Contents
Blood in the urine of a child (or hematuria, erythrocyturia) is not an independent disease, but a consequence of any disease of the genitourinary system. Sometimes the appearance of blood in the urine of a child can be a variant of the norm that does not require medical intervention and anxiety, and sometimes it can be a formidable clinical symptom of a life-threatening pathology.
Normally, only 1-2 erythrocytes are found in the urine test. If the number of red blood cells is much higher (3 or more) – this is already hematuria. There are two variants of this pathology: microhematuria (when blood in the urine is detected only during examination under a microscope, the child’s urine itself does not change its color) and gross hematuria (when blood in the urine is visible to the naked eye, sometimes even blood clots are found).
Symptoms
With microhematuria, the blood in the urine of a child cannot be seen with the naked eye, but can only be detected during examination under a microscope. With gross hematuria, blood in the urine is enough for the child’s urine to change color – from pale pink to bright red and even dark, almost black. At the same time, parents should remember that a change in the color of urine can cause the use of certain coloring foods (beets, cherries, blueberries), drugs (analgin, aspirin), and there is nothing dangerous in this.
Sometimes blood in the urine of a child can be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back and when urinating. Difficulty urinating or its complete absence, fever, chills, weakness and general malaise may appear – it all depends on the disease, the consequence of which was hematuria.
Causes of blood in the urine in a child
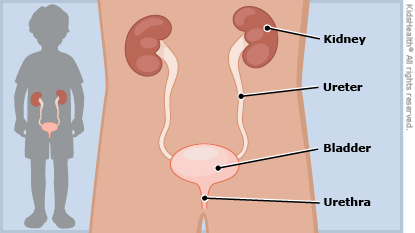
The main causes of blood in the urine in children are diseases of the genitourinary system (kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra):
- cystitis (inflammation of the walls of the bladder);
- urethritis (inflammation of the urethra);
- pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidney tubules);
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the renal glomeruli);
- hydronephrosis of the kidney (narrowing of the ureteropelvic segment, leading to a violation of the outflow of urine);
- urolithiasis disease;
- malignant formations of the kidneys or bladder (very rare in children);
- injury to the kidneys or bladder.
– The most common cause of blood in the urine of a child is various inflammatory diseases of the urinary system. These are nephritis, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, that is, kidney inflammation, and cystitis, inflammation of the bladder. Urolithiasis is also possible. Salts in the urine can produce red blood cells, various hereditary diseases (nephritis) and all sorts of problems with blood clotting – coagulopathy (in this case, in addition to the kidney, there will be other manifestations of bleeding). Blood in the urine can be a variant of the norm in the first days after the birth of a child – the so-called uric acid infarction. A small presence of erythrocytes in the urine of a child is acceptable immediately after acute respiratory infections. In this case, if the child is no longer worried, and there are few erythrocytes, the doctors simply recommend retaking the urine in two weeks and checking, – explains pediatrician Elena Pisareva.
Treatment
The most important rule: if you notice blood in the urine of a child, you do not need to self-medicate or let everything take its course. It is important to seek medical advice immediately.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hematuria in children includes a consultation with a pediatrician, during which he will take an anamnesis, clarify symptoms and ask about previous statements. After that, a urine test is prescribed (general and special – according to Zimnitsky, according to Nechiporenko), as well as such laboratory tests as: a complete blood count, a blood test to determine coagulation, to detect urea and creatinine, as well as ultrasound of the abdominal organs, bladder and ureter, CT or MRI, if necessary, or consultation of other specialists – a urologist, a surgeon.
Modern treatments
Again, it is not hematuria itself that is treated, but its cause, that is, the disease that caused the appearance of blood in the urine. In case of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, the doctor prescribes the necessary therapy – anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, uroseptics, as well as a course of vitamins to increase immunity. If blood in the urine appeared after the child had ARVI, then no treatment is prescribed, and the child is simply observed so that his condition does not worsen.
Prevention
As such, the prevention of hematuria in a child does not exist. It is necessary to monitor the health of the child, to prevent hypothermia, infections, injuries that can lead to diseases of the genitourinary system, and at the first symptoms, consult a doctor and undergo a full examination.
Popular questions and answers
Pediatrician Elena Pisareva answered popular questions about enuresis in children.