General description of the disease
The turbulent 21st century has radically changed the living conditions of people. And the changes that have arisen do not always have a beneficial effect on health. Diets, foods high in sugar, fat, cholesterol, salt, low mobility at work and at home contribute to the rapid development of arrhythmias in people – a violation of the pace and rhythm of heart contractions. The causes of this disease include conflicts at home, at work, in transport, smoking and alcohol abuse. And once the foundation is laid, then any insignificant reason for the occurrence of arrhythmia is sufficient.
See also our dedicated article Nutrition for the Heart.
Signs of a possible onset of the disease can be:
- strong and sometimes uneven heartbeat;
- trembling hands;
- heaviness in the heart when walking on foot;
- sweating;
- feeling short of breath;
- darkening of the eyes;
- dizziness and discomfort in the heart in the morning.
The following diseases can also cause a heart rhythm failure:
- infection;
- inflammatory diseases;
- cardiac ischemia;
- disorders in the thyroid gland;
- hypertonic disease.
The first thing a person should do if an arrhythmia is suspected is to measure the pulse. The norm is considered to be 60 – 100 beats per minute. If the pulse is less than or more than 120, it is necessary to immediately seek help from a doctor to receive timely treatment.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to get rid of such attacks forever. But with the right regime, you can achieve a minimum of them. This requires:
- revise your menu and remove from the diet dishes from foods rich in sugar and cholesterol;
- you should make a diet of plant foods and low-fat foods;
- eat a little so that a crowded stomach does not irritate the vagus nerve, which can, in turn, negatively affect the functions of the sinus node, which is responsible for heart impulses;
- take as a rule daily reasonable physical activity in the form of gymnastics in the morning and walking in the evenings in the fresh air, which will allow the heart muscle to work more efficiently;
- you should avoid static loads, do not lift weights, do not move bulky objects so as not to cause an increase in blood pressure.
Useful foods for arrhythmia
Correct food intake is the key to health. Therefore, you should adhere to the following rules:
- 1 it is never recommended to sit at the table if you do not feel like eating;
- 2 food should not be eaten in an agitated state or in a bad mood, immediately after cooling or overheating;
- 3 when eating, it is best to focus on its usefulness, not to be distracted by reading, talking or watching TV;
- 4 food must be chewed thoroughly;
- 5 with arrhythmias, the amount of fluid consumed should be reduced in half;
- 6 you should stop eating when you want to eat a little more;
- 7 do not take food both cold and very hot;
- 8 be sure to break food intake 3-4 times;
- 9 vegetable products in the daily diet should be 50-60% of the total amount, carbohydrate up to 20-25%, protein 15-30%.
Useful gifts of nature for arrhythmia include:
- pear, which has an invigorating and refreshing effect, is able to reduce tension, improve mood, aids in the digestion of food, and normalizes the heartbeat;
- irga is a shrub with excellent anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic properties, which is a capillary-strengthening agent that helps after a heart attack, reduces blood clotting, relieves vasospasm, prevents the development of thrombosis, improves the nerve conduction of the heart muscle, strengthening it;
- plum – lowers blood cholesterol and strengthens the walls of blood vessels;
- raspberries – as a remedy that perfectly strengthens the walls of blood vessels, lowers blood pressure and cholesterol levels, containing organic acids, tannins, pectin, vitamins B2, C, PP, B1, carotene, iodine, potassium, folic acid, magnesium, sodium, iron and phosphorus;
- red pepper and tomato, which have a beneficial effect on the walls of blood vessels and normalize the function of the cardiovascular system;
- rosemary, which helps to raise low blood pressure and strengthen blood vessels
- all types of currants containing vitamins: B1, PP, D, K, C, E, B6, B2 and oxycoumarins – substances that reduce blood clotting, and which are also effective for the prevention of thrombosis and as a means of lowering blood pressure, improving hematopoietic processes and toning the work of the heart;
- apricot – improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- cucumber seeds – remove cholesterol and perfectly clean the walls of blood vessels from the inside;
- watermelon – removes excess cholesterol;
- melon – removes cholesterol from the blood;
- turnip is an excellent remedy for calming a strong heartbeat;
- beets – a vasodilator, effectively lowers blood pressure;
- parsley – a diuretic necessary for arrhythmias;
- grapes – eliminates shortness of breath and swelling, improves heart rate and tone of the heart muscle, “cleans” the blood;
- corn – reduces cholesterol deposits;
- apples – reduce the risk of developing cancer and heart disease, promote weight loss, reduce swelling, improve digestion and normalize blood pressure, due to the content of plant fiber and vitamins in them;
- avocado – contains a complex of vitamins: E, B6, C, B2 and minerals, copper, iron and enzymes that prevent the development of anemia, and help in the assimilation of nutrients necessary for the work of the heart;
- cabbage and potatoes – a source of potassium, normalize the functions of the heart muscle;
- grapefruit – rich in glycosides, vitamins C, D, B1 and P and plant fiber, which contribute to the regulation of physiological processes in the body, improve heart function, normalize digestion;
- pomegranate helps to lower cholesterol and thin the blood;
- flaxseed oil, which is so necessary for arrhythmias and is rich in monounsaturated fats, which prevent blockage of blood vessels;
- cereals rich in fast-dissolving fiber that prevent the absorption of cholesterol;
- Lentils and red beans contain vegetable fiber and potassium, which help strengthen the heart;
- beans rich in flavonoids, fiber, iron and folic acid;
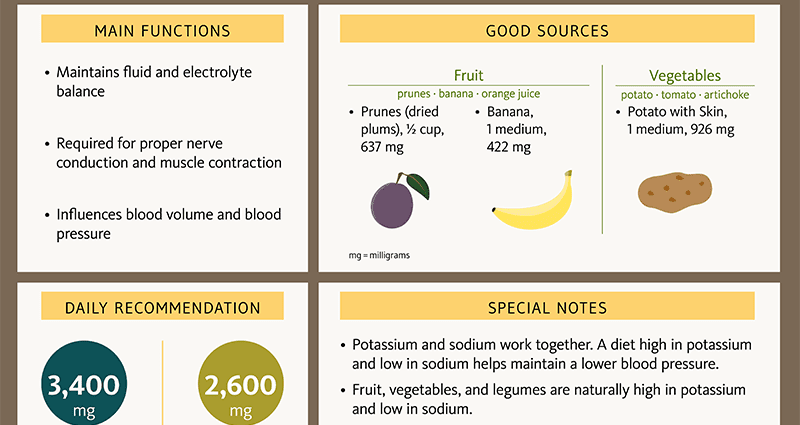
- pumpkin containing beta-carotene, vitamin C and potassium, which normalize the water-salt balance and lower blood pressure;
- garlic, which contains nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide, which reduce vascular tone;
- broccoli is rich in vitamins C, B and D, potassium, magnesium, iron, fiber, phosphorus and manganese;
- fish is a natural source of Omega – 3 acids;
- wheat germ oil containing oleic acid, alpha-linolenic and linoleic acids.
Nontraditional methods of treatment
Non-traditional therapy is a storehouse for the treatment of heart diseases in all sorts of ways and methods. To do this, use treatment with herbs, substances of animal, mineral and other origin, etc. These include:
- hawthorn – “bread of the heart”, which eliminates arrhythmia and relieves heart pain, increases blood circulation, lowers cholesterol;
- yarrow, in the form of juice, used with a strong heartbeat;
- rose hips – vitamin remedy;
- clay – which is rich in quartz, aluminum oxide, helps with increased nervous heartbeat;
- copper, in the form of copper applications, is effective for arrhythmia attacks;
- bee honey helps with severe heart diseases, with a weakened heart muscle, with high blood cholesterol;
- raw bovine heart;
- a mixture of lemon, honey, apricot pits;
- infusion of viburnum with honey;
- a mixture of lemons, honey and dried apricots;
- onions + apple;
- peppermint;
- a vitamin mixture of lemons, dried apricots, raisins, walnut kernels and may honey;
- asparagus.
Dangerous and harmful products for arrhythmias
In case of arrhythmia, the following should be avoided:
- fatty meat;
- fat;
- sour cream;
- eggs;
- strong tea;
- coffee;
- hot and salty seasonings and spices;
- regular chocolate, due to its high sugar and high calorie content, which contributes to weight gain;
- products that contain preservatives, GMOs and growth hormones that provoke the development of cardiovascular diseases;
- not fresh or artificially grown;
- fried, smoked or deep-fried foods.
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!