Contents
Biceps brachial
The biceps brachii (from the Latin biceps, coming from bis, meaning two, and from caput, meaning head) is a muscle located in the anterior part of the arm, a region of the upper limb located between the shoulder and the elbow.
Anatomy of the biceps brachii
Position. The biceps brachii is one of the three flexor muscles in the anterior muscle compartment of the arm (1).
Structure. Made up of muscle fibers, the biceps brachii is a skeletal muscle, that is to say a muscle under voluntary control of the central nervous system.
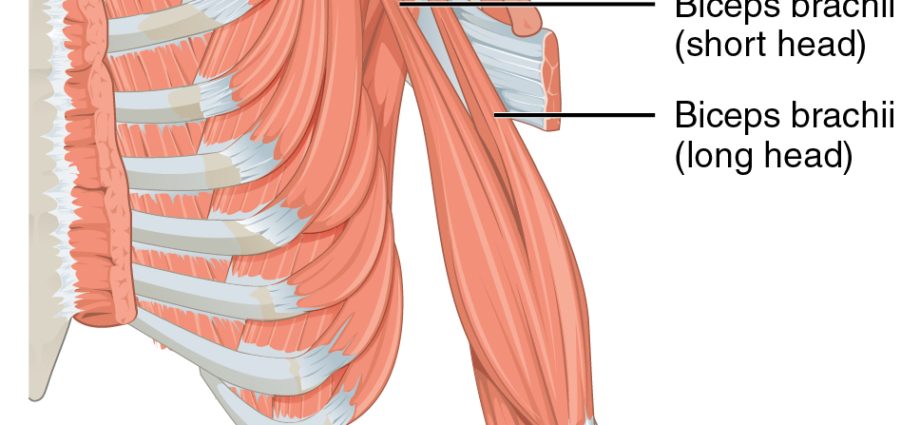
Zones d’insertions. Spindle-shaped in shape, the biceps brachii is made up of two different insertion sites: the short head and the long head (2).
- Origin at the upper end. The short head of the biceps brachii fits over the coracoid process of the scapula, or scapula, located on its upper edge. The long head of the biceps brachii is inserted at the level of the supraglenoid tubercle and glenoid bulge, located on the lateral aspect of the scapula, or scapula (2).
- Termination at the lower end. The tendons of the short head and long head of the biceps brachii join to insert at the level of the radial tuberosity, located at the level of the proximal end of the radius, bone of the forearm (2).
Innervation. The biceps brachii is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve originating from the C5 and C6 cervical vertebrae (2)
Biceps brachii movements
Movements of the upper limb. The biceps brachii is involved in various movements of the upper limb (2): supination of the forearm, flexion of the elbow and to a lesser extent, flexion of the arm towards the shoulder.
Pathology associated with the biceps brachii
Pain in the arm is frequently felt. The causes of these pains are varied and can be associated with different muscles such as the biceps brachii.
Muscle pain in the arm without lesions. (5)
- Cramp. It corresponds to an involuntary, painful and temporary contraction of a muscle such as the biceps brachii.
- Contracture. It is an involuntary, painful, and permanent contraction of a muscle such as the biceps brachii.
Muscle injuries. The biceps brachii can be damaged in the muscles, with pain.5
- Elongation. First stage of muscle damage, elongation corresponds to a stretching of the muscle caused by micro-tears and resulting in muscle disorganization.
- Breakdown. Second stage of muscle damage, the breakdown corresponds to a rupture of muscle fibers.
- Rupture. The last stage of muscle damage, it corresponds to a total rupture of a muscle.
Tendinopathies. They designate all the pathologies that can occur in the tendons. (6) The causes of these pathologies can be varied and can for example be related to the tendons associated with the biceps brachii. The origin can be intrinsic as well with genetic predispositions, as extrinsic, with for example bad positions during the practice of sport.
- Tendinitis: It is an inflammation of tendons such as those associated with the biceps brachii.
Myopathy. It includes all the neuromuscular diseases affecting muscle tissue, including those of the arm. (3)
Treatments
Drug treatments. Depending on the pathology diagnosed, different treatments may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical treatment. Depending on the type of pathology diagnosed, a surgical operation may be performed.
Physical treatment. Physical therapies, through specific exercise programs, can be prescribed such as physiotherapy or physiotherapy.
Examination of the biceps brachii
Physical examination. First, a clinical examination is performed to assess the symptoms perceived by the patient.
Medical imaging examination. X-ray, CT, or MRI exams can be used to confirm or further the diagnosis.
History
When one of the tendons of the biceps brachii ruptures, the muscle can retract. This symptom is called “Popeye’s sign” by comparison to the ball formed by the biceps of the fictional character Popeye. (4)