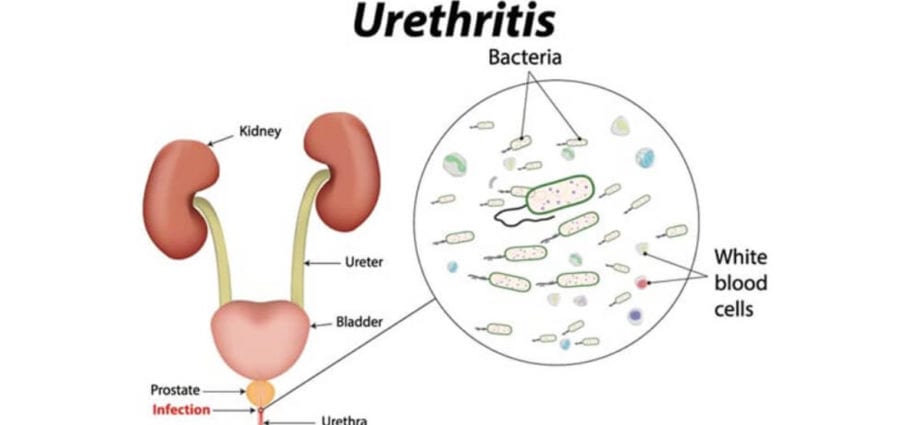
General description of the disease
Inflammation of the walls of the urethra is considered one of the most common urological pathologies.[3]… Women and men are equally susceptible to this ailment.
Anyone can get urethritis, but, as a rule, infection occurs during sexual intercourse with an infected partner. The course and development of the disease depends on the state of the patient’s immune system. The incubation period can be up to several months.
To determine the etiology of the disease, a smear is taken from the urethra and urine and blood tests are prescribed.
Types and causes of urethritis
- infectious species causes pathogenic viral or bacterial microflora. Pathogenic microbes from an infected kidney or bladder enter the urethra and cause inflammation;
- non-infectious species provoke injuries of the urethra, which occur during diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. The causes of non-infectious urethritis can also be allergic reactions to medicines, condoms, soap and food, as well as metabolic disorders, in some pathologies;
- acute urethritis most often develops after casual unprotected sexual intercourse. Moreover, it can be caused not only by venereal bacteria, it is enough for someone else’s bacterial microflora to enter the urethra;
- chronic appearance provoke infectious diseases such as tonsillitis and pneumonia;
- nonspecific urethritis – inflammation of the urethra caused by streptococci or E. coli;
- gonorrheal form provokes gonococcus. Infection from an infected person can occur not only through sexual contact, but also through common hygiene items;
- candidal urethritis causes yeast fungus. Most often, it affects the urethra with prolonged use of antibiotics.
Symptoms of urethritis
Chronic form pathology may not manifest itself in anything for a long time. Redness of the external opening of the urethra, minor pain during urination and scanty discharge from the urethra are possible;
Acute form the symptoms resemble cystitis: the patient complains of cramps during urination and mucopurulent discharge. Edema of the mucous membrane on the external opening of the urethra is possible.
With urethritis, an increase in temperature or general malaise is rarely observed. The disease can appear literally in a couple of hours after infection, or maybe in a few months. Common symptoms of urethral inflammation include:
- change in the shape and color of the external opening of the urethra;
- in men, pain during an erection is possible;
- a high indicator of the concentration of leukocytes in the urine;
- the urge to urinate is very frequent;
- cloudy urine, sometimes bloody;
- feeling of glued urethra in the morning;
- aching pain in the pubic area;
- in the morning, purulent foamy or mucous discharge with an unpleasant specific odor from the urethra;
- during urination, the bladder does not empty completely.
Complications of urethritis
With incorrect therapy of this pathology, the disease can develop into a chronic form. In men, chronic urethritis can cause prostatitis, impotence, and even infertility.
Prevention of urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra is a pathology that is easier to avoid than cure. This requires:
- 1 observe personal hygiene;
- 2 use condoms for casual sex;
- 3 do not supercool;
- 4 timely treat infectious diseases and pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- 5 if you need a study with instrumental intervention in the urethra, then make sure that this manipulation is carried out by an experienced doctor;
- 6 visit a urologist regularly;
- 7 drink enough fluids;
- 8 exercise moderately;
- 9 always empty the bladder completely;
- 10 do not wear too tight jeans;
- 11 give preference to underwear made from natural fabrics;
- 12 avoid stool disturbance.
Treatment of urethritis in mainstream medicine
The therapy of urethritis is based on antibacterial treatment. Among the many drugs, the urologist chooses the most optimal and affordable, focusing on the results of laboratory tests.
The duration of therapy depends on the stage, type of disease and the general condition of the patient and can take from 5-7 days to several months. As a rule, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.
In chronic urethritis, standard antibacterial treatment is supplemented by the introduction of drugs and immunostimulating agents into the urethra. Good performance in the treatment of urethritis gives hirudotherapy and visceral massage.
If urethritis is accompanied by cystitis, then the patient is shown physiotherapy procedures. During treatment, the patient needs to drink plenty of fluids and sexual intercourse is contraindicated until complete recovery.
Useful products for urethritis
The main goal of nutritional therapy for urethritis is to minimize irritation of the inflamed urethra. The diet should have a diuretic and antimicrobial effect.
The patient’s diet should consist of the maximum amount of products of natural origin. Since the human urinary system functions more intensively in the first half of the day, then most of the daily diet should be eaten before and during lunch. In the evening, it is necessary to give preference to light food, in this case, the urinary organs will not experience a large load.
The daily rate of fluid intake in patients with urethritis should be at least 2-2,5 liters. From drinks, it is better to give preference to fruit drinks, dried fruit compote, juices made with your own hands, weak tea, cranberry or lingonberry compote.
With urethritis, products are shown that promote urination, prevent constipation and strengthen the general condition of the patient, namely:
- 1 in the warm season: fresh carrots, zucchini, which are rich in fiber, as well as cucumbers and watermelons as a powerful diuretic effect;
- 2 steamed lean meat and lean fish;
- 3 high-quality fermented milk products;
- 4 honey;
- 5 buckwheat and oatmeal, which normalize intestinal motility;
- 6 garlic and onions are powerful antibacterial agents;
- 7 cabbage dishes;
- 8 Pine nuts;
- 9 asparagus and celery, which have a powerful antibacterial effect;
- 10 olive oil;
- 11 stew and fresh vegetable puree.
Traditional medicine for urethritis
Treatment of inflammation of the urethra in combination with drug antibiotic therapy gives good results:
- drink a decoction of black currant leaves as tea;
- every 2-2,5 hours, take 3 tbsp. spoons of parsley broth, which has not only a diuretic, but also a strong anti-inflammatory effect;
- linden tea has a good diuretic effect;
- douching with sage or chamomile decoction[1];
- drink 10-15 ml of parsley infusion in milk every hour;
- excellent antimicrobial properties are possessed by blackcurrant and cranberry juice;
- drink as tea during the day an infusion of blue cornflower baskets;
- lotions or warm baths with a decoction of oak bark are effective;
- trays based on a decoction of chamomile have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties; extracts of essential oils can be added to them;
- take inside 1/5 teaspoon of chopped parsley seeds twice a day[2];
- Add 5 drops of tea tree oil to 2 liters of water and use the resulting solution to douche or take baths.
Dangerous and harmful products with urethritis
To achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, patients with urethritis should refuse the following products:
- sour fruits such as lemons, peaches, apples, oranges. They irritate the inflamed mucosa and slow down the healing process;
- alcoholic beverages – contribute to dehydration, as a result of which the urine becomes more concentrated and irritates the inflamed urethra;
- store sauces, as they are high in fat, salt and preservatives;
- frequent sugar, baked goods, chocolate and sweets. It is an excellent food for microbacteria, which multiply rapidly, release toxins and slow down recovery;
- sorrel, radish, tomatoes – irritate the inflamed mucous membranes of the urethra.
- Herbalist: golden recipes for traditional medicine / Comp. A. Markov. – M .: Eksmo; Forum, 2007 .– 928 p.
- Popov A.P. Herbal textbook. Treatment with medicinal herbs. – LLC “U-Factoria”. Yekaterinburg: 1999.— 560 p., Ill.
- Wikipedia, article “Urethritis”.
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!