Contents
One of the diseases of modern society is gout. And although it refers to metabolic diseases, its main manifestation is damage to the joints.
The process is very specific, characterized by a persistent and long course. It can cause severe destructive processes in the joints, which requires getting to know the true face of this enemy of humanity.
What is gouty arthritis?
Gouty arthritis – this is one of the varieties of inflammatory lesions of the joints, which is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the articular structures, its destructive effect on hyaline cartilage and periarticular tissues. In the above definition of the disease, all the key mechanisms of development and manifestation of this process are clearly indicated.
If you explain everything in order, then the complex of pathological changes consists of a sequential chain:
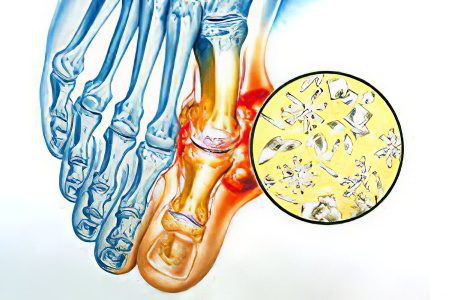
Violation of the metabolism of uric acid in the direction of increasing its amount in the blood;
Settling of its crystals (urates) on the surface of the hyaline cartilage of the joints;
Irritation and damage to articular structures with the development of an inflammatory response, which is actually called arthritis;
Development of the consequences of a destructive process;
Periarticular tumor-like growths.
Gout is also characterized by kidney damage, accompanied by the development of nephritis and urolithiasis, since urate stones are also deposited in the renal pelvis and ureters.
In most cases, gouty arthritis affects small joints (toes), less often – the ankle and knee joints, fingers, wrist and elbow.
The disease is more susceptible to males in adulthood (25-50 years). The manifestation of gouty arthritis may also occur at an earlier period. It is characterized by a long course of the process with constant relapses. The small joints of the feet are predominantly affected, less often the ankle joint.
True gout is quite rare, older people often call gout a manifestation of arthrosis. Women suffer from it 5 times less than men. The risk group includes men 40-50 years old and women over 60 years old (postmenopausal), as this disease has some connection with male sex hormones.
There are also such forms of gouty arthritis, when almost all large and small joints of the upper and lower extremities are exposed to the process. With a slowly progressive course, only small joints are gradually involved in inflammation. The disease rarely causes severe systemic reactions, although they can also occur. In addition to articular manifestations, gout is characterized by renal symptoms, which are the result of the formation of urate stones.
Medical practice knows cases of severe gout with severe intoxication and massive destructive processes simultaneously in several large joints. Fortunately, such cases rarely occur. But, nevertheless, long-term gouty arthritis sooner or later leads to dysfunction of the affected joint with possible disability of patients.
Symptoms of gouty arthritis
There are three periods in the development of the disease:
Latentwhen there are no clinical symptoms and the onset of the disease can be diagnosed only by an increased content of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia);
Acute recurrent, when joint damage causes severe gouty attacks;
Chronic, in which long periods of remission are possible.
The frequency of attacks can vary from 1 time per week-month to 1-2 times a year.
The clinical picture of the disease is quite typical, which allows it to be diagnosed in time.
The first manifestations are acute and consist of:
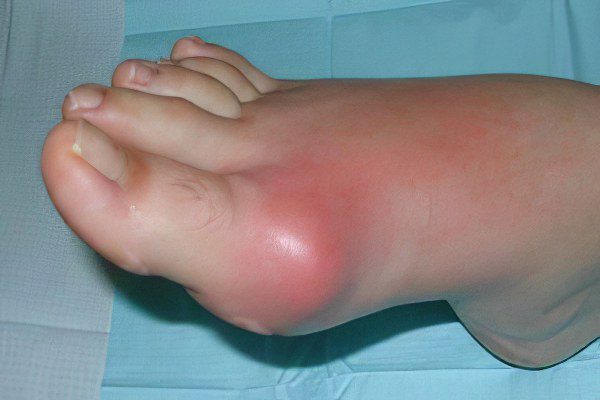
Pain in the joint of the big toe;
Redness of the skin over the inflamed joint;
Increased pain on movement
An increase in body temperature above normal numbers;
Unilateral defeat;
The appearance around the joints, which were inflamed, whitish subcutaneous growths (tophi);
Successive periodic pains in various small joints.
On some of these manifestations of the disease, it is worth dwelling separately and detailing the main points. First of all, it is a manifestation of the process. The thumb is affected first in 90% of cases. If against this background adequate therapeutic and diagnostic measures are not taken, then the disease will certainly acquire a progressive course. Gradually, other small joints will begin to inflame and hurt.
When gouty arthritis is characterized by high activity, the skin over the affected joint necessarily turns red, which is complemented by a general temperature reaction. The prolonged course of inflammation in gout leads to the formation of tophi (subcutaneous nodules) around the joints. They are represented by elements of articular tissues and uric acid.
The articular cartilage is gradually destroyed, and so-called “punches” are formed in the bones adjacent to the joint – cavities filled with sodium monourate crystals. Also, crystals of uric acid salts can be deposited in the tissues surrounding the joint and directly under the skin above the joint in the form of whitish dense nodules – tophi. Nodular deposits and bony growths lead to significant changes in the appearance of the leg. In the absence of treatment, the result may be a complete loss of ability to work and the ability to self-service.
In women, the disease is much milder than in men. Attacks are not so strong and sharp, tophi and punches are extremely rare. Therefore, in women it can be difficult to differentiate gouty arthritis from arthrosis.
Causes of gouty arthritis
The etiology of the disease is not fully understood. The main risk factors for its occurrence include:
Genetic predisposition;
Improper nutrition: excessive abuse of meat products, sausages, chocolate, strong coffee and tea, alcohol. (Earlier, gout was called the “disease of aristocrats”);
The presence of concomitant diseases, such as heart failure, hemoblastosis, kidney disease, hormonal abnormalities;
The use of certain drugs: drugs for high blood pressure, diuretics, cytostatics, etc.
There are also primary and secondary gouty arthritis:
Primary gout develops as a result of a combination of genetic predisposition and high consumption of purines with the foods listed above;
Secondary gout occurs due to the presence of these diseases and medication.
The accumulation of sodium urate microcrystals in the joint cavity can occur asymptomatically for a long time, until any factor provokes an acute attack: physical overwork (long walking), trauma, infection, stress, hypothermia, starvation, or the use of a large amount of “purine” foods in combined with alcohol.
Diagnosis of gouty arthritis
The key point of diagnostic procedures is the detection of sodium urate crystals in the synovial fluid of the joints, both during an attack and during remission. Synovial fluid for analysis can be taken from any large joint, even never subject to inflammation, for example, from the knee. Also, the contents of tofus or any other biological material can be taken for research.
Hyperuricemia (high levels of uric acid in the blood) in combination with periodic inflammation of the big toe joint is not considered a confirmation of gout, it is only a marker of purine metabolism disorder. Many people with hyperuricemia do not have gout.
With a long course of the disease, it makes sense to conduct an X-ray study. At an early stage of the disease, there are no characteristic changes. Then, on x-rays, signs typical of gout appear: cartilage destruction, defects in the end sections of the bones, punches.
With the development of gout on the upper limbs, it is quite difficult to differentiate it from other joint diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, etc.
How to treat gouty arthritis?
For many decades, official medicine has not come up with anything new in the treatment of gout and gouty arthritis. The entire treatment process also consists of two stages: the removal of inflammation and maintenance anti-relapse therapy.
When an exacerbation or primary occurrence of gouty arthritis occurs, it is necessary:
The introduction of drugs of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory origin. The most effective for gout are indomethacin, ibuprofen (Imet, Nurofen), movalis, rheumoxicam. It is good to use their step-by-step appointment with the phased use of injection forms with replacement with tablets;
The use of the drug colchicine – a specific anti-inflammatory agent for gout;
Local use of ointments based on NSAIDs: indomethacin, dip-relief, dolobene, remisid;
Lotions and compresses based on a semi-alcoholic solution or dimexide in a 25% concentration;
Physiotherapeutic procedures: paraffin and other thermal procedures, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, exercise therapy, massage, gymnastics.
Treatment of the disease itself includes the following components:
Dieting (normalization of purine metabolism);
The use of medications that reduce the synthesis of urates;
Elimination of the causes of hyperuricemia.
To eradicate the problem completely, you need to act on its basis – an excess of uric acid. For this purpose:
Allopurinol. Refers to drugs that reduce the production of uric acid in the body. Its analogue is zilorik;
Probenecid. Promotes the excretion of excess uric acid crystals in the urine, which reduces the symptoms of gout. The drugs in this group include sulfinpyrazone, etebenecid, anturan;
Uricozyme. It has a direct destructive effect on already existing urate crystals in the body.
Allopurinol (Allupol, Purinol, Remid, Milurit), belonging to the drugs of the first group, is most preferable. Indications for its use are high hyperuricemia (over 0,6 mmol / l), frequent acute attacks of arthritis, the presence of tophi, renal failure. The initial dose is 300 mg / day. In case of inefficiency, it is increased to 400-600 mg / day, and when significant results are achieved, it is gradually reduced. The maintenance dose is 100–300 mg/day, depending on the level of hyperuricemia.
Allopurinol helps to reduce seizures and soften tophi, normalize uric acid levels. In the first week of taking it, a slight exacerbation of symptoms is possible, so at this stage of therapy it is combined with anti-inflammatory drugs, low doses of colchicine or NSAIDs. If a gout attack has occurred for the first time, and Allopurinol has never been taken before, it is absolutely impossible to start taking it to reduce pain. If an attack occurs while taking Allopurinol, you need to continue taking it at the same dosage. During treatment, allergic reactions (skin rash) are possible.
The drugs of the second group are less important in the treatment of gouty arthritis. They are not used with a high content of uric acid in the blood, with nephropathy and renal failure. Sulfinpyrazone is taken at 200-400 mg / day in 2 divided doses with a large amount of alkaline liquid. An additional contraindication is gastric ulcer.
Probenecid (a derivative of benzoic acid) is prescribed at a dose of 1,5–2,0 g/day. Benzoic acid is found in cranberries, as well as in lingonberries and their leaves. Therefore, cranberry and lingonberry decoctions and fruit drinks are very useful for patients with gout.
Drugs of different groups can be combined with each other, however, as mentioned above, with a serious pathology of the kidneys, uricosuric drugs are contraindicated. Also, they can be used only after the complete relief of an attack of acute arthritis, otherwise another exacerbation can be provoked. During treatment with drugs of this group, the daily water intake should be at least 2,5-3 liters.
Treatment is long (from several months to several years), interruptions in treatment usually lead to relapses. Subject to all medical recommendations, the condition of patients normalizes within the first month. It is recommended to carry out monthly monitoring of the level of uric acid and, depending on the results of the tests, adjust the dosage of the drugs. The main therapy can be supplemented with physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy.
In the presence of excess weight, it is recommended to lose weight, since there is a relationship between excess weight, increased synthesis of urate and their reduced excretion by the kidneys. You should also stop taking thiazide diuretics to lower blood pressure and aspirin. These drugs increase the level of uric acid in the body and can provoke an attack.
During exacerbations, the load on the affected joint should be reduced as much as possible. Additionally, you can do ice compresses several times a day for 5-7 minutes.
Only a comprehensive treatment approach that includes anti-inflammatory therapy, topical treatments, diet, and drugs that affect uric acid metabolism can help in the fight against gouty arthritis.
Diet for gouty arthritis
Given that gout is a consequence of malnutrition, then its complete cure cannot be achieved without the strict implementation of the necessary dietary recommendations. That is why gouty arthritis in most cases has a progressive course. But I would like to focus the attention of patients on the importance of such a therapeutic measure as diet therapy. According to the medical nomenclature, it belongs to the dietary table number 6.
Main principle – Exclude foods that are a source of purines. Indeed, during their decay, a powerful release of uric acid occurs, which does not have time to bind and be excreted from the body. Its approximate composition is given in the table.
One can | Must not |
|
|
As can be seen from the above data, much is prohibited, but there are enough products for a normal healthy diet. The main thing to remember is to avoid excess. Even if it happened that a person could not resist and ate a forbidden food, it is advisable to immediately take the appropriate drugs that remove or bind the metabolic products of uric acid.

Monday:
Breakfast: cottage cheese with fruit jelly, coffee with milk;
Lunch: Tomato juice;
Lunch: vegetable rice soup, bread, compote;
Snack: apple, weak tea with marmalade;
Dinner: potato pancakes, green tea.
Tuesday:
Breakfast: porridge with milk, rye bread, pineapple juice;
Lunch: pear, walnuts;
Lunch: Braised rabbit, vegetable stew, compote;
Afternoon snack: Orange juice;
Dinner: cheese sandwich, tea with milk.
Saturday:
Breakfast: Carrot cutlets with sour cream, fruit drink;
Lunch: Banana;
Lunch: Vegetarian borscht with sour cream, rosehip broth;
Afternoon snack: grapefruit, tea with jam;
Dinner: pumpkin casserole, green tea.
Thursday:
Breakfast: boiled egg, cheese sandwich, tea with lemon;
Lunch: a glass of cherry juice;
Lunch: Trout baked with potatoes, vegetable salad with butter, fruit drink;
Afternoon snack: Kefir, marshmallow;
Dinner: Muesli with nuts, fruit drink.
Friday:
Breakfast: buckwheat porridge boiled in milk, green tea;
Lunch: baked apples with honey and nuts;
Lunch: vegetable salad, boiled rice, bread, orange juice;
Afternoon snack: tomato juice;
Dinner: stewed potatoes, fresh vegetable salad, a glass of skimmed milk.
Saturday:
Breakfast: scrambled eggs, a piece of rye bread, jelly;
Lunch: peach juice, almonds;
Lunch: cabbage soup on lean meat broth, rosehip broth;
Afternoon snack: banana;
Dinner: cereal soup, cheese sticks, tea with milk.
Sunday:
Breakfast: corn porridge with milk, coffee with milk;
Lunch: kefir, marshmallow;
Lunch: vinaigrette, bread, fruit drink;
Afternoon snack: apple;
Dinner: boiled tuna with fresh or stewed vegetables.
After a year of treatment, with satisfactory health and no relapses, severe dietary restrictions can be lifted. In this case, you can choose: either continue to adhere to the diet and reduce the dosage of the drugs taken or stop them altogether, or continue taking the medication and allow some indulgence in the diet.









