Contents
Definition of brain MRI
THEIRMBrain (magnetic resonance imaging) is an examination that can detect abnormalities in the brain and determine the cause (vascular, infectious, degenerative, inflammatory or tumor).
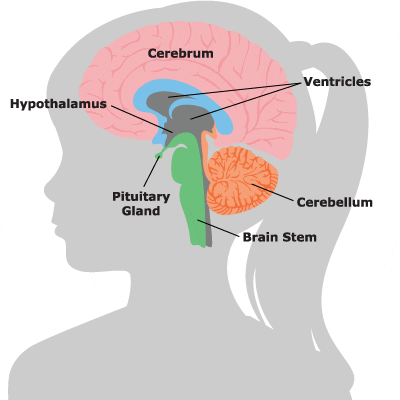
MRI makes it possible to visualize:
- the superficial part (white matter) of the brain
- the deep end (gray matter)
- the ventricles
- venous and arterial blood supply (especially when using a dye)
In many cases, MRI provides information that cannot be seen by other imaging analysis techniques (radiography, ultrasound or even computed tomography). MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to visualize all the tissues in the three planes of space.
Why perform a brain MRI?
Brain MRI is done for diagnostic purposes. It is a test of choice for all brain pathologies. In particular, it is prescribed:
- to determine the cause of headaches
- to assess the blood flow or the presence of blood clots to the brain
- in case of confusion, disorder of consciousness (caused for example by diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s)
- in case of’hydrocéphalie (accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain)
- to detect the presence of you die, ofinfections, or evenabscess
- a cas de demyelinating pathologies (such as multiple sclerosis), for diagnosis or monitoring
- in the event of abnormalities leading to suspicion of brain damage.
The exam
For a brain MRI, the patient lies on their back on a narrow table capable of sliding into the cylindrical device to which it is connected.
Several series of cuts are made, according to all plans of the space. While the images are being taken, the machine will make loud noises and the patient must avoid any movement in order to obtain the best possible quality images.
The medical staff, placed in another room, manage the settings of the device and communicate with the patient through a microphone.
In some cases (to check blood circulation, the presence of certain types of tumors or to discern an area of inflammation), a dye or contrast product may be used. It is then injected into a vein before the exam.
The exam takes quite a long time (30 to 45 minutes) but is painless.
What results can we expect from a brain MRI?
Brain MRI allows the doctor to detect the presence of, among other things:
- an tumor
- bleeding or swelling (edema) in or around the brain
- an infection or a inflammation (meningitis, encephalitis)
- abnormalities that may reflect the presence of certain diseases: Huntington’s disease, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s disease
- bulge (aneurism) or malformation of blood vessels
Depending on the diagnosis that he will establish on the basis of the MRI images, the doctor may propose an appropriate treatment or support.