Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Allergic swellings, which are usually of a limited nature, arise more or less fleetingly as a consequence of an allergic reaction. This happens, for example, after a mosquito bite, a bee sting or after eating certain foods (such as strawberries) that are an allergen for a given organism that triggers its reaction with antibodies. The swellings are the result of a temporary increase in the permeability of the capillaries.
What are allergic edema?
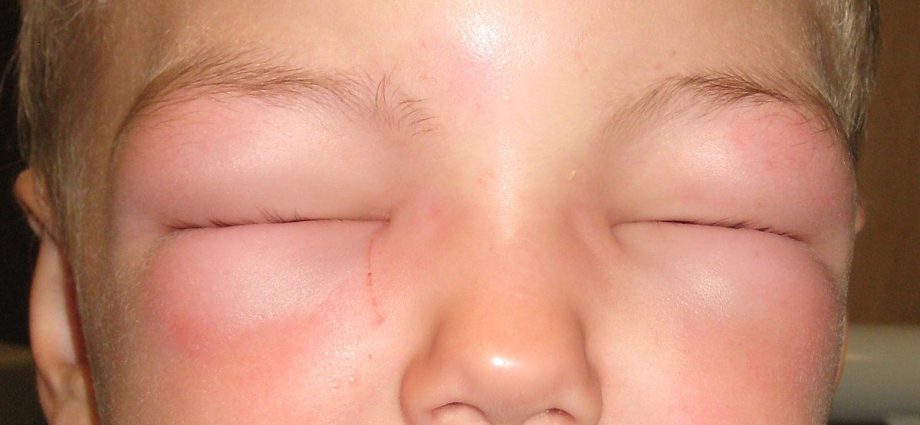
Allergic swelling, also known as angioedema or Quincke’s, is an allergic reaction similar to urticaria, but slightly deeper localized. It attacks the deeper layers of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, and is prone to occurring around the eyes and mouth. It can sometimes affect other parts of the body, such as the genitals or the hands. Allergic swelling generally does not itch, the skin is pale and disappears after 24-48 hours. Swelling usually occurs after food, medication or a sting. Allergic edema affecting the mucous membranes of the glottis or larynx is dangerous, as the patient may die from suffocation. Allergic swelling and nettle are common conditions in the human population. Single episodes occur in approximately 15-20% of people. Relapses of symptoms are observed in about 5% of the population, usually middle-aged people (more often women).
Read also: Proper breathing – how does it affect our body?
The causes of allergic edema
The most common causes of allergic edema are:
- Foods you eat – The most allergenic foods are eggs, fish, milk, nuts, peanuts, wheat and shellfish. Symptoms usually begin at night and reach their maximum in the morning. Find out if you have food allergies with a 10 allergen test done in your own home.
- Drugs taken – among the preparations that can sensitize you can find: painkillers, cephalosporins, contrast agents, especially high molecular weight drugs, insulin, streptokinase, tetracyclines, sedatives.
- Parasitic infections.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Viral, bacterial and fungal infections.
- Allergens in the form of pollen or latex.
- Spontaneous predisposition to angioedema.
If there are puffiness, bags and dark circles under your eyes, reach for the Serum for dark circles and puffiness under the eyes in the Punica roll-on, which you can buy at Medonet Market at a discounted price.
Types of allergic edema
Taking into account the cause of the occurrence of allergic edema, its different types are distinguished:
- idiopathic allergic edema – the cause of its occurrence is unknown, although there are certain factors that increase its risk, e.g. iron and folic acid deficiency in the body, stress, thyroid dysfunction, vitamin B12 deficiency and previous infections.
- allergic angioedema – a very common condition that usually occurs in people who are allergic to certain products. An acute allergic reaction to consumed food can manifest itself not only in swelling, but also with difficulty breathing and a sudden drop in blood pressure. To get rid of allergies, avoid consuming allergenic products;
- hereditary allergic swelling – occurs as a result of inheriting abnormal genes from parents. It occurs relatively rarely. Its symptoms include the throat and intestines, and the patient may experience severe stomach pain. The severity of disease symptoms is influenced by factors such as pregnancy, taking oral contraceptives, infections and injuries;
- Drug-induced allergic swelling – the symptoms of this swelling appear as a result of taking certain pharmacological preparations, e.g. drugs for high blood pressure. Disease symptoms may appear at any time during drug use and persist for up to three months after discontinuation of the drug.
Diagnosis of allergic edema
In the diagnosis of allergic edema, the medical history and the morphological features of the edema as well as the effectiveness of antiallergic preparations are very important. During diagnostics, skin tests are carried out for substances that may cause allergies, as well as elimination and provocation tests.
There are certain medical conditions that may manifest as allergic edema. They should be ruled out before starting treatment.
1. Lymphoedema – the cause of the symptoms lies in the obstructed outflow of lymph from the tissues and its retention in the form of edema.
2. Rose – is characterized by facial swelling due to inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue.
3. Shingles – it is a viral disease that can affect the area of the face.
4. Dermatomyositis – is a condition in which, apart from the swelling of the eyelids, redness may appear.
5. Crohn’s disease of the mouth and lips – may be associated with swelling and ulceration in these areas.
6. Acute allergic contact dermatitis – can affect any part of the body; the reaction may occur, for example, after contact with metal.
7. Appendicitis, ovarian cyst torsion (these ailments may be confused with the food form of allergic edema).
8. Superior vena cava syndrome – causes swelling and redness due to obstructed outflow of venous blood from the head, neck or upper chest.
9. Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome – is accompanied by, among others, swelling of the face.
Facts and myths about air purification
Are you looking for a dietary supplement that soothes swelling and inflammation? Order Echinacea Complex 450 mg capsules by choosing a product from the Medonet Market offer.
Pre-treatment procedures in allergic edema
Allergic swellings become a direct threat when they occur mainly in the head, especially the tongue, or in the larynx. In home pre-medical procedure in such situations you should:
- apply cold compresses to the site of the allergic swelling or apply cold objects, e.g. metal (provided the allergy site is accessible).
- use antiallergic drugs once,
- make an appointment with a doctor, especially when the symptoms are violent and the allergic reaction affects the upper torso, in order to shorten the time of medical assistance as much as possible.
The risk of an allergic reaction can be reduced by using probiotics, eg TribioDr. in capsules that you can buy on Medonet Market.
Allergic edema – treatment
Treatment of allergic edema is always an individual matter. Each time it is necessary to take into account the cause of the ailments. The choice of treatment also depends on: the location of the edema (larynx, face, neck, throat, tongue, mucosa); development speed; size and response to administered drugs. It is recommended to use temporarily:
- adrenaline 1/1000 subcutaneously;
- glucocorticoids, e.g., Dexaven;
- antihistamines (Clemastin);
- calcium preparations.
In turn, in the case of recurrent edema, individually selected p-histamines are administered or glucocorticosteroid therapy is implemented. In all cases of allergic edema, it is very important to keep the airway open. Involvement of the larynx or pharynx may cause suffocation and death. In extreme situations, the patient should be provided with patency of the airways by endotracheal intubation – the trachea is incised, and then a tube is inserted into the airway.
Allergic edema with urticaria is treated with glucocorticosteroids in combination with antihistamines. Moreover, patients are obliged to avoid allergenic factors, e.g. certain medications or foods. As an auxiliary, you can use Propolia BeeYes BIO gel for contusions and bruises with anti-swelling properties.
In the case of congenital allergic or acquired edema with C1-INH deficiency, a concentrate of this substance is used, especially when the patient’s life is at risk. Pain medications or androgens can also be used. Drug effects are monitored by concentration or activity measurements, including C1-INH.
Read also: Edema