Contents
Macrophage myofasciitis
What is it ?
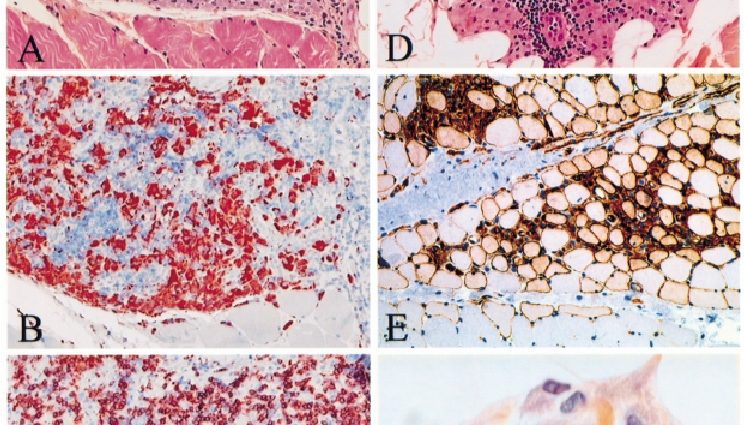
Macrophage myofasciitis is characterized by histopathological lesions (disease affecting the tissues). These are myopathological consequences, that is to say that impact muscle tissue.
This disease has been described following a human biopsy, from an adult patient and in 3 children. Damage within muscle fibers has been highlighted without the presence of necrosis. Examinations of these lesions (nuclear microprobes, radiographic microanalyses, atomic absorption spectrometry) made it possible to understand that this damage was composed of aluminum salts. These substances are widely used in a large number of vaccines administered intramuscularly. It has also been shown that no underlying reason was causing the disease. Indeed, healthy people (not sick, having a healthy lifestyle, etc.) can be affected by the disease following a vaccination. (1)
Initially, the exact origin of the disease was not known. Suspicions about an environmental, infectious and other cause had been raised. Scientific work carried out between 1998 and 2001 determined that the exact cause of the disease was the absorption of aluminum hydroxide present in vaccines. Microscopic imaging examinations of internal components: macrophages have shown the constant presence of inclusions caused by these aluminum salts. These compounds are used as adjuvants in vaccines. Macrophage myofasciitis is found exclusively in the deltoid in adults and in the quadriceps in children.
Symptoms
The main symptoms associated with the disease are as follows:
– chronic pain in the muscles: the development of which is rather slow (over a period of a few months). These symptoms affect between 55 to 96% of patients affected by the disease. It has been shown that these clinical manifestations generally develop at a distance from the small ribs and gradually spread throughout the entire body. For a minority of patients, this muscle pain leads to functional complications. In addition, pain in the spine is frequently identified. These pains are often felt as soon as the person wakes up and are accentuated during physical exercises and daily activities;
– chronic fatigue, which concerns between 36 and 100% of patients. This intense fatigue usually causes a reduction in the person’s daily activities, both mental and physical;
– cognitive abnormalities, consequences long neglected in the disease. These manifestations result in depression, decreased cognitive and intellectual performance, attention disorders, etc.
Other characteristic signs can also be associated with the disease. These include psychiatric manifestations, particularly mood disorders.
Dyspnea (difficulty breathing) and headaches have also been reported in some patients.
The origins of the disease
The origin of the disease is the presence of aluminum hydroxides in vaccines injected into patients by intramuscular route.
Macrophage myofasciitis affects both men and women, adults and children, with no specific underlying condition, following vaccination. Adults are usually affected after a vaccine in the deltoid, while children are affected after an injection in the quadriceps.
The vaccines most affected by the presence of aluminum salts as an adjuvant are:
1. hepatitis B vaccine: 84%;
2. the tetanus vaccine: 58%;
3. vaccine against hepatitis A: 19%.
In addition, it has been demonstrated that the presence of aluminum salts in the body is persistent. Or that the realization of a muscle tissue biopsy can testify to the presence of these compounds whose origin is a vaccine dating back several years. (3)
It would also seem that there are predispositions in some people, not allowing them to properly eliminate the aluminum salts found in vaccines and in this sense, see them accumulate in muscle tissue.
Risk factors
The individual risk factors for the development of the disease have not been clearly demonstrated.
A link between systemic symptoms and disease development has been shown in a small proportion of cases of macrophage myofasciitis.
In addition, genetic predispositions have been suspected, particularly in repeated cases of the disease within the same siblings. Some scientific research has shown that a particular genetic heritage could have an impact on the persistence of aluminum salts in muscle tissue. The pathology is characterized by an increase in circulating CCL2 / MCP-1, a cytokine involved in the penetration of nanoparticles into the brain. Genetic changes in genes encoding this molecule could be an additional risk factor for developing the disease.
Prevention and treatment
The diagnosis of the disease is made according to various more or less visible clinical signs. Indeed, the first relates to the presence of aluminum salts, from a vaccine injection, in muscle tissue.
In addition, the presence of myalgia (muscle pain) in the deltoid associated with the identification of aluminum hydroxides within this tissue, and evidence of the development of the pathology in adults.
The determination of the clinical manifestations (chronic muscle pain, chronic fatigue and cognitive abnormalities) also makes it possible to establish or not the diagnosis of the disease.
A positive diagnosis of the disease involves the detection of lesions in the deltoid macrophages in adults and in the quadriceps in children.
In 1/3 of cases, an increase in the level of plasma creatine kinase is characteristic of the pathology. However, this abnormally high cytokine level may be linked to other inflammatory or immune system diseases. In this sense, additional examinations to eliminate any suspicion of another cause must be carried out.
The electrodiagnosis, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) of the muscles generally make it possible to approve or not the first opinions.