Myocardial Infarction: What is it?
L’myocardial infarction corresponds to the destruction of part of the heart muscle called myocardium. It occurs when, for example, a clot prevents blood from circulating normally through the coronary artery, an artery that supplies blood to the heart. The latter is then poorly irrigated and the heart muscle damaged.
Myocardial infarction, sometimes called a heart attack or acute coronary syndrome, is fatal in almost 10% of cases. As soon as the first symptoms appear, it is essential to prevent help. First aid will be given in the ambulance and then hospitalization will be necessary. Then, long-term care will be offered, in particular to avoid a new heart attack or the appearance of cardiovascular complications. This post-infarction care will consist of drug treatment, cardiovascular rehabilitation or lifestyle changes.
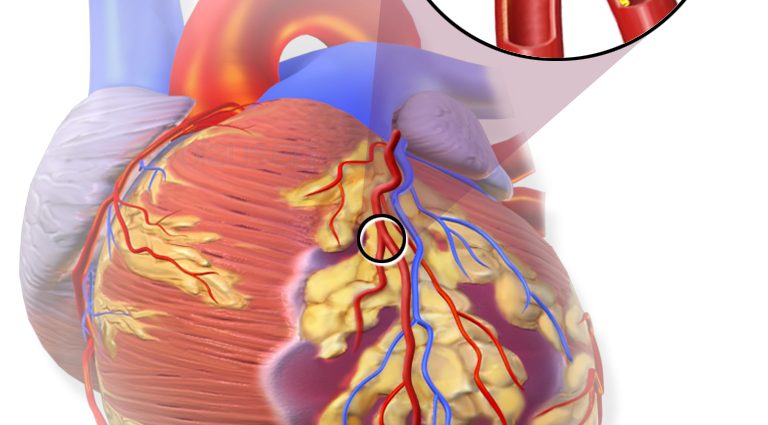
Myocardial infarction is caused by an artery that clogs up, which leads to poor oxygenation of the heart, and therefore to the destruction of part of the myocardium. Deprived of oxygen, the cells of this muscle die: we are talking about necrosis. The myocardium contracts less well, a heart rhythm disorder appears and then, if nothing is done, the heart stops beating. To avoid this fatal outcome, it is necessary to unblock the artery as quickly as possible.
But how can an artery become blocked? The culprits are atheroma plaques. Mainly made up of cholesterol, these plaques can form at the level of the walls of the blood vessels, and therefore of the coronary arteries, which supply the heart. If the atheromatous plaque ruptures and forms a clot, it can cause a myocardial infarction.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction are quite characteristic: pain in the chest, shortness of breath, sweating, irregular heartbeat, discomfort in the hand or arm, etc.
Nevertheless there are infarct silent. The person who has it does not experience any symptoms. The silent heart attack may go unnoticed but be discovered during an exam such as an EKG. This silent heart attack more generally concerns people who suffer from diabetes.
Rappel : The heart is a pump that distributes blood to all organs. The myocardium is responsible for irrigating the body with blood and therefore oxygen.
Prevalence
There are in France nearly 100.000 myocardial infarctions per year. More than 5% of those affected would die within an hour, nearly 15% in the following year. This mortality rate has fallen significantly in 10 years, in particular thanks to the responsiveness of the SAMU and the establishment of interventional cardiology services. US figures speak of 8000.00 annual cases and 90 to 95% survival for patients hospitalized after a myocardial infarction.
Diagnostic
The symptoms of a heart attack are usually very characteristic and allow the doctor to make a diagnosis very quickly. This diagnosis will be confirmed by various tests and examinations such as an electrocardiogram. The ECG will allow visualization of theelectrical activity of the heart and thus, to detect an anomaly. It will reveal if a heart attack has started or is happening. A blood test will detect the presence of heart enzymes in the blood that reveal damage to part of the heart. An x-ray may be necessary, especially to make sure the lungs are not affected. A coronary angiography, an x-ray which allows the visualization of the coronary arteries, can also make it possible to detect a decrease in the diameter of these arteries and the presence of an atheromatous plaque.
Causes
The presence of atheroma plaque, composed mainly of cholesterol, may explain the appearance of a heart attack. This plaque can block a coronary artery and prevent the heart from being supplied with proper blood.
A heart attack can also occur as a result of some kind of spasms at the level of a coronary artery. The blood flow is then interrupted. This spasm can be caused by a drug like cocaine. It can also appear following a tear in the artery of the heart or when the blood flow is very reduced, in the event of very low blood pressure for example, what is called hypovolemic shock.
Complications
The complications of a heart attack vary depending on the extent of the area of the heart muscle affected by the heart attack. The larger the area, the more serious the complications are. The person may have arrhythmia, that is to say heart rhythm disturbances, heart failure or even problems with one of the heart valves, a valve that may have been damaged during the attack. A heart attack can also be complicated by a stroke. A new heart attack can also occur.
The risk of complications will be assessed using new examinations: ECG, ultrasound, coronary angiography, scintigraphy (to assess the functioning of the heart) or a stress test. Drug treatment will also be prescribed.