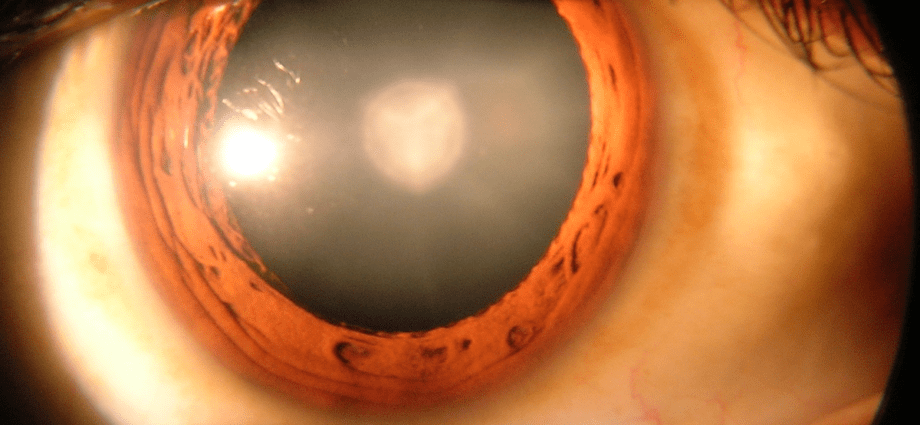
Cataract
La cataract is a disorder of the vision which occurs when the lens, this small oval lens located behind the pupil, loses its transparency.
When the crystalline becomes cloudy, the light rays reach the retina less well, which explains why the vision blurs. The word cataract was chosen to describe this feeling of looking through a waterfall (from the Latin cataract, which means waterfall). The lens plays the same role as the objective lens of a photographic camera: to focus the image according to the distance from the observed object. The lens does this by deforming to change its curvature.
Most often, cataracts form slowly, with the aging. Over time, the structure of the lens changes. We don’t know exactly why, but the main hypothesis is that lens proteins are altered by free radicals, substances produced naturally by the body and which contribute to aging. Free radicals are partially neutralized by antioxidants, mainly obtained from consumed fruits and vegetables.
The cataract represents the 3e cause of blindness in Canada. The main causes of blindness – macular degeneration, glaucoma and cataracts – usually occur with aging.
Who is affected?
From 65 years, the majority of people have an early cataract. The opacification of the lens does not cause significant visual discomfort if it is done in the peripheral layers of the lens.
After the age of 75 years, two-thirds of Americans have cataracts advanced enough to interfere with their vision. The vision loss tends to get worse with age. Cataracts affect both men and women.
Types
There are several forms of cataracts, of which the following are the main ones.
- Senile cataract. The majority of cataracts occur in the elderly. The normal aging process can lead to hardening and clouding of the lens. Age-related cataracts often affect one eye more than the other.
- Secondary cataract. Certain illnesses (especially diabetes, if poorly controlled), taking certain medications (for example, cortisone taken by mouth), or exposure to high doses of radiation can be the cause of cataracts. In addition, having had eye surgery or having certain eye problems (such as high myopia, glaucoma or retinal detachment) makes you more at risk of cataracts.
- Traumatic cataract. It occurs as a result of an eye injury that damages the lens: a blow, a cut, exposure to intense heat, a chemical burn, etc.
- Cataracts in children. Cataracts can start from birth, but it is rare. It may accompany a congenital disease (for example, trisomy 21) or result from an infectious disease from the mother transmitted to the fetus during pregnancy, such as rubella, toxoplasmosis, genital herpes or syphilis.
Evolution
When’visual acuity drops to the point of severely restricting daily activities, this is a possible sign of cataracts. Usually, this loss of vision occurs slowly, over several years. However, sometimes it happens more quickly (within a few months).
When the cataract is more advanced, the pupil no longer appears black, but rather gray or a milky white. In an advanced stage, vision may be limited to the perception of light.
When to consult?
La cataract is usually detected during a eye exam by an ophthalmologist. Any change in the quality of vision should prompt to see an ophthalmologist.