Contents
- Pancreas: Anatomy, Functions, Treatments
Pancreas: Anatomy, Functions, Treatments
The pancreas is a vital organ of the body. This organ is a gland with several secretory functions. These are particularly essential for the digestion of food and the regulation of blood sugar.
Anatomy: the characteristics of the pancreas
Location
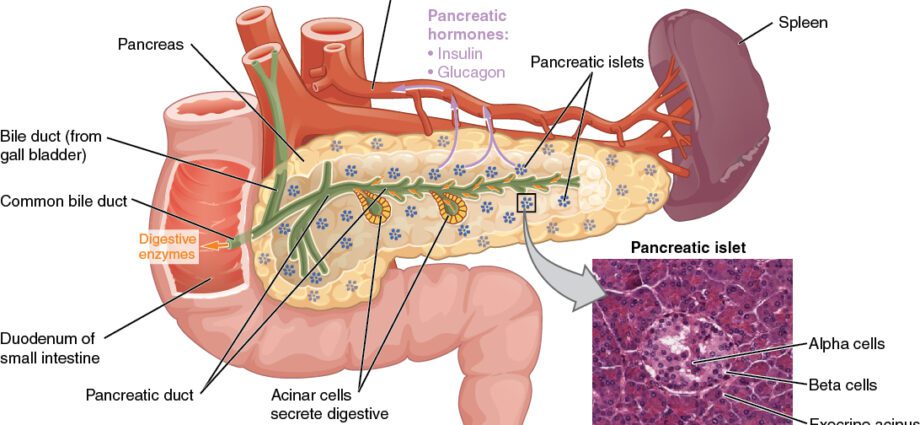
The pancreas is an organ located at the level of theabdomen. It is located behind the stomach and in front of the first and second lumbar vertebrae (L1 and L2). It is in direct contact with the intestine, and close to the spleen.
Look
The pancreas is a elongated and flattened gland measuring on average 20 centimeters long and 2 centimeters high. It has a total weight of between 60 and 80 grams. It has a pinkish yellow color. Although it has a firm consistency, this organ remains fragile.
Structure
The pancreas is often presented with three parts: the head, the body and the tail. In some cases, a fourth part is attributed to it: the neck or isthmus, which is located between the head and the body. The pancreas also has two ducts:
- The Wirsung Canal : It constitutes the main pancreatic duct. It starts at the tail of the pancreas and runs the entire length of the gland. Before reaching the level of the head of the pancreas, it forms an elbow to move towards the duodenum. This channel allows most of the gland to be drained.
- The Santorini canal : This secondary pancreatic duct originates at the elbow of the Wirsung’s duct. Like this duct, it passes through the head of the pancreas to join the duodenum. This secondary channel allows part of the head to be drained.
Physiology: the secretory functions of the pancreas
Mixed gland
The pancreas is considered a mixed gland because it has two functions:
- An exocrine function, which allows substances to be secreted in the duodenum;
- An endocrine function, which allows substances to be secreted into the bloodstream.
Pancreatic exocrine secretion
Via the Wirsung duct, this gland secretes the pancreatic juice in the duodenum. Essential for digestion, this juice contains:
- bicarbonate ions, which allow neutralize acidity chyme, the liquid from the stomach containing in particular the pre-digested food;
- digestive and pancreatic proenzymes, which allow the digestion lipids, carbohydrates and proteins.
Endocrine secretion of the pancreas
This gland is also known to secrete two substances essential for the regulation of blood sugar:
- insulin, secreted by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans, which makes it possible to decrease the level of glucose in the blood;
- glucagon, secreted by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans, which increases the level of glucose in the blood.
Anomalies: pathologies associated with the pancreas
Diabetes type 1
This type of diabetes is caused by the destruction of the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. This leads to an abnormal rise in the level of glucose in the blood.
Pancreatitis
It corresponds to an inflammation of the pancreas. It can be acute or become chronic. It can have many causes including:
- gallstones, which is characterized by the presence of stones in the bile ducts;
- excessive alcohol consumption ;
- infectious development, often of viral or parasitic origin;
- an autoimmune disease ;
Pancreatic cancer
A malignant tumor can develop in the pancreas. The most common form is adenocarcinoma.
Treatments: management of pancreatic pathologies
Prevention of pancreatitis
Alcohol abuse is a major risk factor for pancreatitis.
Medical treatments for the pancreas
Treatment depends on the pathology diagnosed. In the case of type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is put in place. In cancer, chemotherapy may be used.
Surgical intervention
In the most serious cases, surgery can be performed on the pancreas.
Diagnosis: the various examinations of the pancreas
Medical imaging exam
The pancreas can be examined with medical imaging techniques such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Endoscopic examination
Thanks to a luminous optical tube, endoscopy, or fibroscopy, makes it possible to analyze the pancreas.
Biological examination
To further or confirm a diagnosis in the pancreas, a stool test may be performed.
The future: artificial pancreas projects
Several artificial pancreas projects are currently being tested. The first positive results open promising prospects for type 1 diabetics.