Contents
Translated from Greek, its name means “sweet”. It is because of its sweet nature that this amino acid is able to give people a sense of satisfaction and peace. It is used to treat nerves and irritability. Improves mood and suppresses anxiety. At the same time, it is produced exclusively from natural ingredients, without the use of modern chemistry.
Glycine is involved in DNA synthesis. It is an indispensable aid for traumatic brain injuries and strokes. Also, it is able to significantly reduce the toxicity of alcohol and drugs. Glycine is a probiotic that activates the body’s internal defenses.
Interesting fact:
According to the research of American scientists, glycine molecules are also present in cosmic dust, which is more than 4,5 billion years old. Based on this, it can be assumed that the primary amino acids that gave rise to life on Earth were brought to our planet from Space.
Glycine Rich Foods:
Indicated approximate quantity in 100 g of product
General characteristics of glycine
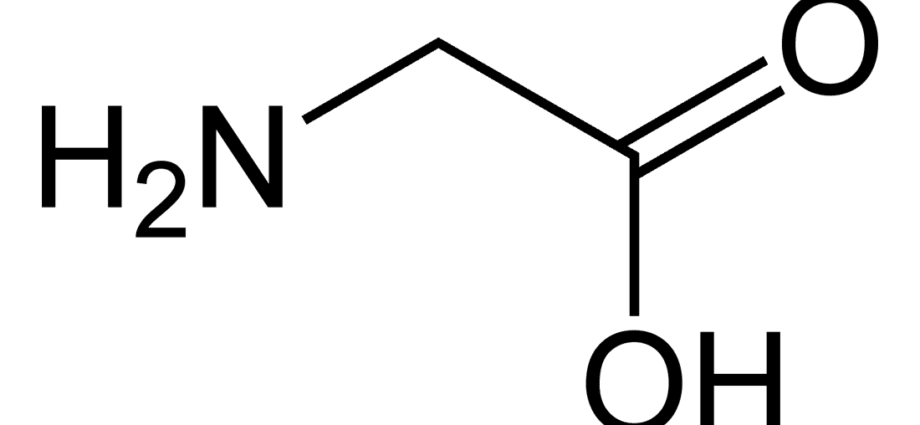
Glycine or aminoacetic acid Is an amino acid belonging to the group of nonessential. Under favorable conditions, glycine can be produced by the body on its own. In the cells of our body, purine bases (xanthine, adenine, guanine, etc.) and natural pigments, porphyrins, are synthesized from glycine, which are involved in the most important biological processes. Glycine is a component of many biologically active compounds and proteins. Glycine chemical formula: NH2 – CH2 – COOH. Usually glycine is formed by the interaction of proteins with water, as well as through chemical synthesis.
Glycine, obtained chemically, is a colorless, sweetish powder, tasteless and odorless. It dissolves well in water.
In the food industry, the amino acid glycine is used to improve the palatability of food. On the labels it is usually listed as E-640, and for most people it is completely safe.
Daily requirement for glycine
The amount of glycine that should be consumed per day is 0,1 grams for children and 0,3 grams for adults. As for athletes experiencing increased physical activity, the use of this amino acid can be increased to 0,8 grams per day.
The need for glycine increases with:
- stressful situations;
- weakness of the central nervous system;
- alcoholic and drug intoxication;
- traumatic brain damage;
- vascular accidents – strokes and heart attacks.
The need for glycine decreases with:
- individual intolerance to amino acids;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- hypotension;
- work requiring a quick response.
Digestibility of glycine
In the process of metabolism, glycine breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. It does not accumulate in the body.
According to studies conducted at Simon Fraser University of Vancouver, the absorption of glycine depends primarily on How long the body feels its lack. Naturally, provided that the body itself was not subject to genetic abnormalities and is sensitive to the lack of this amino acid.
Useful properties of glycine and its effect on the body:
Glycine is an essential component of the brain and spinal cord. Glycine consists of receptors that transmit inhibition signals to neurons. This amino acid reduces mental and emotional stress. It has a positive effect on metabolic processes in the body, helps to restore brain performance.
Glycine makes it easier to fall asleep, counteracts insomnia, normalizes sleep rhythms, and is an excellent tool for a good mood. Scientific studies have shown that glycine helps to reduce the damaging effects of alcoholic beverages on the human body. It normalizes the processes of inhibition of the central nervous system. In neurology, glycine is used to relieve increased muscle tone.
Interaction with essential elements
Glycine interacts with iron and calcium. Due to the combination of these microelements with an amino acid, their more complete assimilation by the body takes place. In addition, glycine interacts with several essential amino acids. As for the synthesis of glycine, choline (one of the B vitamins) takes an active part in it.
Signs of a lack of glycine in the body:
- increased nervous irritability;
- poor sleep;
- trembling in the body;
- weakness;
- depression.
Signs of excess glycine in the body:
- hyperactivity;
- heart palpitations;
- various allergic reactions;
- redness of the face;
- fatigue.
Factors affecting the content of glycine in the body
Medical sources indicate the importance of following all the rules of a healthy lifestyle for the full absorption of glycine. Among those, the following can be noted:
- compliance with the drinking regime;
- gymnastics;
- stay in the fresh air;
- balanced diet.
Glycine for beauty and health
To keep the body healthy for a long time, you should regularly consume glycine-containing foods that are able to streamline the processes of excitation and inhibition. They will remove the feeling of hopelessness, and also help to feel happy and needed by others. At the same time, the quality of sleep improves, energy and sociability appear.
Glycine and its compounds have shown themselves well as beauty stimulants. In combination with other nutritional components, glycine is responsible for the condition of the hair, improving its structure and shine. In addition, this amino acid has proven itself in the production of creams and ointments that are responsible for the nutrition and blood supply of the skin.