynamia;
- chronic stressful situations;
- chronic pathologies of the digestive, endocrine and genitourinary systems;
- the use of thyroid hormones;
- living in regions with low insolation levels.
Prevention
Prevention of symphysiopathy should begin long before conception. At the stage of pregravid preparation, it is recommended to determine the level of vitamin D in the blood (an analysis called 25-hydroxycholecalciferol). If there is a deficiency or deficiency, then therapeutic doses of vitamin D are prescribed in combination with calcium and magnesium. At a normal level of 25-hydroxy-cholecalciferol in the blood, prophylactic doses of vitamin D are indicated.
After conception, pregnant women should discuss with the obstetrician-gynecologist the possibility of taking vitamin-mineral complexes. Unfortunately, modern food products are not able to meet the needs of maternal and fetal organisms in these nutrients. And, as you know, vitamin and mineral deficiency predisposes not only to dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system, but also to other systemic disorders that can also develop in children after birth.
Symphysitis Rehabilitation
The pathogenetic treatment of symphysitis prescribed during pregnancy is recommended for pregnant women to continue for several months after childbirth under the supervision of a specialist. This is due to the fact that the synthesis of relaxin in the body continues after delivery for 4-12 weeks. Premature withdrawal of vitamin and mineral preparations can lead to aggravation of clinical symptoms.
Popular questions and answers
Obstetrician-gynecologist Natalia Osokina answers frequently asked questions about symphysitis in pregnant women.
Is symphysitis an indication for a caesarean section?
How to relieve pain with symphysis?
What can and cannot be done with symphysis?
What are the symptoms that should promptly see a doctor?
- pulling shooting pains above the pubis – they can occur or intensify with movement, physical exertion;
- changes in gait;
- stiffness in movements, it is difficult to perform individual movements.
To check the condition, an ultrasound of the pubic joint is performed. In rare cases, radiography of the pelvic bones is used.
What can be done to prevent symphysitis?
Sources of
- E.V. Mozgovaya, A.G. Dedul, T.I. Oparina, N.N. Tkachenko. A new look at the causes of symphysiopathy in pregnant women and the search for effective methods of treatment. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/novyy-vzglyad-na-prichiny-razvitiya-simfiziopatii-u-beremennyh-i-poisk-effektivnyh-metodov-lecheniya
- L.S. Logutova, M.A. Chechnev, S.N. Lysenko, N.Yu. Cherkasov. Ultrasound diagnosis of the state of the pubic joint in women. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/ultrazvukovaya-diagnostika-sostoyaniya-lonnogo-sochleneniya-u-zhenschin-3