Contents
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) belongs to the smallpox group of viruses. The disease occurs in people of any age, although it is believed that children are more susceptible to it. However, it has been observed that in the adult population of Russia, this disease often occurs after returning home from countries with a hot climate.
“The source of infection is primarily a person, although the infection can also be transmitted through household items,” says dermatovenerologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor Andrey Bakulev. – In adults, rashes of molluscum contagiosum most often affect the face, lower abdomen, inner thighs, skin of the external genital organs. In this case, the rashes cannot go away on their own. If the patient walks for a long time with signs of illness, he poses a threat to others.
Causes of molluscum contagiosum in adults
“Mollusk” is not in vain called contagious. Despite the fact that its name has nothing to do with the inhabitants of the seas, except perhaps for a fantasy appearance, the word “contagious” means that it is transmitted through direct contact, for example, skin to human skin. Therefore, this disease can be safely attributed to sexually transmitted infections.
In addition to the fact that adults can catch the virus through sexual contact, any accidental or non-accidental touching must also be taken into account. Molluscum contagiosum in adults can also be transmitted through wrestling or any other sport that involves close contact.
The household route of infection is also not excluded: through the use of shared towels, bed linen, washcloths, dishes, etc. for a long time.
Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum in adults
The incubation period ranges from 1 week to several months, on average – 2-7 weeks.
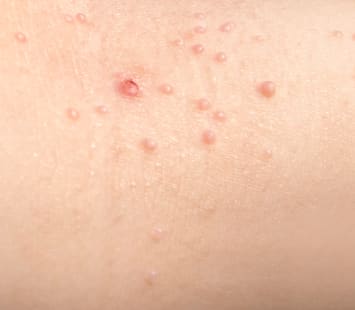
The main symptom of molluscum contagiosum in adults is a rash, represented by clusters of domed, waxy or pearl-like papules with an depression in the center. The number of elements of the rash is different: from 5 – 10 to several tens or more. Usually they are 2 – 5 mm in diameter, but can reach 10 mm. Most often occur on the face, in the pubic area, abdomen, genitals of men and women. They can also occur on any part of the skin, including the skin of the scalp, soles, and eyelids.
Discomfort, itching, pain are usually not accompanied.
When these nodules are squeezed from the sides, a white, crumbly (mushy) mass will be released from their central opening, which contains virus particles. As the body fights it off, molluscum contagiosum lesions can become inflamed and itchy. But in general, these rashes may not carry heavy sensations and represent only a purely cosmetic problem.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in adults
There is no specific treatment, there are several types of therapy:
- physical removal (curettage, cryosurgery, laser coagulation or electrocoagulation);
- the use of external agents that cause destruction (Cantharidin, trichloroacetic acid, Tretinoin, Tazarotene, podophyllotoxin, potassium hydroxide);
- combination therapy (may include immunomodulatory and antiviral agents).
Diagnostics
An experienced doctor, based on the clinical picture, can always assume the presence of molluscum contagiosum in adults. In some cases, microscopic and / or pathomorphological examination of skin biopsy specimens will be required if the clinical picture of the disease is not completely clear.
Molluscum contagiosum in adults is important to differentiate with flat or vulgar warts, keratoacanthoma – especially in men over 50 years of age.
Modern treatments
At the moment, there are several options for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum in adults, but the optimal technique is selected only by the attending physician. This can be local drug therapy, surgical removal of molluscum contagiosum with a laser, freezing with liquid nitrogen, radio wave treatment, electrocoagulation, curettage. However, in the latter case, there is a danger of spreading the disease to healthy areas of the skin. Therefore, it is better to trust the recommendations of a specialist who observes you.
Prevention of molluscum contagiosum in adults at home
First of all, these are protected sexual relations and observance of the rules of personal hygiene in everyday life and public places. It should also be borne in mind that in the presence of this disease, self-infection is possible. By scratching or squeezing the rash, an infected person can spread the virus to other parts of the body.
Popular questions and answers
We asked an expert to answer the most frequently asked questions about molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum in adults is best prevented at an early stage!