General description of the disease
It is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremors, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. This disease shares symptoms with Parkinson’s disease, from which it takes its name. However, “parkinsonism” is a separate set of symptoms that is still different from progressive and neurodegenerative Parkinson’s disease. The latter is the most common cause of the development of parkinsonism. However, a number of other causes can lead to its development, including toxins, certain metabolic diseases, and neurological conditions. This will be discussed in more detail below.
7% of people with parkinsonism develop this syndrome after taking specific medications. It can manifest itself as a side effect of neuroleptic antipsychotics, thioxanthenes, phenothiazines, and sometimes antidepressants.[1].
The reasons that provoke the onset of parkinsonism
Not everyone with Parkinson’s disease has Parkinson’s disease. There are many other causes of parkinsonism, including:
- medicines, for example, used to treat psychosis, underlying mental disorders and nausea;
- exposure to toxins such as carbon monoxide, cyanide and organic solvents;
- certain brain lesions, such as tumors or fluid accumulation;
- metabolic and other disorders such as chronic liver failure and hypoparathyroidism;
- brain trauma;
- diffuse Levy’s body disease;
- encephalitis;
- HIV AIDS;
- meningitis;
- multiple systemic atrophy;
- progressive supranuclear palsy;
- stroke;
- Wilson’s disease.
Other causes of secondary parkinsonism include:
- brain damage caused by drugs used for anesthesia;
- carbon monoxide poisoning;
- poisoning with mercury and other chemicals;
- drug overdose[3].
Parkinson’s symptoms
Most often, parkinsonism is characterized by the same symptoms as Parkinson’s disease. Among his symptoms are the following:
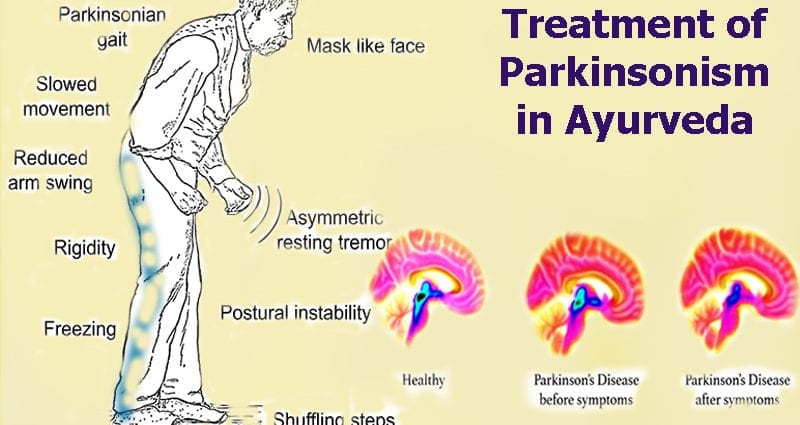
- 1 Tremor. Tremors or shaking usually begin in a limb, most often in the hand or fingers. One of the characteristic features of Parkinson’s disease is a tremor of the hand in a relaxed state (at rest).
- 2 Slow motion (bradykinesia). Over time, Parkinson’s disease can reduce a person’s ability to move and slow down, making simple tasks difficult and time-consuming. The sick person’s steps may become shorter or it may be difficult for them to get up from a sitting position.
- 3 Stiff muscles. Muscle stiffness can occur anywhere in the body. Tight, tight muscles can limit range of motion and cause pain.
- 4 Poor posture and balance. A person’s posture can become a stoop, or as a result, coordination is impaired.
- 5 Loss of automatic movements. With Parkinson’s disease, a person may have reduced or no ability to perform unconscious movements, including blinking, smiling, or waving their arms when walking.
- 6 Speech changes. A person with parkinsonism may speak softly, quickly, sloppily, or be embarrassed before speaking. Speech becomes more monotonous in most cases.[2].
Other symptoms that can also occur with parkinsonism include the following:
- noticeable memory loss that occurs during the first year of the disorder (including dementia);
- low blood pressure, difficulty swallowing, constipation, and trouble urinating (sometimes due to multiple systemic atrophy);
- hallucinations and visual-spatial problems (for example, with orientation in the house or in the parking lot at the very beginning of the development of the disease);
- abnormalities in eye movement[2].
Types of parkinsonism
Parkinsonism can be classified into three different types. It:
- 1 Primary parkinsonism. It is caused by Parkinson’s disease. Includes sporadic and familial cases and accounts for about 80% of cases of parkinsonism.
- 2 Secondary parkinsonism. This form of parkinsonism can be caused by a variety of problems. These include drug addiction, infections, toxins, trauma or brain tumors, normal pressure hydrocephalus, hypoxia, and metabolic dysfunction.
- 3 Atypical parkinsonism. This is a type of disease that includes additional neuropsychological and neurological deficits, such as hemiatrophy-hemiparkinson syndrome, juvenile form of Huntington’s chorea, corticobasal degeneration, and others.[4].
Complications of parkinsonism
Parkinsonism resulting from Parkinson’s disease can be accompanied by additional complications. In most cases, they require separate treatment. Among them are the following:
- Difficulty thinking. A person with Parkinson’s disease may experience cognitive problems (dementia) and difficulty thinking, which usually occur in the late stages of Parkinson’s disease. These cognitive problems are not very drug-sensitive.
- Depression and emotional changes. The latter include changes in emotional state such as fear, anxiety, or loss of motivation. Often, doctors prescribe additional treatment in such cases.
- Swallowing problems. The person may have difficulty swallowing as the disease progresses. Saliva can build up in the mouth due to slowed swallowing, leading to drooling.
- Sleep disorders. People with Parkinson’s disease often have trouble sleeping, including waking up frequently at night, waking up early, or falling asleep during the day.
- Bladder problems. Parkinson’s disease can cause an inability to control urination or difficulty in the process.
- Constipation. Many people with Parkinson’s disease develop constipation, mainly due to a slow digestive tract.
- Changes in blood pressure. A person may feel dizzy due to a sudden drop in blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension).
- Fatigue. Many people with Parkinson’s disease lose energy and tire quickly.
- Pain. It can occur both in certain areas of the body and throughout the body.[5].
Prevention of parkinsonism
The most common cause of parkinsonism, as we mentioned above, is Parkinson’s disease. Because the cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, proven ways to prevent the disease have not yet been developed.
However, studies have shown that caffeine, which is found in coffee and tea, may reduce the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Regular aerobic exercise is also helpful. Equally important is a healthy lifestyle, avoidance of drugs and alcohol.[6].
Parkinsonism diagnosis
Diagnosis of this disease includes a doctor’s assessment – the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, asks him about complaints, lifestyle. Tries to establish whether the human body has been exposed to toxins, drugs and other substances or factors that could provoke the appearance of parkinsonism.
In some cases, neuroimaging, tests such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are prescribed. They are needed to look for a structural disorder that can cause Parkinson’s symptoms.
If the diagnosis is unclear, doctors may give the person a special drug used to treat Parkinson’s to rule it out. If the drug leads to a clear improvement, it helps to establish that the likely cause of parkinsonism is Parkinson’s disease.[2].
Treatment of parkinsonism in mainstream medicine
In mainstream medicine, the treatment of parkinsonism includes measures to treat the primary source of the disease, as well as medication to relieve symptoms and general measures.
So, if parkinsonism has arisen as a consequence of taking medications, then stopping their intake can help eliminate the disorder.
Often, drugs that are used to treat Parkinson’s disease are ineffective in eliminating the signs of parkinsonism. But general measures that help people suffering from Parkinson’s disease maintain mobility and mobility can be helpful. For example, the patient should try to be as active as possible, to simplify the daily routine, and if necessary, use assistive devices for movement. It is also very important to secure the environment in the house – for example, remove rugs on which a person with difficulty in movement may stumble. It is also important to undergo physical therapy and maintain proper nutrition.[2].
Healthy foods for parkinsonism
In Parkinson’s disease (which is the main contributor to parkinsonism), it is important to include the following foods in your diet:
- Vegetables, fruits, legumes and bran Are those foods that contain high amounts of fiber. Due to the fact that constipation is one of the complications of parkinsonism, it is very important to eat food that will help the intestinal tract to function properly. But before you give a person fruits or vegetables with a dense skin that are difficult to chew, they need to be peeled. Take care to remove the bones. Vegetables are best eaten not raw, but boiled.
- Water – for an adult, the daily norm is a volume equal to one and a half to two liters of water. It is important to adhere to this in a weakened body.
For a person suffering from parkinsonism, it is necessary to ensure that vitamins and nutrients enter the body with food. You need to eat spinach, carrots, eggs, peas, beef liver, nuts, onions, in small quantities – cottage cheese and meat. All meals should be divided into 5-6 portions. This will help distribute and consume the necessary calorie intake per day, as well as get all the necessary elements. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe an additional intake of a vitamin complex or adjust the diet, depending on what caused the development of parkinsonism. It is worth noting that the level of calorie content of the daily diet for each person is individual – it depends on the characteristics of the course of the disease, as well as on the activity of the person’s lifestyle.
Traditional medicine for parkinsonism
With Parkinson’s disease or primary parkinsonism, foot baths are often taken. One of them is prepared on the basis of 5 tbsp. fern roots and 5 liters of water. You need to boil this mixture for two hours, and then cool it and use it to take foot baths.
Another useful bath is prepared on the basis of a decoction of rosehip roots. You need to pour 3 tbsp. crushed roots with a liter of boiling water, heat in a water bath for half an hour. You need to take such a bath twice a week. The optimal time for keeping the legs in it is 40 minutes before bedtime. And the water temperature must be maintained at 40 degrees.
A useful recipe, if suddenly parkinsonism is a consequence of atherosclerosis, is considered a diuretic from a decoction of the drop cap. A spoonful of table herbs is poured with a glass of hot water, wrapped and insisted for about 2 hours, but not less. Then the broth is filtered, and 1/3 cup is taken 4 times a day.
You can also prepare oil for rubbing on the basis of laurel leaves. They need to be cut, and then pour 0,5 liters of sunflower oil, boil for 10 minutes, and then send them to a warm place for two days. Before use, the oil must be boiled again, allowed to cool and rubbed into the diseased limbs.
Dangerous and harmful foods for parkinsonism
- Sweets – you should refuse to take them for the duration of the illness. It is important to maintain blood sugar levels. It is also not recommended to abuse salt.
- Alcohol – for the period of treatment and recovery, it must be completely abandoned. At least because most medications are not compatible with it. It is also worth remembering how harmful alcohol affects the central nervous system. After taking it, tremors may worsen, as well as other symptoms of parkinsonism.
- Fatty foods – they should be discarded because they raise blood cholesterol levels.
Also banned are solid, spicy foods, foods that can provoke constipation, semi-finished products, fried foods, smoked meats. The meat should not be served in one piece, but in the form of cutlets, casseroles.
- Wikipedia article “Parkinsonism”
- Parkinsonism (Secondary Parkinsonism; Atypical Parkinsonism)
- Parkinson’s disease, source
- Different types of parkinsonism
- Complications, source
- Prevention, source
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!