General description of the disease
This is a pathology in which a section of internal organs leaves the cavity that it occupies. It can protrude into the internal cavity, under the skin, or into the space between the muscles. [3]… As a result of this disease, the internal organs are partially displaced, but their integrity is not violated.
This dangerous pathology is quite common; about 20% of people suffer from it. The risk zone includes preschoolers and people over 50, and men are more susceptible to this disease than women.
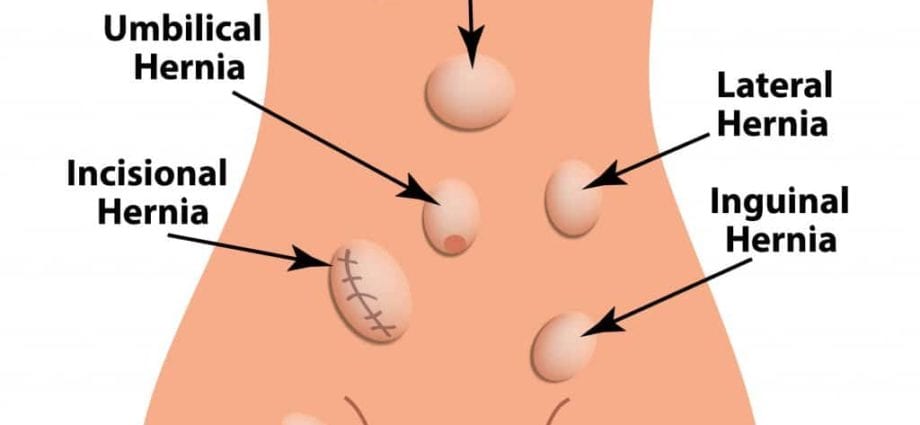
Hernia classification
Hernias are distinguished depending on the place of their formation:
- 1 Inguinal… This form is diagnosed in 66% of patients. As a rule, it is rare in women. In men, the inguinal canal is wider, so increased intra-abdominal pressure often provokes a hernia. In turn, an inguinal hernia can be straight and oblique. An oblique hernia forms under the skin and passes through the inguinal canal and may be congenital. A straight hernia is usually defined on 2 sides. This form of hernia can only be acquired;
- 2 Femoral… Femoral hernias are susceptible to women after 40 years. At the age of 40 to 60 years in women, the femoral ring weakens and increases in size. Femoral hernia is formed gradually, while part of the intestine through the femoral canal extends beyond the boundaries of the abdominal wall;
- 3 Navel… This form most often develops in women who have given birth several times, in this case the stomach, small or large intestine may be the contents of the hernial sac, which is localized in the umbilical ring;
- 4 Hernia of the white line of the abdomen… The white line of the abdomen is represented by the fibers of the tendons. If the hernia does not protrude through the holes and crevices of the fibers, then it is considered hidden. Most often, this type of hernia develops in patients with peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, or stomach cancer;
- 5 Postoperative… It is localized in the area of the scar that formed after the operation. Incisional hernia occurs in 31% of persons who have undergone surgery on the abdominal organs.
The causes of hernias
In the process of evolution in humans, an elastic frame was formed from muscles and tendon fibers, which fixes the internal organs and resists intra-abdominal pressure. A hernia is formed as a result of defects in the elastic frame, which can provoke the following factors:
- violation of the elasticity of muscle tissue as a result of depletion of the body or old age;
- a sudden increase in intra-abdominal pressure;
- suppuration in the anterior abdominal wall;
- obesity;
- carrying a child;
- congenital abnormalities in the abdominal wall;
- unhealthy diet and unhealthy lifestyle;
- lifting weights;
- chronic respiratory diseases;
- prolonged constipation;
- frequent, uncontrolled crying in infants;
- abdominal trauma;
- numerous childbirth;
- genetic predisposition;
- suture inflammation after surgery;
- low immunity;
- surgeon’s mistakes during the operation;
- fast weight loss;
- frequent sneezing during allergies.
Hernia symptoms
Despite the fact that all types of hernia have their own characteristic signs, there are general symptoms:
- 1 pain when coughing or during exercise;
- 2 nausea and retching;
- 3 spherical protrusion of internal organs, which can be seen from the outside visually, especially when standing and sitting. When the patient is in a supine position, the protrusion disappears;
- 4 Difficulty or frequent urination
- 5 pain in the groin or abdomen;
- 6 discomfort while walking;
- 7 a feeling of heaviness in the abdominal region.
Complications with a hernia
The most dangerous and common complication of a hernia is infringement. It can be provoked by a strong tension of the abdominal muscles, in which the contents of the hernial sac are compressed. Infringement can also cause cicatricial constrictions.
When the small intestine is infringed, feces accumulate, blood circulation is disturbed, the intestine becomes thinner, which is fraught with intestinal obstruction. When any organ that is in the hernial sac is clamped, blood circulation is disturbed, and the organ cannot function normally.
Untimely treatment of a hernia can lead to serious consequences:
- uncontrolled hernia;
- stagnation of feces in the intestines;
- bleeding;
- peritonitis;
- intoxication of the body;
- renal failure;
- inflammation of neighboring internal organs.
Hernia prophylaxis
For prevention purposes, it is necessary to normalize the stool, and also try not to lift weights. The main reason for the appearance of umbilical and inguinal hernias is considered to be a loose abdominal wall, so you need to strengthen the lower press. To do this, you should do health-improving gymnastics, pump the press every day and do the exercise “bike”. Swimming well strengthens the muscles of the abdominal wall. At the same time, it is important not to overdo it and correctly combine exercise with rest.
Obesity should be avoided, and if you plan to lose weight, then try to do it gradually, rather than rapidly losing weight.
During childbirth and after childbirth, women need to wear a bandage, do fitness, prevent constipation and treat coughs in time.
In newborn babies, it is important to properly care for the navel in the first week after childbirth, it is necessary to avoid swaddling too tight and not toss the baby up. To prevent the appearance of an umbilical hernia in infants, overeating should be avoided, the stool should be monitored and the baby should be laid on his stomach 2-3 times a day to train the abdominal muscles.
Patients who have undergone surgery on the abdominal organs should avoid sharp turns and tilts of the body to the side, wear a bandage for a month after the surgery and do not try not to lift heavy objects.
Hernia treatment in official medicine
Using a bandage or external dressings can only temporarily stop the development of the hernia. Any hernia can only be cured with surgery. Moreover, each type of hernia requires its own method of treatment.
From umbilical hernia can be eliminated with laparoscopy. Laparoscopic hernioplasty is performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon dissects the hernial sac and places the protruding organ in place. After that, a mesh implant is placed for adults, and the navel ring is sutured in children.
An alternative surgery option could be laser vaporization… This technique makes it possible to eliminate the protrusion without traditional surgery. The advantage of this method is the absence of large cuts and scars and fast recovery.
Modern herniology includes many hernia repair techniques, and each of them has its own disadvantages and advantages. The method of operation is chosen by the doctor, focusing on the severity of the disease, the patient’s age and individual intolerance to materials.
Useful products for hernia
In order to prevent hernia, the diet should be focused on preventing the development of constipation.
After the operation, you must adhere to a diet. It is necessary to give preference to grated soups, cereals, low-fat broths, boiled eggs. Before the operation and during the rehabilitation period, before meals, you need to take a spoonful of vegetable oil or 2 tablespoons of oatmeal, this simple method will help to normalize the bowel function.
After eating, it is better not to go to bed, it is recommended to walk along the street or do something around the house. Nutritionists recommend eating small meals at regular intervals 6 times a day. Solid foods should be discarded, or hard foods should be softened during cooking. During the day, it is necessary to drink non-carbonated alkaline mineral water, which reduces acidity.
Recommended products:
- 1 weak broths;
- 2 dairy products;
- 3 porridge, with the exception of rice and semolina;
- 4 pears and raspberries;
- 5 a fish;
- 6 tofu cheese;
- 7 unsteady fruits and vegetables;
- 8 fruit jellies;
- 9 boiled soft-boiled eggs;
- 10 compotes;
- 11 seafood;
- 12 lean meat.
Traditional medicine for hernia
Patients with hernia in the preoperative period should strengthen the body and try to delay the development of the hernia using the following folk remedies:
- prepare a decoction from young oak bark… To do this, pour 20 g of raw materials in 200 ml of boiling water, cook for 5 minutes, cool, filter and drink 1 tablespoon each. three times a day;
- drink daily acorn coffee with the addition of honey;
- as an antispasmodic agent has proven itself well belladonna leaf juice, which can be replaced with powder or tincture. Doses should be minimal, as the plant is poisonous.[1];
- a decoction of herb of smooth hernia perfectly relieves pain syndrome that occurs when lifting weights. To do this, pour 50 g of fresh raw materials with a liter of boiling water, insist and drink 4 rada a day, 1 / glass;
- as an external agent have shown good results pine baths… You can also make warming body wraps from a warm decoction of pine twigs;
- with an umbilical hernia in children, a trunk hay dust decoction wrap;
- dissolve vinegar with water in a ratio of 1: 1 and the resulting solution, quickly wash the body[2];
- a good therapeutic effect can be achieved with sauerkraut compress, cabbage leaves or a cloth soaked in brine should be applied to the bulge and kept for 20-30 minutes.
Dangerous and harmful foods for hernia
In the postoperative period, the following foods must be completely excluded from the diet:
- alcoholic drinks, strong tea and coffee;
- sweets;
- sour, fatty, smoked, salty foods;
- strong broths;
- fatty fish and meat;
- spicy sauces and condiments;
- carbonated drinks;
- lard and margarine;
- fast food;
- semi-finished products;
- mushrooms.
If possible, limit the use of such products:
- peas and other legumes;
- bakery products;
- grapes;
- all types of cabbage;
- minimize salt intake
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to apply any recipe, advice or diet, and also does not guarantee that the specified information will help or harm you personally. Be prudent and always consult an appropriate physician!
Attention!
The administration is not responsible for any attempt to use the information provided, and does not guarantee that it will not harm you personally. The materials cannot be used to prescribe treatment and make a diagnosis. Always consult your specialist doctor!