In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Hirsutism is a problem for almost every woman with hirsutism. In times when one of the determinants of beauty is a smooth body, we often search for a disease symptom in the hair too quickly. But when hair appears in typically male areas, the problem cannot be underestimated any longer.
The causes and occurrence of hirsutism
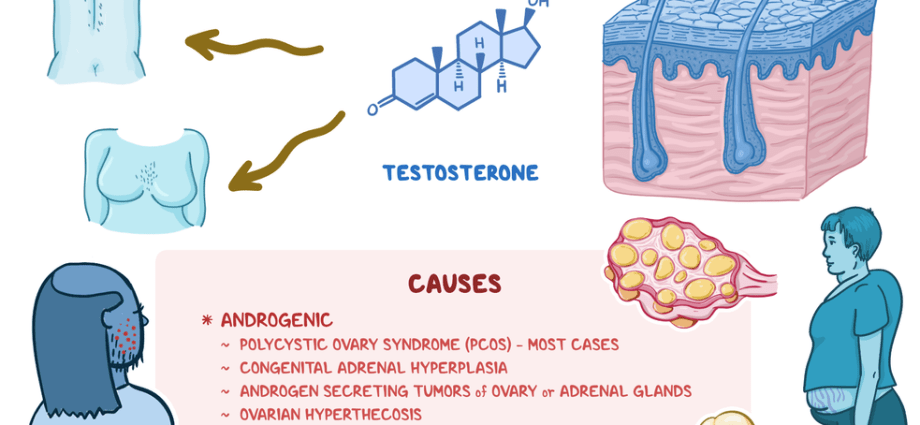
Hirsutism is found in 5-10 percent. girls and women. This is the occurrence of coarse, dark and thick hair in areas typical of men. Its main cause is the increased concentration of androgens. The androgen-dependent areas include: the area above the upper lip, chin, chest, neck, lumbar region, abdomen, as well as the thighs and feet. Other effects of hormonal disorders can include low voice, menstrual irregularities, infertility, and acne. Excessive hair is sometimes also diagnosed in women who have regular periods and normal serum androgen levels. In their case, the causes of hirsutism are most often genetic predisposition and increased sensitivity of the hair follicles to androgens, i.e. male sex hormones. This is called idiopathic hirsutism. The disease can also be caused by hormonal drugs: androgens, progesterone derivatives (most often contraceptives) or steroids.
During puberty, slight hirsutism may be transient. Then there are dynamic changes in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis. The secretion of luteinizing hormone increases, the volume of the ovaries increases and there is an increased secretion of testosterone, androstenedione and estradiol. The effects of these hormonal changes include, among others rare, nonovulatory menstrual cycles and symptoms of hyperandrogenism (hirsutism, male pattern baldness, acne, lower voice tone, obesity, changes in the external genitalia). Two years after the onset of the first menstruation, menstrual cycles become ovulatory and regular, and the features of hirsutism, if they were present before, disappear. However, hirsutism is on the rise for some girls. Ovarian enlargement and the development of dangerous polycystic ovary syndrome (PCO) may occur.
In order to identify the cause of the disturbing symptoms, it is worth performing a set of tests available in the hormonal package for women. By analyzing a blood sample, you can detect abnormalities that indicate hirsutism, PCOS, or thyroid problems.
Some women also experience increased hair growth during pregnancy as a result of a hormonal imbalance. Sometimes, however, hirsutism can accompany serious systemic diseases. This is called Secondary hirsutism, which may be a consequence of diseases of the adrenal glands, ovaries (most often polycystic ovary syndrome or ovarian cancer), pituitary gland (Cushing’s syndrome), hypothalamus, as well as adrenal gland syndrome, adrenal cortex tumors and hypothyroidism.
Hirsutism can take many forms, from slight chest hair and facial hair to pronounced facial hair, often accompanied by seborrhea, acne, and temporal alopecia. Hirsutism also often occurs with obesity, hypertension, stretch marks, and type 2 diabetes.
Diagnosis and treatment of hirsutism
In diagnostics, the most important thing is a thorough history (especially family and menstrual history), finding the male type of hair and determining the causative factor. However, it is essential to distinguish androgen-related hirsutism from hypertrichosis (excessive growth of hair all over the skin or limited to certain areas of the skin), in which androgens play no role and hair is absent in typically male areas.
For this purpose, hormonal tests are performed on designated days of the cycle to assess the concentration of testosterone and its derivatives, and in justified cases also of substances secreted by the thyroid gland and pituitary gland. These are: progesterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEA-S), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxin, anti-thyroid-peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies and androstenedione.
Treatment of hirsutism involves normalizing the level of androgens with antiandrogen drugs. Oral contraceptives are the most commonly used. You have to wait at least six months for the effects of the therapy, because that is how long the hair growth cycle lasts.
In the case of genetically determined excessive hair, taking any medications is ineffective. Then, the only effective method is cosmetic epilation, i.e. permanent hair removal on limited sections of the skin, e.g. with the use of strongly alkaline chemical depilatories: barium sulphide and thioglycolates, which, however, may be irritating to the skin. There are also laser therapy and electrolysis treatments in which individual hair follicles are removed by means of a low-voltage current. In some cases, it is enough to discolor the hair with hydrogen peroxide. Unfortunately, treatments such as waxing, shaving or hair removal using chemical depilatories are effective, but give a short-term effect.
How the hair of a healthy woman should look like:
- It is normal for slight hair on the calves, arms and armpits. Consult your doctor when hair becomes intense and appears on lower legs and arms.
- Small hairs above the upper lip are also not a sign of hirsutism. They should arouse anxiety when they become prominent or appear on the chin and cheeks.
- If fine hairs cover the toes of your toes, don’t worry. But if you notice that they appear all over your feet consult your doctor about the problem.
- The individual hairs around the nipples shouldn’t bother you either. But if there are more of them, or they grow between the breasts, on the stomach, or on the back, ask your doctor for help.
- The pubic hair should cover a medium-sized area. If the area covered is extensive and they grow on the inside of the thighs and around the navel, consult a specialist.
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website. Do you need a medical consultation or an e-prescription? Go to halodoctor.pl, where you will get online help – quickly, safely and without leaving your home.