Contents
In this publication, we will consider what the scope of a function is, how it is designated and specified. We also list these areas for the most popular features.
The concept of scope
Domain is a set of values x, on which the function is defined, i.e. exists y. Sometimes called task area.
- x – independent variable (argument);
- y – dependent variable (function).
Conventional notation of a function: y=f(x).
Function is a relationship between two variables (sets). At the same time, each x matches only one specific value y.
The geometric interpretation of the domain of definition of a function is the projection of the graph corresponding to it onto the abscissa axis (0x).
Set of function values – all values yaccepted by the function on its domain. From the point of view of geometry, this is the projection of the graph onto the y-axis (0y).
The domain of definition is denoted as D (f). Instead f, respectively, a specific function is indicated, for example: D(x2), D(cos x) etc.
Then an equal sign is usually put and specific values are written:
- Through a semicolon, we indicate the left and right boundaries of the interval corresponding to the values on the axis 0x (strictly in that order).
- If the boundary is within the definition area, put a square bracket next to it, otherwise, a round bracket.
- If there is no left border, we specify instead “-∞“, right – “∞“ (read as “minus/plus infinity”).
- If necessary, if you want to combine several ranges, this is done using a special sign “∪”.
For example:
- [3; 10] is the set of all values from three to ten inclusive;
- [4; 12) – from four inclusive to twelve exclusively;
- (-2; 7] – from minus two exclusively to plus seven inclusive.
- [-10; -4) ∪ (2, 8) – from minus ten inclusive to minus four exclusively and from two to eight exclusively.
Note:
- All numbers greater than zero are written like this: (0; ∞);
- All negative: (-∞; 0);
- All real numbers: (-∞; ∞) or simply R.
Domains of different functions
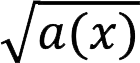 «>
«>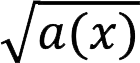
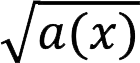
| General view | Function | Domain of definition (D) | |||
| Linear | With a shot | «>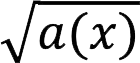 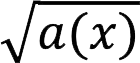 | Root | «>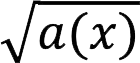 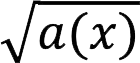 | |
| with logarithm | Demonstration | All real numbers, with specific range dependent on value apositive or negative, integer or fractional. | |||
| Power | Just like the exponential function. | ||||
| Sinus | Cosine | ||||
| Tangent | Cotangent | Previous record Previous entry: Sharing Excel Workbooks The next entry The next entry: Conditional Formatting in Excel PivotTables Leave a commentОтменить ответ |









