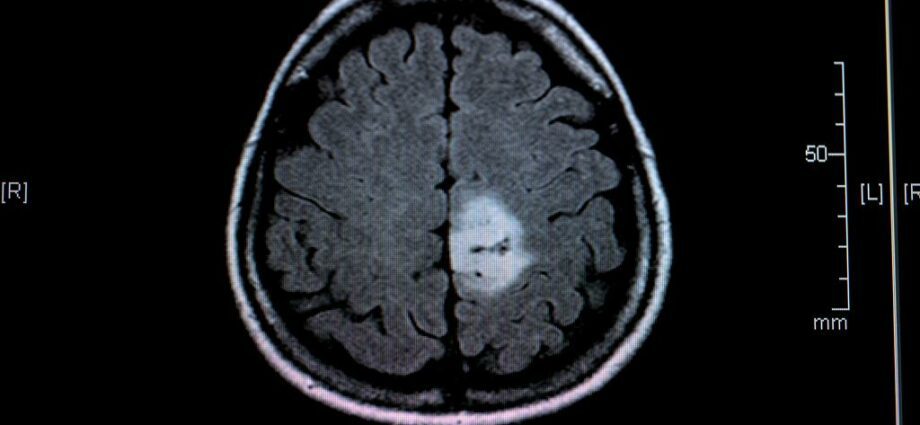
A brain tumor (brain cancer)
A brain tumor is a mass of abnormal cells which multiply in the brain uncontrollably.
There are 2 main types of brain tumors depending on whether they are cancerous or not:
- The benign tumors (non-cancerous). They form quite slowly and most often remain isolated from neighboring brain tissue. They do not spread to other parts of the brain or other organs and are usually easier to remove with surgery than malignant tumors. However, some benign tumors remain ineradicable because of their location.
- The malignant tumors (cancerous). It is not always easy to distinguish them from neighboring tissues. As a result, it is sometimes difficult to extract them entirely without damaging the surrounding brain tissue.
Examinations, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), PET scan (positron emission tomoscintigraphy) and computed tomography (“CT scan”), allow the tumor to be located precisely. A biopsy (sample of tumor tissue for analysis) is essential in determining the benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) nature of the tumor.
Brain tumors are also distinguished by their origin and location.
We distinguish:
- The you die brain primary, are those that originate in the brain. They can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Their name comes from the brain tissue in which they develop.
Among the most common malignant tumors are:
– Glial tumors, or gliomes (malignant tumors) representing 50 to 60% of all brain tumors. They are formed from glial cells, cells that act as a supporting structure for nerve cells (neurons).
– The medulloblastoma (malignant tumors), develop from the spinal cord in the embryonic stage. These are the most common brain tumors in children and.
– Finally, among benign primary tumors, rarer than primary malignant tumors, we find hemangioblastomas, meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, osteomas, pinealomas, etc.
- The secondary tumors ou metastatic are malignant (cancerous) and originate from other organs where cancer exists and whose tumor cells have migrated to the brain and multiply there. Tumor cells are carried by the blood and most often develop at the junction between white matter and gray matter in the brain. These secondary tumors are more frequent than primary tumors. Moreover, it is estimated that 25% of people who die from cancers of all kinds are carriers of brain metastases.1. Among the tumors most frequently causing brain metastases: breast cancer, lung cancer, skin cancer (melanoma), kidney cancer, colon cancer, etc.
Who is affected?
Each year in France, approximately 6.000 people are diagnosed with a primary brain tumor. They represent 2% of all cancers2. In Canada, primary brain tumors affect 8 out of 100 people. As for metastatic tumors, they affect around 000 out of 32 people. Large epidemiological studies show that the number of brain tumors in the West has been on the rise for several decades, without anyone really knowing why. However, intensive cell phone use seems to be implicated in the increase in the number of certain primary brain tumors, as numerous studies show.3,4,5. When it comes to cell phone use, children are more exposed to brain tumors than adults.
When to consult?
See your doctor if you experience symptoms such as a persistent and severe headache, accompanied by nausea and vision disorders.