Parakeratosis: definition, causes and treatments
A parakeratosis is a dermatosis which is characterized by an abnormal maturation of the keratin, the constituent protein of the skin, at the level of the most superficial layer of the epidermis, also called the horny layer. It designates a skin lesion caused by too much production of this keratin. Parakeratosis is characterized by the formation of small red patches and scales (tiny skin scales) on the skin. This lesion is found in patients with psoriasis, eczema, or Gibert’s pink tincture. In infants, it is often associated with diaper rash or cephalic dermatitis. The treatment is based on the administration of corticosteroids, antihistamines and the application of a moisturizer which can improve the symptoms and make them disappear within a few weeks.
What is parakeratosis?
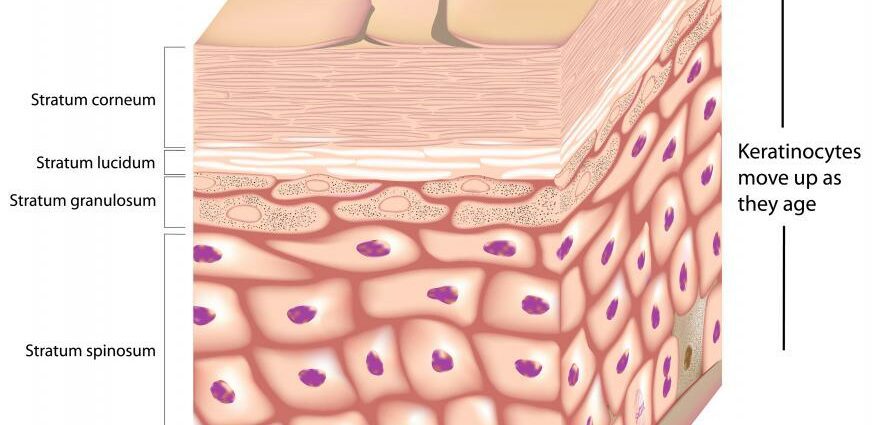
Parakeratosis is a skin condition, or dermatosis, which is characterized by the appearance of small, slightly red plaques, covered with scales or very thin white skin. They can appear anywhere on the body. They are due to the excessive production and abnormal maturation of keratin, the constituent protein of the skin. They reflect in fact a keratinization disorder which results from:
- the absence of a granular layer, i.e. the last layer of cells containing nuclei, of the epidermis;
- the fact that the epidermal cells which constitute the stratum corneum on the surface of the skin retain their nucleus, when they should have lost it.
The result is the formation of more or less thick scales.
What are the causes of parakeratosis?
Most often, parakeratosis is secondary to:
- dermatological diseases such as psoriasis, eczema or even Gilbert’s pityriasis pink;
- repetitive trauma to the epidermis, which results in the skin no longer playing its usual role as a protective barrier;
- a reaction of the skin to an infection with a germ or fungus.
In infants, it is often associated with diaper rash or cephalic dermatitis.
What are the symptoms of parakeratosis?
One of the peculiarities of parakeratosis is the fact that it practically does not itch.
A distinction is made between pitiriasiform parakeratosis and Brocq psoriasiform parakeratosis.
Pityriasiform parakeratose
This is characterized by:
- a rash similar to that of psoriasiform parakeratosis;
- a less intense red coloration of the spots compared to those of psoriasiform parakeratosis;
- the presence of scales or tiny skin scales;
- sometimes the presence of pigments in abnormally high quantity.
Brocq’s psoriasiform parakeratose
Brocq’s psoriasiform parakeratosis, also called psoriasiform eczematide, is characterized by:
- a variety of eczematids, or pests, which sit on the trunk and at the roots of the limbs;
- in some patients, it can also be localized on the scalp, in particular on the periphery of the latter;
- the presence of patches of red coloration;
- the presence of scales, or tiny scales of skin, the color of which is white, and reminiscent of those of psoriasis;
- an evolution which takes place in spurts, generally quite spaced apart.
How to treat parakeratosis?
There is no specific treatment. The management of parakeratosis is essentially symptomatic. It uses prescription and administration:
- local antiseptics in case of local superinfection;
- local corticosteroids in the event of inflammation or eczematization, that is to say transformation of the lesions into eczema;
- antihistamines for itching.
Applying moisturizers can improve symptoms and make them go away within a few weeks.
Parakeratosis of the cervix – the causes of the development of pathology
One of the leading causes of cellular changes are inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. They are diagnosed in almost 70% of women who come to see a specialist at our gynecological clinic on Tsvetnoy Boulevard . What is dangerous,  the clinical manifestations of inflammatory processes of the vagina and cervix often have a latent, long-term asymptomatic course, which in turn creates difficulties in treatment, prerequisites for the development of relapses. During the entire time that a woman does not go to the doctor, pathogenic microorganisms negatively affect the adjacent tissues of the uterus!
the clinical manifestations of inflammatory processes of the vagina and cervix often have a latent, long-term asymptomatic course, which in turn creates difficulties in treatment, prerequisites for the development of relapses. During the entire time that a woman does not go to the doctor, pathogenic microorganisms negatively affect the adjacent tissues of the uterus!
Often the risk of inflammation with an increased likelihood of damage to the cervical mucosa, as well as carcinogenesis, including the uterus, is associated with infectious diseases, which has been proven by scientists in numerous studies. Among the possible infectious agents often associated with cellular transformations, including oncology, there are sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including:
- trichomonas;
- chlamydia;
- herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2);
- human papillomavirus (HPV, HPV 16, HPV -18, HPV-31 are recognized as the most dangerous).
By the way, it is viruses that are currently the main infections detected in women and leading to problems with reproductive health. They are inferior in frequency of detection to syphilis, gonorrhea. Particularly alarming is the fact that up to 600 thousand cases of oncological pathology associated with HPV are registered annually in the world. When infected with this virus, women may develop papillomatosis affecting the periuterine region. Often, condylomas are located in the thickness of the tissue lining the neck, and are detected with the development of pronounced keratinization foci, which requires differential diagnosis directly with parakeratosis. It is important to note that these manifestations can be combined.
Another trigger for the development of parakeratosis can be considered therapeutic measures with the cervix, which also affect the structure of tissues.
Additional provocateurs of deterioration in reproductive health and concomitant prerequisites for negative transformations at the cellular level can be:
- hormonal disorders and disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- recurrent erosion and pseudo-erosion on the mucous membrane, the presence of ectopic foci;
- problems in the work of the immune and nervous systems, stress.
To clarify the nature of pathological changes, the doctor must necessarily conduct a colposcopy and take a smear. A biopsy is also indicated to rule out atypia, a precursor to cancer. After receiving the results of the tests, the specialist can draw up an optimal scheme for curing parakeratosis and restoring damaged cervical tissue due to the disease.
Treatment Methods
At the beginning, the tactics of treating the underlying disease, damage, against which parakeratosis has developed, is determined.
- in the presence of infectious agents, inflammation, antibiotic treatment is carried out, means are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
- with HPV, removal of condylomas is also indicated.
If we talk about the direct work of the doctor with the affected areas of the cervical mucosa, then minimally invasive methods are used to remove keratinization foci.
Your doctor may recommend the following options:
- Diathermoelectrocoagulation is a method in which treatment is carried out by applying high-frequency current to epithelial cells, which leads to tissue melting. The method is not the most popular among doctors due to the high risk of bleeding during manipulation and in the recovery period.
- Laser vaporization is based on the use of infrared light concentrated into a beam, which leads to tissue vaporization. The mini-operation is also performed on an outpatient basis and does not require long-term preparation. It is characterized by a low risk of bleeding, makes it possible to act on parakeratosis, even on small areas of keratinization of the epithelial layer. What is important, after the intervention, women can quickly return to their usual rhythm of life. Treatment can be achieved in more than 97% of patients. One of the most innovative and modern devices for manipulation that Russian clinics can be equipped with is a CO2 laser.
Radio wave surgery is a type of treatment that is a technique for cutting and coagulating soft tissues without destroying them. The removal of pathology occurs due to the energy of high-frequency radio waves, which enhances the formation of molecular energy inside each cell and provokes its self-destruction. The technique is recognized as low-traumatic, rarely causes bleeding. The procedure is not performed on the background of inflammatory diseases. One of the most commonly used devices for radio wave surgery “Surgitron”. With the help of the device, not only treatment is carried out, but also a biopsy is taken to exclude oncological pathology. The device is also widely used for cauterization of erosion, removal of polyps of the cervical canal, dissection of vaginal cysts.