Contents
Mirtazapine is a medicinal substance that is the active ingredient of many antidepressants and hypnotics available at the pharmacy only with a prescription. Preparations containing mirtazapine include drugs with the trade name such as: Remirta, Mirzaten, Mirtagen, Mirtor, Mirtazapine. Chemically, mirtazapine is an organic substance with a multi-ring structure with the chemical formula C17H19N3. It is in the form of a white solid.
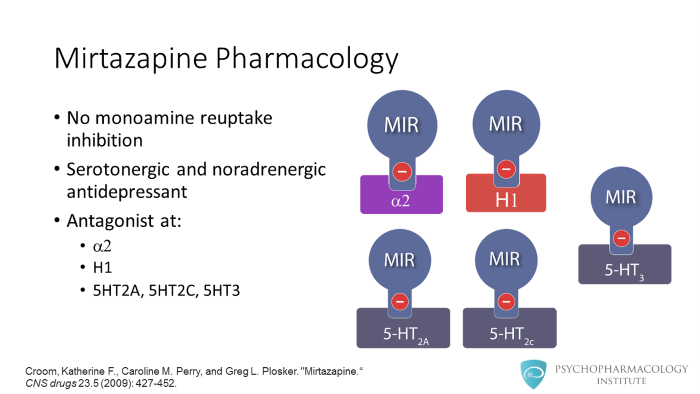
What is the mechanism of action of mirtazapine?
Mirtazapine is a medicinal substance that acts on the central nervous system. It is an antagonist of some receptors in the membrane of nerve cells, by blocking them it increases nerve conduction of a different kind: transmission with norepinephrine and serotonin. Especially serotonin is colloquially known as the “happiness hormone” and disturbances in its production and conduction are manifested primarily by depression. The enhancement of noradrenergic and serotonergic transmission has an antidepressant effect. In turn, blocking other types of receptors (histamine H1 receptor) by mirtazapine produces a hypnotic effect.
Indications for the use of mirtazapine
Mirtazapine is currently mainly used as an antidepressant in episodes of major depression in adults. Drowsiness after using it is now treated as a side effect. It is not used as a sleeping medicine, as there are other sleeping pills that do not have such a large effect on the central nervous system.
The dosage of mirtazapine should be determined by the physician each time. After oral ingestion, the substance is quickly and well absorbed, and its highest concentration in the blood plasma can be recorded after about 2 hours.
Contraindications to the use of mirtazapine
Medicines containing mirtazapine should only be used in adults over 18 years of age. The use in children is absolutely contraindicated. It must not be used if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs after its administration. It is definitely not recommended to take the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding – during pregnancy it can be used only when absolutely necessary and should be decided jointly by the psychiatrist and the doctor in charge of the pregnancy. There are no unequivocal data and no clinical trials that would confirm the effect of mirtazapine on the child when taken by a pregnant mother. However, it has a C category – animal studies indicate a teratogenic or fetal lethal effect. After giving birth, doctors also decide to continue the therapy – fortunately, mirtazapine passes into breast milk only in small amounts.
It must also not be used together with substances with which it interacts: mainly antidepressants from the group of MAO inhibitors and alcohol. If you are taking any other medicines, consult your doctor before taking mirtazapine and read the package leaflets of both medicines very carefully to make sure that there is no risk of interactions.
Patients with autoimmune diseases should not use mirtazapine chronically.
Adverse reactions and side effects after ingestion of mirtazapine
From the very definition, mirtazapine, acting on the central nervous system, is a medicinal substance that may impair psychomotor performance and affect driving. The main side effects of taking mirtazapine can be drowsiness, headache, dry mouth, increase in appetite and weight gain. Often, dizziness, digestive system complaints (diarrhea or constipation, nausea and vomiting), rashes, muscle pain, sudden pressure drop after changing body position, symptoms of fatigue, disorientation and, paradoxically, insomnia may also appear. Complete lists of side effects can be found in the package leaflets of the medicines containing mirtazapine. Less frequently, seizures and aggressive behavior may occur as a result of the use of mirtazapine. Therefore, special care should be taken in the case of people suffering from epilepsy. The patient should also be monitored and the effect of the drug on his mood at the beginning of administration, as there have been cases of suicidal thoughts and suicidal behavior after initiating mirtazapine treatment.
Undesirable symptoms may also occur in the event of sudden discontinuation of mirtazapine (the so-called withdrawal syndrome). These can include, but are not limited to, dizziness, headache, nausea, and sudden agitation.










dali mozam da go pijam a da ne smeta na regeneracija na myskil zosto pravev operacija na nogata i imam atrofija ve molam za odgovor.