Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Cancer sounds like a sentence. However, not all cancers develop at a dizzying pace, and not all metastasize. Some cancers are easily and quickly treatable and do not even leave a trace of them in a short time. Some, however, especially malignant ones, require long-term and invasive treatment. What are cancers and what are their types?
What are tumors?
Simply put, cancer is a group of diseases in which cells in the body divide out of control. The newly formed cells, called cancer cells, do not differentiate into typical tissue cells. The lack of control over these divisions is associated with mutations in the genes encoding proteins that participate in the cell cycle. Mutations make the cell unresponsive or not responding properly to signals sent from the body. For a cancer to be malignant, several mutations must occur, which is why most often the most dangerous tumors develop in the body for a very long time and without symptoms. People with a family history of cancer inherit some of these mutations. The causes of neoplasms are not fully understood, but there are physical and chemical factors, viral infections, types of diets or stimulants that may affect the development of neoplastic cells. Cancer develops in several stages. The neoplastic process may last several years, and in the case of an aggressive neoplasm, even up to a month.
Benign and malignant neoplasms — differences
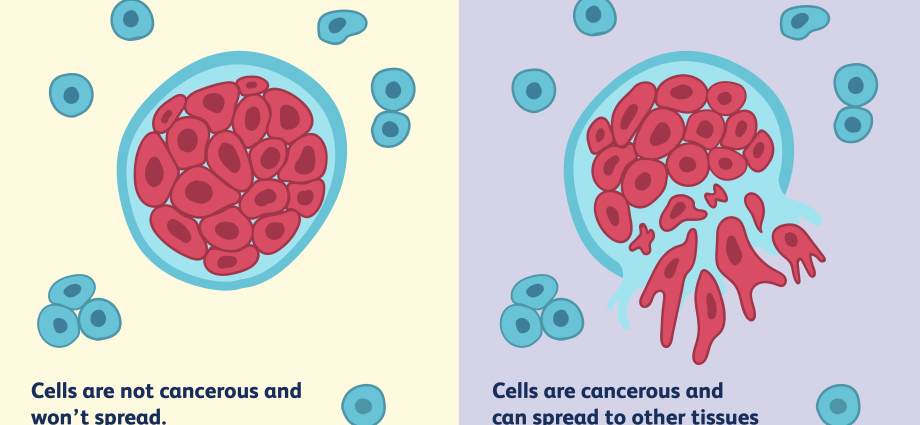
There are two basic types of cancer: benign and malignant. Benign neoplasms are composed of differentiated and mature tissues, and their structure does not differ significantly from the image of normal tissues. Benign tumors usually develop very slowly, are relaxing and do not metastasize. After removal of this type of neoplasm, there is usually no remission of the disease. This means that benign tumors are completely curable. The harmful effect of benign tumors on the body is manifested; hormone secretion, bleeding, vessel lumen closure or placement in an organ important for life, e.g. heart or brain. Malignant neoplasms, on the other hand, are composed of immature cells, the structure of which differs significantly from the image of normal tissues. They are characterized by rapid growth, atypia and the absence of a purse. Malignant tumors spread throughout the body by invading other tissues. Infiltration of the lymphatic and blood vessels causes cancer cells to enter the bloodstream and along with it can be transported to distant places in the body where they will metastasize. The time and extent of disclosure is one of the factors that determine the degree of malignancy of a neoplasm.
Malignant tumors are classified according to the type of tissue they originate from.
Tumors — cancer
Cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the epithelial tissues of the respiratory, digestive, and genitourinary systems. Cancer is most often diagnosed in adults, and is extremely rare in children. Men most often suffer from lung, prostate, head or neck cancer, while women struggle with breast or cervical cancer. A feature of cancer are regional and distant metastases. The sooner cancer is diagnosed and treated, the better the chances of a cure. Treatment for cancer is most often aggressive and affects the patient’s condition and well-being.
Also read: Birthmarks and benign neoplasms
Tumors — sarcoma
Sarcomas are cancers that originate in soft tissues. This type of cancer is less common than cancer. Sarcomas are much less diagnosed because they develop in deep tissues and organs. The prognosis for sarcoma is serious, but surgery and radiochemotherapy can completely cure the tumor. Some of the sarcomas grow very quickly and have a tendency to remission, and are also prone to metastasis, often multiple.
Cancer — lymphoma
Lymphomas, as the name suggests, develop in the lymphatic system. The first symptom of lymphoma is enlarged lymph nodes. Treatment of lymphomas is based on multi-drug chemotherapy, but the prognosis is very favorable. Lymphomas are a group of cancers that more often affect young people. In older people, the course of the disease is slower, with greater chances of recovery.
Tumors — melanoma
Melanoma is a malignant tumor that originates in pigment cells. Most often it affects the skin. The first symptom of malignant nevus is an inflammatory rim, growth or ulceration. Melanoma is a cancer that grows very quickly and causes multiple metastases to various internal organs. Prophylactic moles are removed, especially those that are prone to abrasions.
Check: She downplayed a small spot on the buttock – the star warns of melanoma
Tumors of the central nervous system
Tumors of the central nervous system are most often brain tumors that originate from various cells of the nervous system. Multiform gliomas have the least favorable prognosis. Treatment in this case includes surgery and, as an auxiliary, radiotherapy. Some tumors in this group can be completely cured.
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website.