Contents
Wrist tendonitis, what is it?
Wrist tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons in the wrist. This assignment affects, more particularly, athletes practicing a racket sport, or workers whose activity requires significant strain on the wrists.
Definition of wrist tendonitis
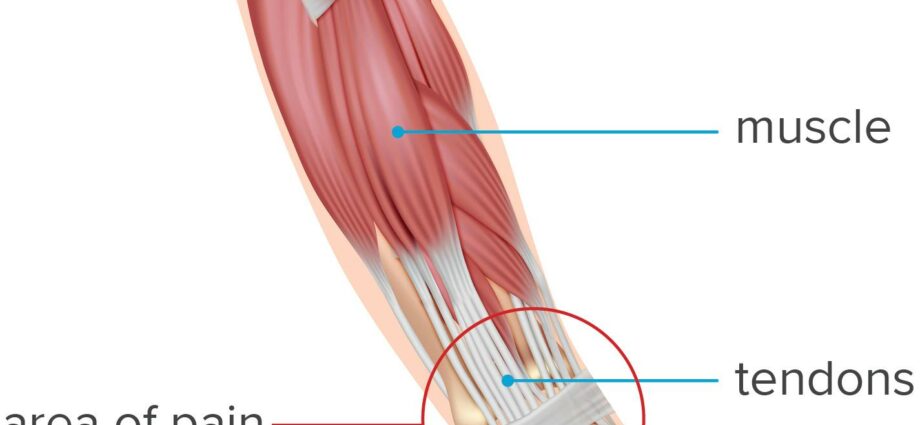
Tendons are small, elastic structures that allow muscles to attach to bones. They participate in setting the body in motion, by putting the bones into action, during muscle contraction.
Tendinitis is one of the tendon conditions. Wrist tendonitis is therefore defined by damage to the tendons in the wrists. It is an inflammation of these tendons, the origin of which can be various: sports practice, activities requiring excessive strain on the wrists, sudden movement, and others.
Certain work activities may be at the origin of the development of such an impairment. These include work on computers, or even activities in the production chain, requiring significant repetitiveness of actions.
Anyone can therefore be affected by a risk of tendonitis of the wrist. Nevertheless, athletes (particularly those practicing racket sports), as well as workers whose activity requires excessive strain on the wrists, are more prone to this risk.
A particular case of tendonitis is more and more noticeable: texting tendonitis. As the name suggests, the increasingly common use of the cell phone, and thus the repetition of gestures involving the fingers and wrists, leads to an increased risk of tendonitis.
Causes of tendonitis of the wrist
The causes of tendonitis of the wrist can be various.
The risk of wrist tendonitis is increased by playing racket sports: tennis, table tennis, badminton, etc.
Certain work activities, requiring excessive strain on the wrist or even repetitive gestures at a more or less constrained pace, can also lead to an increased risk of this type of affection.
The evolution of technology and the use of digital technology is also at the origin of an increased risk of tendonitis. Indeed, the important use of the computer (keyboard, mouse), as well as the abuse of SMS, are not negligible factors with regard to the tendon risk.
Symptoms of tendonitis of the wrist
The most common symptoms of wrist tendonitis are:
- pain, more and more intense, in the wrists. These pains are felt, in particular, in the execution of movements of the wrists.
- stiffness of the wrists, more important when waking up.
- muscle weakness, or even the inability to perform certain movements.
- a sensation of crunching tendons.
- swelling, sometimes with a feeling of heat and redness (characteristic signs of inflammation).
- the appearance of nodules deeper, affecting the tendons.
Risk factors for tendonitis of the wrist
The risk factors associated with wrist tendonitis are repeated: the intensive practice of racket sports, activities (professional and / or personal) involving excessive strain on the wrists, sudden and harmless movements.
How to prevent wrist tendonitis?
The risk of tendinitis can be reduced, by the following means:
- warm up well before practicing a sports activity
- ensure that you are properly equipped for an activity requiring excessive strain on the wrists: mouse pad with wrist support (also for the keyboard), wrist support accessories for athletes, etc.
- avoid recourse to repetitive gestures, as much as possible
- take regular breaks, allowing the recovery of the tendons and the muscular system.
How to treat tendonitis of the wrist?
Stopping the activity responsible for tendonitis is the first phase in the management of wrist tendonitis. Rest is highly recommended. When the symptoms gradually disappear, a return, also gradual, to activity is recommended.
Prescribing paracetamol, or ibuprofen, helps reduce the pain experienced in the context of tendonitis of the wrist. In addition, the application of an ice pack is recommended in order to deflate the affected area.
Persistent tenfinitis may require physiotherapy, corticosteroid injections or shock waves. Surgical intervention is possible, but remains exceptional and for the most important cases of tendonitis.