Contents
Prostate cancer is diagnosed by registering the proliferation of glandular cells of the prostate gland, the presence of which is characteristic only for men. Due to its significant contribution to the sexual life of the body, the prostate is called the “heart” of the masculine principle – the release of androgens (male sex hormones) and the liquid part of the ejaculate, which is necessary for transporting and feeding spermatozoa during fertilization, depend on it.
Just like tumors of the mammary glands, ovaries and uterus in women, prostate carcinoma is the most common malignant neoplasm in men. At the same time, there is a special correlation by race: among Negroids, about one and a half times more often than among Caucasians, and representatives of the Mongoloid race, in particular, the Japanese, are twice as rare.
It has been established that age is a determining risk factor for prostate cancer, since after 35 years it is found only in one out of 10 thousand men, after 60 – already in every hundredth, and among those who have reached 75 years, every eighth man suffers from carcinoma. In connection with this situation, WHO experts recommend that all men who have reached the age of 50 pass all the necessary tests to prevent aggravation of the disease.
What is prostate cancer?
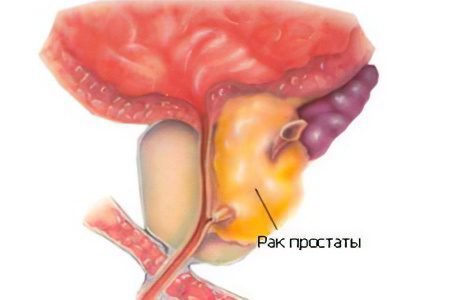
Prostate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that develops from prostate cells.
Anatomy of the prostate. The prostate is an endocrine gland that is located in men in the pelvic area, its average size is 3-4 cm. Due to the fact that the prostate is located around the urethra, its enlargement, provoked by a cancerous tumor, causes urinary dysfunction.
The prostate gland is located inside a capsule of connective tissue, contains elastic septa separating the prostatic glands. Consists of three parts – right, middle, left. In this gland, prostatic juice is produced, it is excreted during the contraction of smooth muscle muscles. The prostate is involved in the production of spermatozoa, increases their activity and vitality, is responsible for the quality of sperm and its excretion. Plays an important role in the implementation of male sexual function.
Functions of the prostate. For a more accurate understanding of the nature of the disease, it is necessary to understand in detail the main functions of the prostate gland. The main features of the functioning of the prostate are that it produces a certain part of the seminal fluid. According to experts, we are talking about more than a third of the total. She is also responsible for participating in the process of eruption of the seed.
Another key function of the prostate is that it has everything to do with any man’s ability to retain urine. That is why this gland is of great importance for the health of the male body.
How long do people live with prostate cancer?

In this, as in any other case related to oncology, it is very important to detect the disease as early as possible. However, the prognosis is most often unfavorable due to late detection and the occurrence of a significant number of early metastases. Thus, approximately 90% of cases of prostate cancer are detected at the third or fourth stage.
Therefore, answering the question of how long they live with prostate cancer, we can say that everything depends on the stage of the disease at which treatment was started. Radical type prostatectomy, which was carried out at an early stage of oncology in patients under the age of 70, is a guarantee of 10 or even 15 years of survival. In general, after a timely treatment course, the five-year survival rate for the first or second stage is 85%, the third -50%, the fourth – no more than 20%.
Metastases of prostate cancer capture distant areas, due to the spread of cancer cells through the blood and lymphatic vessels. Most often, pain in the pelvis, swelling of the legs in the area of the ankles or feet with prostate cancer means an increase in the number of metastases and the fact that the cancer has become aggressive.
Causes
Modern research links the causes of prostate cancer with chronic diseases and inflammatory processes that affect the prostate and provoke pathological changes in its tissues.
Common causes of prostate cancer include:
Hormonal imbalance – since a prostate tumor is hormone-dependent, its occurrence and growth can be triggered by an increase in the level of dihydrotestosterone and androstenedione (male sex hormones).
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland, as a result of which blood circulation and oxygen exchange in its tissues are disturbed;
Prostate adenoma – benign neoplasms contribute to the emergence of cells that do not normally appear in the prostate gland, they are more prone to mutation and malignancy, which provokes the onset of the oncological process;
Bacterial lesions of prostate cells and autoimmune processes damage the genetic apparatus of cells, contributing to their uncontrolled division and tumor formation.
Precancerous conditions, which include atypical adenosis and prostatic hyperplasia, lead to the formation of a cancerous tumor. With atypical adenosis, nodular formations appear in the center of the gland, the cells of which divide rapidly, and under the influence of mutagenic factors can degenerate into malignant ones. Hyperplasia – active focal cell division followed by degeneration or malignancy; the risk of developing an oncological tumor is significantly increased.
Risk factors for developing prostate cancer are related to hereditary predisposition and lifestyle. Thus, an increased content of animal fats in the diet, the intake of carcinogenic substances in the body as part of tobacco smoke and alcoholic beverages, harmful production conditions in the textile, chemical industries, welding shops and printing houses can contribute to the development of oncogenic formations. Stagnation of prostatic juice due to a sedentary lifestyle and irregular sexual activity may be a predisposing factor for the development of pathology.
Other risk factors are sexually transmitted diseases, older age, infection with retrovirus, cytomegalovirus, and a depressed immune system.
Prostate Cancer Symptoms
The first symptoms of prostate cancer (at an early stage of the disease) are absent, therefore, it is possible to determine the presence of oncological formations only with a special examination – diagnosis is carried out using a blood test for PSA (specific prostate antigen).
The first symptoms of prostate cancer can be considered difficulty urinating, sexual dysfunction, the presence of blood in the urine and semen. The patient associates all these manifestations with other diseases, the occurrence of any of them does not mean the presence of cancerous neoplasms, but may be one of the symptoms.
Prostate cancer usually manifests itself when the tumor reaches a significant size and puts pressure on the walls of the bladder. As a result, a man may experience frequent urge to urinate – from 15-20 times a day and more than 2 times at night. At the same time, urine comes out slowly, the stream is interrupted, there is a feeling of fullness of the bladder. The process becomes excruciatingly painful, there is a burning sensation, urine comes out in drops. The patient is forced to strain the press, since the tone of the bladder is weakened, in some cases a catheter is necessary.
Urinary incontinence and pain in the groin can also be symptoms of prostate cancer;
Swelling of the lower extremities, genitals, scrotum, provoked by metastases in the lymph nodes;
Kidney stones, pain in the lumbar region – the ureter and renal pelvis expand due to the outflow of urine in the opposite direction, which can be triggered by a cancerous tumor;
If an oncological neoplasm damages the vessels of the urethra or seminal vesicles, then there may be blood impurities in the urine and semen;
Violation of potency occurs when the nerve endings are damaged by a cancerous tumor;
Painful dry cough indicates cancer metastasis to the lungs;
Jaundice of the skin and heaviness in the right side are symptoms of the presence of secondary tumors in the liver;
If a person experiences pain during defecation, then the tumor could affect the intestines;
In the later stages of cancer, bone pain may occur when the tumor metastasizes to the bone tissues.
An increase in the intensity of all the above symptoms can be observed over several years, they appear gradually. Any of the above signs is a reason to see a doctor and be examined by a urologist.
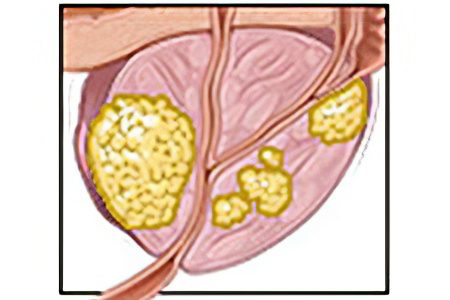
Stages of prostate cancer
It is necessary to distinguish between such concepts as the stage and degree of prostate cancer. The degree of the presented form of cancer should be considered an indicator of the clinical type, which determines the degree of morphological fluctuations in the cells of the prostate gland. That is, a study of the cell type is necessary, for example, a biopsy. It is she who makes it possible to determine the diagnosis literally at the first stage of the formation of the disease.
The stage of prostate cancer determines the increase in the size of the tumor formation and the further growth of the lesion. Identification of the stage is no less important than the degree of the disease, because it makes it possible to determine exactly what exactly is happening with the tumor, and whether there are metastases.
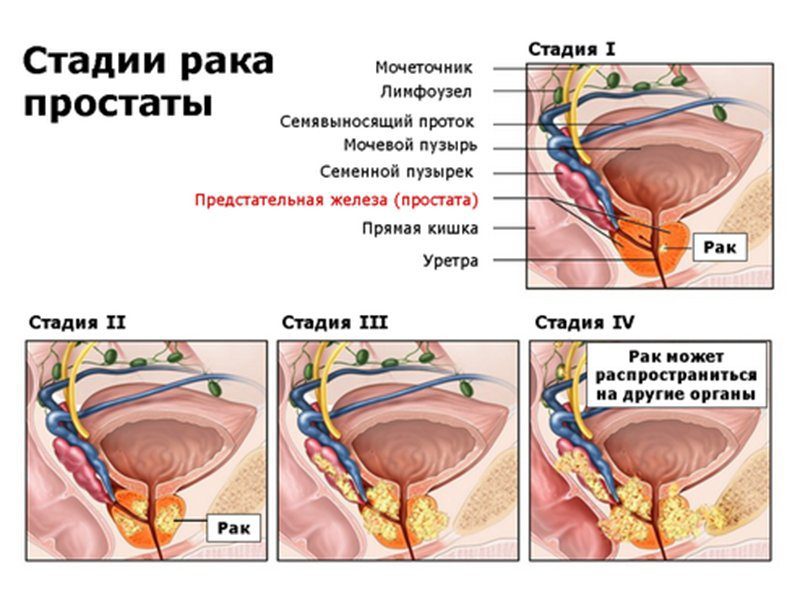
,
The first stage At the first stage, the tumor cannot be felt; any modifications in the structure of the gland and its separately located cells can only be established using microscopic examination. |
The second stage In the second stage, the enlarged lesion is visible on ultrasound, but its location is still limited to just the gland capsule and does not have any other foci of spread. |
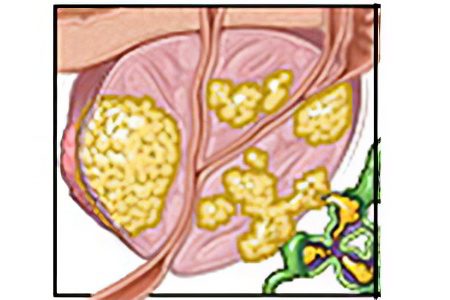
The third stage In the third stage, an invasive tumor spreads beyond the borders of the prostate, which are not directly related to the gland or are located next to it. |
Fourth stage In addition to the significant growth of the tumor focus, metastases at the 4th stage of prostate cancer grow into the liver, lymph nodes, lungs and bone tissue of the skeleton. |
Diagnostics
Even with the most minor problems with urination, it is advisable to contact a specialist in the field of urology as soon as possible. It can be not only prostate cancer, but also adenoma, as well as inflammation in the prostate area.
The primary method of diagnosis is a digital, rectal examination of the rectum. This method is the simplest and makes it possible to suspect oncology. However, in the case when the formation is already possible to probe, this indicates that the disease is at one of the final stages. In this connection, even in the case when the formation cannot be probed, the patient is prescribed an additional study: a blood test for the presence of a prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
To make a more accurate diagnosis, a man can also be prescribed an ultrasound of the prostate, computed tomography, X-ray and radioisotope examinations.
The final diagnosis can be made after a biopsy of the prostate gland – with a specific needle through the perineum or rectum, the specialist takes a small part of the gland in order to conduct a study.
What is the PSA level for prostate cancer?
A cancerous tumor limited to the borders of the prostate gland is often asymptomatic and does not manifest itself in any way. Therefore, for early and timely detection of only emerging aggressive disease, men are advised to regularly undergo a test that determines the level of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in the blood.
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) in the blood is a protein synthesized in the prostate gland, the normal level of which is shown in the following table:
Man’s age (years) | The norm of PSA in blood serum |
40-49 | < 2.5(мкг/л) |
50-59 | < 3.5(мкг/л) |
60-69 | < 4.5(мкг/л) |
70-79 | < 6.5(мкг/л) |
The test must be taken by men, starting at the age of fifty. And if there were cancer patients in the family, then this procedure is recommended to start earlier.
Determining the level of specific prostate antigen correlates with its size. In the presence of a large gland, the level of PSA in the blood is high, but this is not important. A tumor can also form with a low antigen index. The antigen can be found in the blood in both free and bound forms.
There is an inverse relationship between free PSA and cancer. The lower the concentration of the antigen in the blood serum, the higher the likelihood that its elevated level is caused by the presence of a cancerous tumor in the prostate gland.
This relationship is shown in the following table:
Free PSA(%) | Probability of Cancer in Percentage (%) |
0-10 | 56% |
10-15 | 28% |
15-20 | 20% |
20-25 | 16% |
more 25 | 8% |
Prostate Cancer Treatment
The type of treatment for prostate cancer depends on the age of the patient, his state of health, the stage of oncology and his wishes. Elderly men with pathologies of the lungs, heart, blood vessels and severe chronic diseases are recommended expectant management, since surgery can do more harm to the body than a cancerous neoplasm. In this case, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the prostate gland and a PSA test every six months to prevent intensification of tumor growth.
Operative therapy

Surgical treatment of prostate cancer is carried out by the method of radical prostatectomy – a patient under general anesthesia or with epidural anesthesia is excised of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues if the tumor has spread beyond the prostate. Sometimes excision of the lymph nodes is required, removal of part of the tumor in nearby organs, then the prognosis for recovery is less favorable, chemotherapy is additionally performed. Almost one hundred percent chance of recovery in patients whose tumor has not gone beyond the connective tissue capsule.
The duration of the operation is from 2 to 4 hours, it is prescribed for patients under 65 years of age due to possible risks and complications. The incision is made in the groin or abdomen. Modern surgical treatment of prostate cancer is carried out using the Da Vinci robot, controlled by a doctor. The operation is performed without incisions through small punctures, which accelerates the healing process of tissues and reduces the number of postoperative complications, minimizing the risk of impotence and other unpleasant consequences.
Orchiectomy

Another measure to combat prostate cancer is orchiectomy – the removal of either one or two testicles.
The presented surgical intervention leads to a stop in the production of endogenous testosterone and a decrease in the growth rate and further development of malignant formation. Intervention is desirable to be carried out solely on the basis of the diagnosis after the biopsy of the gland.
The intervention can be carried out not only on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia, but also under general anesthesia. During the operation, a technique is used in which visual changes remain unnoticed (reservation of the cord, the introduction of artificial testicles).
An orchiectomy makes sense in the following cases:
the process of treatment with hormonal drugs is not possible as a result of satellite diseases that are in no way associated with malignant formation;
in the absence of the possibility of taking prescribed hormonal drugs or injections every day.
Chemotherapy

Chemotherapy is the use of drugs with toxins that affect rapidly dividing cells. Due to the fact that tumor cells are characterized by rapid growth and division, chemotherapy allows selective action on their shell and nucleus, causing destruction. Such treatment is prescribed at the third and fourth stages of cancer, when the tumor metastasizes – toxic substances are carried throughout the body, destroying pathological cells. In the earlier stages of prostate cancer, such treatment is not advisable, as it has many side effects, the most common of which are nausea, hair loss, fatigue and weakness.
The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs are:
“Mitoxantrone” – most often used in combination with prednisolone in the later stages of the treatment of cancerous tumors, with the formation of metastases in bone tissues;
“Doxorubicin” – is recognized as one of the main components of chemotherapy, which is successfully used not only in the treatment of prostate cancer. The algorithm for the effect of a drug on any cells implies interaction with the DNA of cells. This is accompanied by blocking the production of protein in them, which, in turn, is almost the main building material;
“Paclitaxel” – it slows down the degree of activity of cancerous growths, affecting their skeleton, which consists of a large number of microscopic tubes. Due to this, they acquire greater flexibility, and this provokes the fact that the cells can no longer divide in a normal way and die soon enough;
“Extramustine Phosphate” – is a link between two strands of DNA, which makes the algorithm for copying it failed. The result of this is the impossibility of the development of a cancer cell, which, as a result, dies.
The course of taking chemotherapy drugs is six months, they are available in the form of tablets or injection solutions (Paclitaxel).
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy involves exposing cancer cells to X-rays, which damages their DNA and disrupts their ability to divide. It is carried out using a linear accelerator that spreads neuronal, gamma and beta radiation to the area of the tumor and, in some cases, the zone of the lymph nodes in order to stop its growth and the spread of pathological cells throughout the body.
Remote beam radiation therapy is applied in a course of five days a week for two months. The procedure itself is painless and takes only fifteen minutes, after which the person is recommended to rest for two hours. It is prescribed only for large tumors with metastases, since radiation can affect healthy cells, provoking a number of side effects.
Brachiotherapy has fewer side effects due to its selective action – radioactive substances (iridium, iodine) are injected into the prostate and act directly on the tumor, practically without affecting healthy cells and tissues. Thus, the effectiveness of the procedure is increased and side effects are minimized. Radiator needles are inserted under anesthesia and removed either immediately or during the day.
HIFU therapy is another modern method of radiotherapy, which is used to selectively kill a tumor without damaging healthy tissue. It consists in ultrasonic action on an oncogenic neoplasm, which destroys the structural proteins of pathological cells.
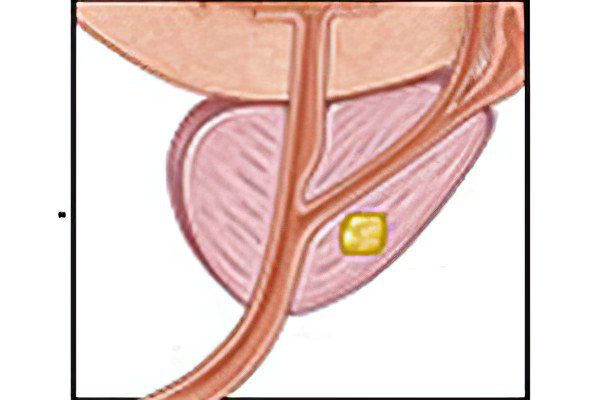
Brachytherapy

An alternative method of radiation exposure to the presented gland at the initial stages of the formation of the disease is brachytherapy. The essence of the method lies in the fact that under the control of ultrasound, iodinated granules with a high degree of radioactivity are injected into the gland. Due to this, an increased ratio of radiation is formed in the area of education, and the tissues located nearby are practically not affected.
The procedure for the introduction of capsules is given no more than an hour and it is carried out in an outpatient setting. This is what distinguishes it from other types of radiation treatment.
Medications for prostate cancer

The growth of prostate cancer is influenced by male sex hormones, an increased concentration of which leads to an increase in the size of the neoplasm. This is the reason for the effectiveness of drug therapy – with a decrease in the amount of androgens and a decrease in the susceptibility of tumor cells to their effects, its growth slows down significantly. The result of such treatment is more pronounced if it is applied at an early stage of the disease. But it is possible to slow down the growth of an oncological tumor and increase the patient’s life expectancy with the help of drug treatment even at an advanced stage of cancer.
Hormone treatment
It is used at the fourth stage of cancer, when surgical treatment is ineffective and can only aggravate the patient’s condition, and remains the only available treatment for oncological tumors in elderly people with chronic diseases.
Hormonal drugs for the medical treatment of prostate cancer:
Analogues of pituitary hormones – after their use, the level of androgens in the blood of men drops to a state that occurs after surgical castration. But unlike surgery to remove the testicles, this phenomenon is reversible – at the end of hormones, testosterone levels are restored. Preparations of this group – Lyukrin, Diferelin, Decapeptil, are used by injection.
Antiandrogens – prevent the interaction of pathological cells with adrenal hormones, the combination of antiandrogens with pituitary hormones in medical practice is called maximum androgen blockade and is one of the most effective methods of drug treatment of cancer. The drugs in this group include Flucin, Casodex, Anandron.
Gonadotropin-rising hormone antagonists, which lower testosterone, slowing down the growth of oncogenic neoplasms, and in addition, stimulate cell differentiation, due to which they turn from pathological into typical cells for prostate tissues. Preparations of this group – Fosfestrol, Firmagon, Diethylstilbestrol.
They begin treatment with antiandrogens – in some cases, Casodex is enough to slow down the growth of the tumor, while maintaining the sexual function of a man.
Hormone therapy in patients under 60 years of age is carried out in combination with cryotherapy – tumor freezing. When freezing, ice crystals form in pathological cells, which destroy them. Hormones are also prescribed in combination with radiotherapy.
A radical method of treating prostate cancer as part of hormone therapy is the removal of the testicles, after which the production of testosterone is irreversibly reduced. It is rarely used due to the severe psychological trauma that most men experience after this operation.
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are classified as methods of cancer immunotherapy, which are rarely used in our country, and were approved in America in 2006. Vaccines are being developed based on these drugs, containing antibodies that the body’s own immune system uses to fight cancer cells.
Virotherapy
One of the modern methods of treating prostate cancer involves the use of viruses that selectively destroy cancer cells, making it easier for the body to fight cancer. One of the most promising drugs in this group is ECHO 7 Rigvir, which allows you to stop tumor growth and activate the immune system to fight pathological cells. It is prescribed in the early stages of cancer before and after surgical treatment.
At the fourth stage of cancer, a therapy is prescribed that does not destroy the tumor, but slows down its growth and the spread of cancer cells throughout the body, and also improves the patient’s well-being, reducing pain. After surgical treatment, patients can live from fifteen years or more with successful therapy. Treatment of prostate cancer in the later stages is difficult due to the intensive growth and spread of tumor cells, but modern research in this direction will make it possible to overcome the disease in the near future.
Forecast
The prognosis for patients with prostate cancer depends on the stage at which treatment was carried out. Experts have the concept of “five-year survival”, which allows to assess the success of treatment. So, for patients who went to the doctor at the first stage of cancer, the five-year survival rate is more than 90% – that is, more than 90% of people live 5 years or longer after treatment. For the second stage of cancer, this figure is 80%, for the third and fourth – 40 and 15%, respectively.
If the patient sought medical help at the first stage of the disease, then as a result of therapy, he manages to fully restore control over the function of the bladder, sexual function, remove the tumor and return to working capacity. After successful treatment, the negative manifestations of prostate cancer are eliminated, the disease does not reduce life expectancy.
At the second and third stages, the success of treatment largely depends on the professionalism of the doctor and the patient’s health, age and general well-being. The therapy takes longer, the treatment is more complex, but the chances of success are quite high – the life expectancy of most patients after treatment is 15 years or more.
At the fourth stage of prostate cancer, the prognosis is unfavorable – few of the patients manage to live more than seven years after long-term combination therapy.
Prevention

To date, medicine cannot offer a XNUMX% way to prevent cancer, but if you follow the general recommendations for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, the risk of cancerous growths is minimized.
Regular sleep is a necessary condition for maintaining the health of the whole organism, it is in the process of sleep that melatonin is produced, a hormone that prevents the occurrence and growth of tumors.
Healthy diet – include more fruits and vegetables in the menu, cruciferous, legumes, garlic, onions, citrus fruits, leafy greens and yellow vegetables are especially useful for maintaining the antioxidant defense of the body. Eat lean meats, fish and seafood, prefer vegetable fats and cereals that are rich in dietary fiber, easily digestible protein, vitamin E and phytosterols.
Avoid carcinogens – carcinogens that provoke the development of tumors can enter the body with food, polluted air or water; tobacco smoke, products with aromatic and flavoring additives contain carcinogenic substances, their concentration is increased at chemical industry enterprises.
Preventive examination by a specialist – over the age of 50, men are recommended to screen the prostate for cancer at least once every two years and once a year for men with adenoma, prostatitis and other pathologies. Screening includes an ultrasound of the prostate and a blood test for prostate antigen.
Physical activity helps to avoid congestion in the prostate, strengthens the walls of blood vessels and is the prevention of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases. Gymnastics in the morning and an evening jog or walk for forty minutes allows you to neutralize the harm caused to the body by a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle.
Regular sex life – prevents congestion and inflammation in the prostate gland, enhances pelvic circulation and metabolic processes in the tissues of the prostate.











አገልግሎታችሁ በጣም ጥሩነው ቀጥሉበት አንድ ጥያቄዬ ግን የPSA 4.265 ያለው ሰው ፕሮስቴት ካንሰር ይባላል