Contents
Nerf facial
The facial nerve is the nerve involved in the sensitivity and motor skills of the face.
Anatomy of the facial nerve
Position. The facial nerve constitutes the seventh cranial nerve.
Mixed nerve. The facial nerve is a pair and mixed nerve, and is therefore made up of motor, sensory, sensory and vegetative nerve fibers (1).
Origin and distribution. The nerve fibers of the facial nerve originate from the central nuclei of the facial nerve located within the brainstem. The nerve fibers emerge between the medulla oblongata and the bridge, and are distributed over the entire face.
Innervation. The nerve fibers of the facial nerve start from the brainstem and extend over a large part of the head. They innervate in particular (1) (3):
- the skin muscles of the face and neck;
- part of the swallowing muscles: the anterior belly of the digastric muscle, the stylohyoid muscle;
- the stapes muscle, or stapes, associated with the ear and innervated by a branch of the facial nerve.
physiology
Mixed nerve, the facial nerve has different functions: motor, sensory-sensory, and vegetative (2).
- Motor function of the facial nerve. Motor nerve fibers are responsible for different facial expressions.
- Sensory-sensory function of the facial nerve. Sensory-sensory nerve fibers are used to record taste information from two-thirds of the tongue as well as from the Ramsay-Hunt area. This area includes part of the auricle called the conch, part of the eardrum and the external auditory canal.
- Vegetative function of the glands. Vegetative nerve fibers are responsible for innervation of the salivary glands, which produce saliva, as well as the lacrimal glands, which produce tears.
Pathologies and associated issues
Facial paralysis. Facial nerve damage can cause facial paralysis. Among these paralyzes, we can distinguish:
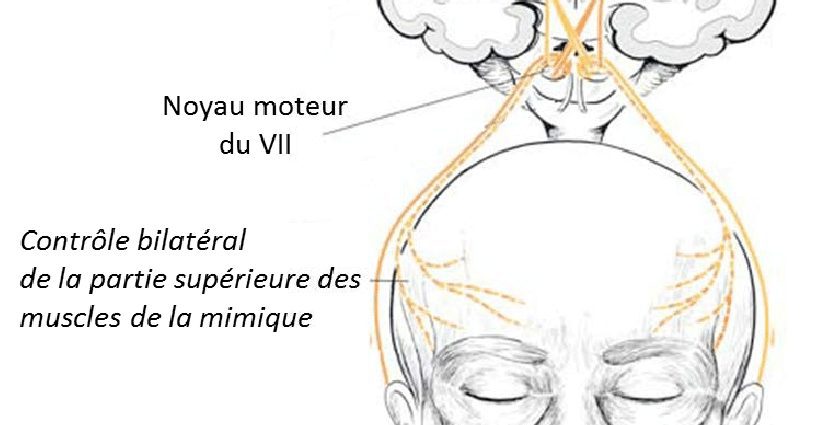
- Central facial palsies, which are rarer, correspond to damage to the nerve upstream from the central nuclei, within the brain. They are manifested by significant damage to the lower part of the face.
- Peripheral facial palsies correspond to damage to the nerve outside the brain, at the level of fibers emerging from the brainstem. They are manifested by damage to both the lower part and the upper part of the face.
These facial paralysis can be linked to pathologies of neurological, vascular, infectious or tumor origin:
- Head trauma. Shock to the skull can cause fractures or injuries that can result in compression or severing of the facial nerve.
- Viral infection. The presence of viruses in the nerve fibers of the facial nerve, such as shingles or herpes, can cause paralysis, usually peripheral.
- Multiple sclerosis. This pathology is an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system and can affect the nerve fibers of the facial nerve. The immune system attacks the myelin, the sheath surrounding nerve fibers, causing inflammatory reactions. (5)
- Stroke. Cerebrovascular accident, or stroke, is manifested by a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain, such as blood clots or a ruptured vessel (6). This pathology can lead to facial nerve damage.
- Brain tumors. Benign or malignant tumors can develop in the brain and lead to facial nerve damage. (7)
Treatments
Medical treatment. Certain medications may be prescribed such as corticosteroids, antivirals, or pain relievers.
Surgical treatment. Depending on the pathology diagnosed and its evolution, surgery may be necessary.
Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy. Depending on the type and stage of the tumor, these treatments may be prescribed.
Thrombolyse. Used during strokes, this treatment consists of breaking up the thrombi, or blood clots, with the help of drugs.
Facial nerve examination
Physical examination. First, a clinical examination is performed in order to identify and assess the symptoms perceived by the patient.
Medical imaging exam. In order to assess damage to the facial nerve, a brain scan or a brain MRI can in particular be performed.
biopsy. This examination consists of a sample of cells to analyze tumor cells.
Angio-IRM/Angioscanner. These tests allow the blood vessels to be analyzed by medical imaging.
History
The so-called paralyzes «Cold» designate the most frequent and suddenly occurring peripheral facial paralysis. They are said ” from the cold Because we thought they were related to a cold snap.