Contents
Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis)
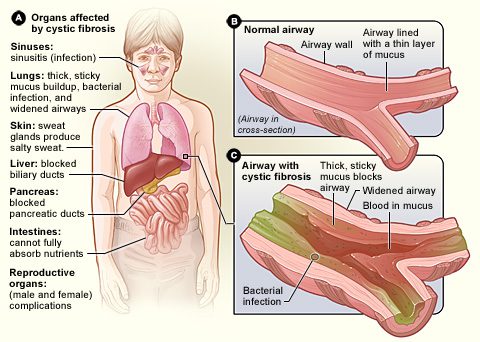
La cystic fibrosis, is here genetic disease the most frequent. The main manifestations concern the respiratory and digestive tracts but almost all organs can be affected. Symptoms often appear early in infancy and vary in severity from person to person. This disease causes a thickening mucus secreted by the mucous membranes of the sinuses, bronchi, intestine, pancreas, liver and reproductive system (see diagram).
The lungs are often the most severely affected. The thick, viscous secretions obstruct the bronchi, making it difficult to breathe. In addition, the mucus that accumulates in the lungs is conducive to the growth of germs. People with cystic fibrosis are therefore more at risk of suffering from frequent and potentially serious respiratory infections.
La cystic fibrosis also touches the digestive system. Mucus tends to block the thin ducts of the pancreas, preventing digestive enzymes produced by the pancreas from entering the intestine and carrying out their activity. As food is only partially digested, especially fats and certain vitamins, significant deficiencies occur. They can give rise to a growth retardation.
The disease also has major repercussions on the liver and reproductive organs, often resulting in subfertility in women and infertility in affected men.
Thanks to a earlier diagnosis and better care,life expectancy and the quality of life of those affected has continued to improve over the past decades, especially since new therapies, targeted at the genetic anomaly, are starting to emerge and will modify the management of patients in the medium term. .
Prevalence
La cystic fibrosis is the genetic disease most common in France with nearly 6000 people affected1.. One in 4 newborns is affected by this disease. It is much rarer among blacks (000 in 1) and Orientals (13 in 000). It affects both men and women. The population of western France is the most affected.
La cystic fibrosis is the genetic disease most common serious disease in Canada. One in 3 newborns is affected1. Cystic fibrosis is somewhat more common in Québec than in the rest of Canada: 3 Canadians are affected, including 500 Quebecers.
Causes
La cystic fibrosis was first described in 1936 by Dr Guido Fanconi, a Swiss pediatrician. The responsible gene, named CFTR (for “Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance Regulator”), was not identified until 1989 by Canadian researchers. In sick people, this gene is abnormal (we say he is transferred). It is responsible for the synthesis of a chlorine channel allowing to regulate the hydration of the mucus. In the event of an abnormality in the CFTR gene, the mucus product is too thick and does not drain normally. More than 1 different mutations in the CFTR gene involved in cystic fibrosis have been identified2, 3,4. They are divided into 6 classes according to the different type of dysfunction2Of these many mutations, the Delta F508 mutation, found in 81% of people affected in France, is the most common.
Cystic fibrosis is not a contagious disease. People who own pathogenic mutations of the CFTR gene develop the disease sooner or later but to varying degrees of severity.
Diagnostic
Usually, cystic fibrosis is diagnosed as early as the first year of life because respiratory symptoms appear very early. In 90% of cases, the disease is detected before the age of 10 years.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor performs a sweat test (or sweat test). Indeed, the sweat of people with cystic fibrosis is much more concentrated in salt (2 to 5 times more than normal). The genetic tests allow the exact identification of abnormalities in the CFTR gene. They are essential for considering targeted therapies.
In France, cystic fibrosis has been systematically screened in all newborns since 20025. It has been shown that early screening improves the quality of life and life expectancy of affected children.Newborns are sampled at 3 days of life after parental consent, before discharge. maternity. The test does not give a definite diagnosis but which will be confirmed or invalidated by specific additional examinations (sweat test, genetic study).
In Quebec, there is no systematic screening of this disease. However, the Canadian Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, supported by several doctors, has been calling for the implementation of newborn screening for several years. Early detection has been shown to improve the quality of life and life expectancy of affected children.
Life expectancy
In the 1960s, thelife expectancy of children with cystic fibrosis did not exceed 5 years. Nowadays, according to the latest statistics, the median survival age is 47 years1. respiratory infections remain the most common cause of death.
Frequent complications
Cystic fibrosis is a disease that gradually damages the lungs, pancreas, and liver. the medical monitoring However, it helps to reduce the severity and frequency of complications.
The respiratory complications are the most frequent, including dilation of the bronchi, causing bronchitis, pneumonia with repetitions. There are periods of worsening respiratory symptoms, when patients are very “congested”, are more out of breath, lose weight, often due to infection. Respiratory damage can be life threatening.
As regards the digestive system, obstruction of the bile ducts that allow bile to flow into the digestive tract can lead to cirrhosis of the liver. Obstruction and progressive sclerosis of the pancreas, can cause nutrient malabsorption and the development of diabetes. These disorders often lead to nutritional deficiencies severe and chronic diarrhea. In general, deficiencies can be corrected by a special diet. Conversely, significant constipation, or even intestinal obstruction, can also occur.
Usually, puberty occurs later in boys and girls with cystic fibrosis. Finally, the fertility is decreased, especially in men who are almost all (95%) sterile due to obstruction of the vas deferens. These ducts carry sperm from the testes to the seminal vesicles. In women, the increased viscosity of vaginal mucus slows down the movement of sperm. The disease can also affect the regularity and frequency of ovulation. Fertility declines, but pregnancy is still quite possible.