Contents
Otitis externa, what is it?
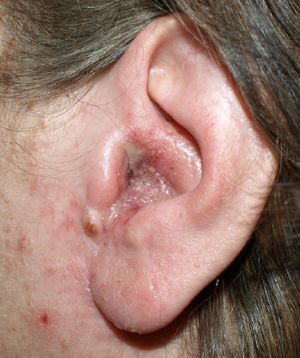
Otitis externa, also called swimmer’s ear, is inflammation of the outer ear canal. This inflammation usually causes pain, more or less intense. These are accompanied by irritation and itching. Appropriate treatment makes it possible to limit the progression of the disease.
Definition of otitis externa
Otitis externa is characterized by inflammation (redness and swelling) of the outer ear canal. The latter is a canal located between the outer ear and the eardrum. In the majority of cases, only one of the two ears is impacted.
This condition of the outer ear is also called: Swimmer’s ear. Indeed, frequent and / or prolonged exposure to water can be the cause of the development of such otitis.
The most common clinical signs of otitis externa are:
- pain, which can be very intense
- itches
- discharge of pus or fluid from the ear
- hearing difficulties or even progressive hearing loss
Appropriate treatment is available, and it alleviates symptoms within a few days. However, some cases can persist and last over time.
Causes of otitis externa
There are different origins of otitis externa.
The most common causes are:
- bacterial infection, mainly by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ou Staphylococcus aureus.
- seborrheic dermatitis, a skin condition that causes irritation and inflammation
- otitis media, caused by a deep ear infection
- a fungal infection, caused by Aspergillus, or Candida albicans
- an allergic reaction as a result of taking medication, using earplugs, using an allergenic shampoo, etc.
Other risk factors are also known:
- swimming, especially in open water
- perspiration
- significant exposure to a humid environment
- a scratch inside the ear
- excessive use of cotton swabs
- excessive use of earplugs and / or headphones
- the use of vaporizers for the ears
- hair dyes
Evolution and possible complications of otitis externa
Although complications, associated with otitis externa, are rare. There is a low risk of a negative course of the disease.
Among the possible changes, we can cite:
- the formation of an abscess
- narrowing of the outer ear canal
- inflammation of the eardrum, leading to its perforation
- a bacterial infection of the skin of the ear
- malignant otitis externa: a rare but serious condition characterized by infection spreading to the bone around the ear.
Symptoms of otitis externa
Otitis externa can cause a number of clinical signs and symptoms. These include:
- pain, more or less intense
- itching and irritation, in and around the outer ear canal
- a feeling of stiffness and swelling in the outer ear
- a feeling of pressure in the ear
- flaking skin around the ear
- progressive hearing loss
Beyond these acute symptoms, chronic signs can also be associated with such a condition:
- constant itching, in and around the ear canal
- persistent discomfort and pain
How to prevent otitis externa?
The prevention of otitis externa is hardly possible. In addition, reducing the risk of developing such a condition is, and involves:
- avoidance of damage to the ear: limit the use of cotton swabs, headphones, or even earplugs
- cleaning their ears regularly, but not excessively
- prevent and treat other conditions in the ear (especially skin problems around the ear)
How to treat otitis externa?
Otitis externa can be treated effectively by using a suitable treatment in the form of drops. This treatment depends on the root cause of the disease. In this sense, it may be a prescription for an antibiotic (for the treatment of a bacterial infection), corticosteroids (limiting swelling), an antifungal (for the treatment of a fungal infection).
In the majority of cases, symptoms tend to worsen at the start of treatment.
In addition, there are ways to limit the worsening of symptoms:
- avoid putting your ears in the water
- avoid the risk of allergies and inflammation (wearing headphones, earplugs, earrings, etc.)
- in the event of very intense pain, the prescription of painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, is also possible.