Contents
Fundus: when to do it, why, normal or not?
The fundus is an ophthalmologic examination that allows you to visualize the deep structures of the eye. It is useful for the diagnosis of ophthalmological diseases but also for the diagnosis and the follow-up of damage to the retina due to general diseases such as diabetes.
What is a fundus?
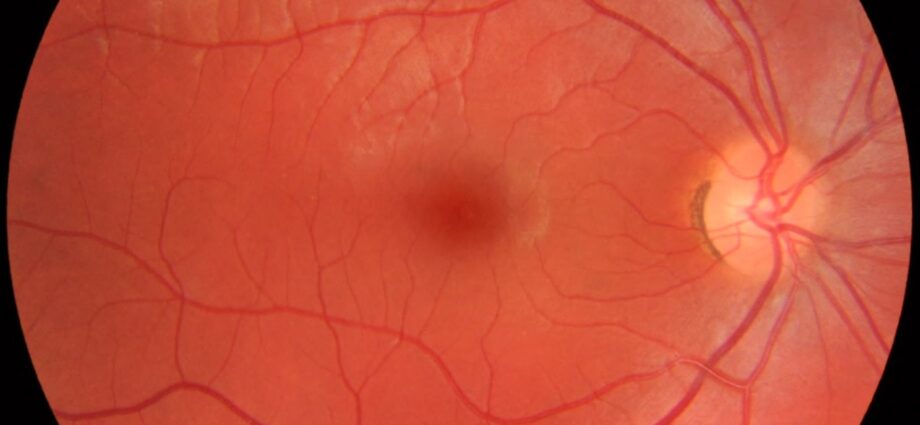
The fundus is a painless ophthalmologic examination intended to study the structures of the eye located at the back of the lens: the vitreous body, the retina, the central part of the retina or macula made up of retinal cells which are called cones which allow color vision and precise vision and rods which are on the rest of the retina and allow night vision and less precise without colors…, the papilla, part of the retina through which the nerve leaves optic and the arteries and vessels of the retina) and more particularly the retina.
The eye is round like a balloon for example and the fundus allows, through the orifice of the pupil (small window, the black circle in the middle of the colored iris of the eye) to see the inside of the “balloon”.
It is used to detect certain ocular disorders (diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, etc.) or to monitor their development. There are several fundus techniques: by ophthalmoscope, by biomocroscope or slit lamp with a 3-mirror glass, by OCT or optical coherence tomography.
Who is affected by this review?
The fundus is an examination that can diagnose and monitor ophthalmological diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), glaucoma, retinal detachment. And the diagnosis and follow-up of hypertensive retinopathy associated with high blood pressure, as well as retinopathy in people with diabetes. Retinopathy is a disease of the retina or the blood vessels in the retina. The fundus can be performed at any age, even in premature babies, by adapting the examination technique.
When to do a fundus?
It is advisable to do a fundus at birth if the baby’s pupil is white, at the age of 1 year, 3 years, 5 years, then every 5 years if there is nothing to watch . From the age of presbyopia, it should be monitored more often. A fundus should be performed annually for known retinal problems (eg diabetic retinopathy) and every two years for visual disturbances such as nearsightedness, presbyopia or hyperopia.
In people with diabetes
In people with diabetes, the fundus is done at least once a year at all ages, more often in diabetic retinopathy which is very effectively treated with laser or injections, preventing loss of the eye.
Emergency cases
A fundus can also be performed urgently if you have certain symptoms such as a sudden drop in visual acuity, visual blurring, pain, the perception of flying flies or the impression of a black veil, or if you have suffered a trauma to detect, for example, a detachment of the retina.
Conduct of the examination
No particular precaution is to be taken before passing a fundus. You just have to take off your contact lenses and don’t put makeup on your eyes. In some cases, examination eye drops are instilled into the eyes to dilate the pupil. It takes between 20 and 45 minutes for the pupils to be dilated.
For the exam, you place your forehead and chin behind the slit lamp. This exam is painless and lasts 5 to 10 minutes. Anesthetic eye drops can be used to numb the cornea.
Be careful, you will have blurred vision after the test if you have had eye drops and you will not be able to drive. Thus, it is advisable to come for a fundus accompanied or by public transport. In bright light, it is recommended that you wear sunglasses after this examination if you have had dilated pupils.
Result and interpretation (depending on the pathologies: diabetes, glaucoma, AMD)
The results of a fundus are immediately known.
Macular degeneration (AMD)
The fundus can detect age-related macular degeneration (AMD) which can be dry or wet. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a set of degenerative lesions secondary to genetic and / or environmental susceptibility factors, which alter the central area of the retina more common in people over the age of 50. . Smokers have 4 times more AMD and earlier. In case of suspicion of AMD in the fundus, additional examinations are performed: angiography and optical coherence tomography (or OCT).
Glaucoma
The fundus can reveal glaucoma when there is an abnormality of the optic papilla (head of the optic nerve) and the optic fibers that is noted. Diagnosing glaucoma also requires measuring eye pressure and examining the iridocorneal angle called a gonioscopy. Optic nerve involvement is confirmed by OCT examination.
Glaucoma is a sneaky disease that makes you blind because during years of evolution the patient has no signs or symptoms, this is only noticed by the ophthalmological examination by taking the eye pressure, analyzing the nerve. optic and its papillae (OCT and fundus) and by detailed analysis of the visual field. There are two kinds of glaucoma that can co-exist: angle-closure glaucoma (the angle is examined by gonioscopy but before the dilation of the pupil), and open-angle glaucoma which corresponds to a disease of the optic nerve by ocular hypertension, by heredity or by poor circulation of the blood.
In closed-angle glaucoma, in the event of a crisis, the optic nerve is destroyed in 6 hours. It hurts so much that you notice the problem right away and go to the emergency room. The fundus helps avoid this situation. When the ophthalmologist notices the risk of closing the angle with the slit lamp (fundus) and with gonioscopy, he can correct the problem with a little laser.
Diabetic retinopathy
Biomicroscopic examination of the fundus after pupil dilation may reveal diabetic retinopathy. Fundus should be supplemented with fundus photographs.
The fundus can be used to make the diagnosis of hypertensive retinopathy in the context of arterial hypertension.
Price and reimbursement of a fundus
The price of a fundus by biomicroscopy is 28,29 euros. The fundus by OCT has a cost of 62,02 euros. The conventional price for a fundus with dilation is € 35,91. The remainder to be paid and any excess fees may be covered by your mutual insurance company.