Contents
Melanoderma, causes, symptoms and treatments
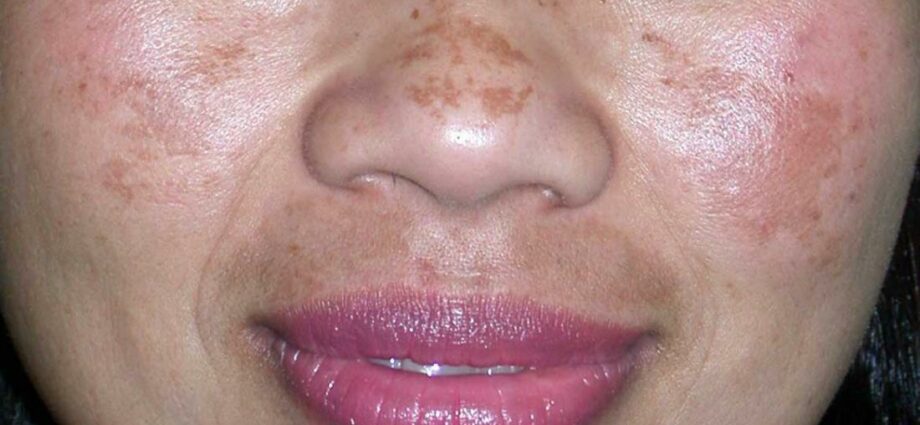
Abnormally dark pigmentation of the skin, melanoderma is a skin symptom that can reflect several diseases or that can occur during pregnancy. It can be localized or be generalized over the entire skin surface.
What is melanoderma?
Linked to an excess of melanin in the skin, melanoderma is a skin symptom of several diseases that can appear on the face of a woman during pregnancy (chloasma) or in the nipples.
Where does melanoderma come from?
It can also occur naturally during tanning on the whole body exposed to the sun which promotes the production of a large amount of melanin in the skin. Melanoderma is also present in areas of friction (thighs, etc.), folds and sometimes in scars.
Under the effect of a contributing factor such as the sun, hormones or metabolic diseases, melanoderma sets in by multiplying the number of cells present in the skin called melanocytes which produce a pigment, melanin. The skin then thickens and this pigment which is present in greater quantity under the skin, with the properties of protecting the skin from the ultraviolet rays of the sun.
What are the causes of melanoderma?
Skin birthmarks (nevus, Recklinghausen’s disease, etc.) are not considered to be actual melanoderma.
Melanoderma comes on gradually and is a symptom of an illness, condition (pregnancy), skin reaction to a substance (some fragrances), chronic skin irritation, or exposure to ultraviolet rays ( tan or tan).
It can be located at different times:
- during pregnancy, it will be localized on the face (pregnancy mask or chloasma) or the nipples (hyperpigmentation);
- during a local skin reaction to a substance such as bergamot in certain perfumes or cosmetics;
- during repeated rubbing of the skin in certain skin folds (armpits, thighs, buttocks, inguinal region, genitals, etc.);
- when taking certain drugs (antimalarials, contraceptive hormone therapy, testosterone treatment) which are likely to cause localized melanoderma especially in the nipples and genitals.
It is sometimes generalized all over the body when it is combined with:
- a general disease such as a metabolic disease (Addison’s disease or slow adrenal insufficiency, hemochromatosis, hyperthyroidism, bronzed diabetes, renal failure, Biermer’s disease, etc.),
- to certain tropical diseases such as malaria;
- to irritation of the skin by scratching as in the disease of vagrants whose skin is variegated (varied colors), with pigmented scars or even patches of eczema;
- exposure to ultraviolet (UVA) in the sun or with artificial tanning lamps.
What are the treatments for melanoderma?
Treatments for melanoderma will depend on the cause. It will consist of early treatment of the metabolic disease which is the cause (Addison’s disease or slow adrenal insufficiency, hemochromatosis, hyperthyroidism, bronzed diabetes, renal failure, Biermer’s disease, etc.).
For melanoderma related to skin irritation, the cause of the irritation should be treated (vagrant’s disease) or prevented as protection from the sun in the presence of certain perfumes or cosmetics.
This is also the case for drugs that can cause melanoderma such as antimalarials, the contraceptive pill or during a current pregnancy.
Finally, whitening treatments are contraindicated because the results are sometimes poor in terms of aesthetics and may cause diseases (skin cancer) or skin lesions (atrophy by the application of corticosteroid ointments).