Contents
- Influenza
- What is the flu?
- How long does the flu last?
- The different influenza viruses
- Flu and contagion: how long does it last?
- The flu, how is it caught?
- Can the flu be caught more easily in cold weather?
- Possible complications of the flu
- When to consult a doctor ?
- How many people get the flu each year?
- When is the flu caught?
Influenza
INFORMATION The flu symptoms are very similar to the symptoms of the coronavirus (Covid-19). To find out more, we invite you to consult our Coronavirus section. |
What is the flu?
The flu, or influenza, is a disease caused by influenzae viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family, RNA viruses. Contagious disease, influenza first affects the respiratory system and can become more complicated or have severe forms.
How long does the flu last?
It usually lasts from 3-7 days and can prevent a person from carrying out their daily activities.
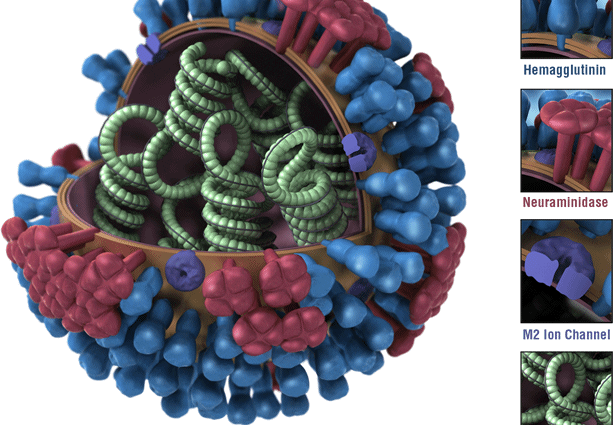
The different influenza viruses
There are 3 types of influenza viruses, with different subtypes classified according to their surface glycoproteins, neuraminidases (N) and hemagglutinins (H):
Influenza Type A
It is the most dangerous. It caused several deadly pandemics like the famous Spanish flu of 1918, which killed more than 20 million people. In 1968, it was the turn of the “Hong Kong flu” to trigger a pandemic. Type A transforms in a very short time, which makes him all the more difficult to fight. Indeed, the body must build an immune response specific to each new strain of influenza in circulation.
The type A virus causes a pandemic about 3-4 times a century. In 2009, a new type A virus, H1N1, triggered another pandemic. According to public health authorities, the virulence of this pandemic was “moderate”, in terms of the number of deaths. For more information, see our Influenza A (H1N1) file.
Avian influenza is also a type A virus that affects birds, whether they are slaughter (chickens, turkeys, quails), wild (geese, ducks) or domestic. The virus is easily transmitted from birds to humans, but rarely between humans. Strain H5N1 has caused several deaths in Asia, usually in people who have close contact with sick or dead poultry or who have frequented live poultry markets.
Influenza Type B
Most often, its manifestations are less serious. It only causes localized epidemics. This type of flu is less prone to mutations than type A.
Type C influenza
The symptoms it causes are similar to those of a common cold. This type of flu is also less prone to mutations than type A.
Do viruses evolve?
This type of virus constantly undergoes genetic modifications (genotypic modifications). This is why having the flu one year does not provide immunity against the viruses that will circulate in the following years. We can therefore contract a new flu every year. Vaccines must be adapted each year to protect the population against new variants of the virus.
Flu and contagion: how long does it last?
An infected person can be contagious the day before their first symptoms and can transmit the virus for 5 to 10 days. Children are sometimes contagious for more than 10 days.
Incubation lasts 1 to 3 days, which means that when you are infected with the influenza virus, the signs can start to appear from 1 day after infection up to 3 days after.
The flu, how is it caught?
The flu spreads easily, by contagion and in particular by contaminated microdroplets which are released into the air when coughing or sneezing. The virus can also be transmitted through saliva. Since the virus can quickly spread to the face and hands of someone with the flu, kissing and shaking hands with sick people should be avoided.
Transmission occurs more rarely through objects touched by saliva or contaminated droplets; the virus persists on the hands for 5 to 30 minutes and in the stool for several days. On inert surfaces, the virus remains active for several hours, so avoid touching the patient’s objects (toys, table, cutlery, toothbrush).
Flu or cold, what are the differences?If you have a cold :
For more information, see our Cold sheet. |
Can the flu be caught more easily in cold weather?
The Italians of the XIVe century believed that episodes of contagion in influenza were brought by the froid. So they named her cold flu. They were not entirely wrong, because in the temperate zones of the northern and southern hemispheres influenza manifests itself more often in winter. But at the time, they were most likely unaware that in the tropics, influenza outbreaks can happen any time of the year (there is no flu season!).
It was long believed that “catching a cold” reduced the body’s resistance to the flu and colds. However, there is no evidence that the cold weakens the immune system or facilitates the entry of the virus into the respiratory tract.6-9 .
If influenza is more common in winter, it seems more likely to be due to confinement inside maisons, which promotes contagion. In addition, the fact that the air is more dry in winter also facilitates contagion, because the mucous membranes of the nose dry up. In fact, the mucous membranes prevent the entry of microbes more effectively when they are wet. In addition, the dry winter air would make it easier for the virus to survive outside the body.23.
Possible complications of the flu
- Bacterial superinfection: complications can occur if at the influenza (viral infection) in addition to a bacterial infection otitis media, the sinusitis, the pneumonia bacterial post influenzae occurring from 4st the 14st day after the onset of infection, most often in the elderly.
- Pneumonia corresponding to a primary malignant influenza. Rare and serious, it leads to hospitalization in medical intensive care.
- Complications affecting organs other than the lungs, such as myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium, the membrane around the heart, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), rhabdmyolysis (severe muscle damage), Reye’s syndrome (if aspirin is taken in children, causing acute hepatitis and encephalitis, very serious).
- Complications in people with reduced immunity,
- During pregnancy, miscarriage, prematurity, neurological congenital malformations.
- And in the elderly, Heart Failurerespiratory or renal disease which may worsen considerably (decompensation).
People with more fragile health, such as the elderly, immunocompromised and those with Pulmonary Disease, are at greater risk of complications and death.
When to consult a doctor ?
In the presence of the following symptoms, it is best to consult a doctor in order to detect and possibly treat any complications that may arise.
- A fever over 38,5 ° C for more than 72 hours.
- Shortness of breath at rest.
- Chest pain.
How many people get the flu each year?
In France, each year, during an influenza epidemic, between 788 and 000 million people consult their general practitioner, ie 4,6 million people affected on average each year by the flu. And nearly 2,5% of them are under 50. During the 18-2014 influenza epidemic, 2015 severe influenza cases and 1600 deaths were observed. But the excess mortality linked to the flu was then estimated at 280 deaths (mortality in fragile people who without the flu would probably not have died).
The flu affects 10% to 25% of the population each year Canadian3. The vast majority of those infected recover without any problem. Still, the flu is involved in 3000 to 5000 deaths in Canada, usually in people who are already debilitated.
When is the flu caught?
In North America as in Europe, the flu season runs from November to April. The seasonal incidence of influenza varies depending on the latitude of the country you are in and the annual virus in circulation.