Contents
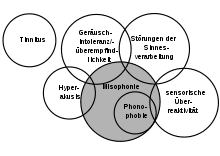
Misophonie
Misophonia is a mental disorder characterized by an aversion to certain sounds made by someone other than yourself. The management is psychotherapeutic.
Misophonia, what is it?
Definition
Misophonia (a term that appeared in 2000 which means strong aversion to sounds) is a chronic condition characterized by an aversion to certain repetitive sounds produced by people (adults) other than oneself (guttural, nasal or mouth noises, tapping of the fingers on a keyboard…) Sounds related to mouth chewing are the most frequently implicated.
Misophonia is not classified as a psychiatric disorder.
Causes
A recent study showed that misophonia was a neuro-psychiatric disease associated with brain abnormalities. They found in people with misophonia an overactivation of the lower insular cortex (the region of the brain that allows us to direct our attention to what is happening in our environment).
Diagnostic
Misophonia is still relatively unknown and this disorder often goes undiagnosed.
The diagnosis of misophonia can be made by a psychiatrist.
There is a misophonia-specific rating scale called the Amsterdam Misophonia Scale, which is an adapted version of the Y-BOCS (Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale, a scale used to measure the severity of OCD).
The people concerned
The prevalence of this disorder in the general population is not known. Misophonia affects people of all ages, even children.
10% of people with tinnitus suffer from misophonia.
Risk factors
There could be a genetic factor: Studies have shown that 55% of people with misophonia have a family history.
It has been shown by studies that misophonia may be associated with Tourette’s syndrome, OCD, anxiety or depressive disorders, or eating disorders.
Symptoms of misophonia
An immediate aversive reaction
People with misophonia have a strong irritability reaction of anxiety and disgust, then anger at certain sounds. They may cry, cry, or even vomit. Those affected also report a feeling of loss of control. Aggressive behavior, verbal or physical, is rarer.
Avoidance strategies
This reaction is accompanied by a desire to stop these noises to relieve the symptoms.
People suffering from misophonia avoid certain situations -These avoidance strategies reminiscent of those of those suffering from phobias -or use means to protect themselves from aversive sounds: use of earplugs, listening to music …
Treatments for misophonia
The management of misophonia is psychotherapeutic. As with phobias, cognitive behavioral therapies are recommended. Tinnitus habituation therapy may also be used.
Antidepressant and anti-anxiety medications do not seem to work.
Prevent misophonia
Misophonia cannot be prevented.
On the other hand, as with phobias, it is better for it to be taken care of early, in order to avoid situations of avoidance and social handicap.