Contents
Disc disease
Wear of intervertebral discs or disc disease is a common cause of back pain. Treatment is above all symptomatic.
Disc disease, what is it?
Definition
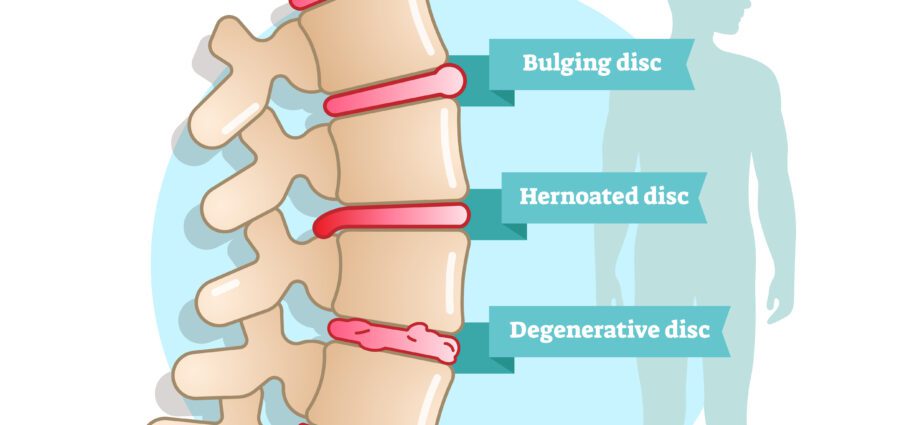
Disc disease is a progressive deterioration of the intervertebral discs, discs located between two vertebrae in the spine. These discs act as a shock absorber. When they wear out, they dehydrate, become less flexible and play their role of shock absorbers less well.
Disc disease can affect one or more discs. The disc most prone to this degeneration is the disc located at the lumbosacral junction between the L5 and S1 vertebrae.
Significant disc disease can lead to the development of local osteoarthritis.
Causes
Disc disease can be due to natural aging. It can also be premature. In the latter case, it is due to excessive constraints (overweight, carrying heavy loads, long transport, working with vibrations), trauma or micro-trauma.
Diagnostic
The diagnosis of disc disease is made through a clinical examination, supplemented by a lumbar x-ray or MRI.
The people concerned
Disc disease is the most common disease of the spine. 70 million Europeans are affected by degenerative disc disease.
Risk factors
It seems that genetic factors play a role in disc disease. Lack of physical exercise promotes disc disease because when there are fewer muscles, the vertebrae are less well supported. Poor posture and incorrect movements can also weaken the intervertebral disc. Finally, smoking and an unbalanced diet promote dehydration of the intervertebral discs.
Symptoms of disc disease
Signs of disc disease: back pain
When a disc is worn, it absorbs shocks less well. This creates local micro-traumas that create inflammation, pain, and muscle contractures. These are low back pain (lower back), back pain (upper back) or neck pain (neck).
The episodes of low back pain, back pain and neck pain last from 15 days to 3 months. They can become more frequent and then become chronic. In some people, the pain is so severe that it constitutes a real handicap in personal or professional life.
Lack of sensitivity or tingling
Disc disease can also be signaled by decreased sensitivity in the arms or legs, tingling, weakened arms and legs, difficulty walking, when a nerve is compressed.
Stiffness
Disc disease can cause stiff back.
Treatments for disc disease
The treatment of disc disease consists mainly in relieving the symptoms during seizures. Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxant drugs are used for this, combined with rest. Corticosteroid injections can be done when the pain is not relieved by medication.
When the pain associated with disc disease becomes chronic, physiotherapy sessions may be prescribed. At the same time, people with back pain due to disc disease learn to protect their spine.
Surgery is only considered when medical treatment and physiotherapy rehabilitation do not relieve chronic pain. However, surgical techniques do not completely eliminate pain. They mitigate them. Several techniques exist. arthrodesis technique involves welding the vertebrae. Blocking and fusing the vertebrae helps relieve pain. Arthroplasty consists of replacing a damaged disc with a prosthesis (artificial disc).
Herbs with anti-inflammatory properties are effective in treating pain associated with inflammation. Among these, Devil’s Claw or Harpagophytum, blackcurrant buds.
What diet in case of disc disease?
Favoring alkaline foods (vegetables, potatoes, etc.) and avoiding acidifying foods (sweets, meat, etc.) can reduce inflammatory pain, as acids aggravate inflammation.
Prevent disc disease
Disc disease can be prevented by avoiding overweight, by practicing physical activity, which guarantees good back muscles, but also by not smoking, by taking good postures, to work or to play sports in particular and when wearing heavy loads.