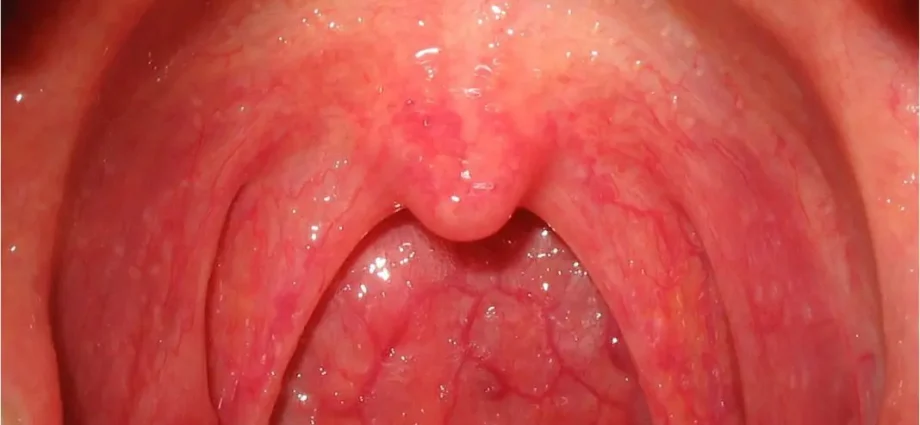
What is pharyngitis?
A pharyngite designates a inflammation of the pharynx. The pharynx is located at the back of the mouth and is shaped like a funnel. He is involved in the swallowing (passage of food from the mouth to the esophagus), breathing (passage of air from the mouth to the larynx), and the phonation (influence on the sounds produced by the vocal cords). Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharynx, most often due to mild infection, caused by a virus or a bacterium. When the inflammation also affects the nasal mucous membranes, it is called rhino-pharyngite.
There are two types of pharyngitis:
– Infectious pharyngitis due to viruses or bacteria.
– Non-infectious pharyngitis, due to various attacks likely to lead to inflammation of the pharynx.
These pharyngitis can be acute or chronic.
Acute pharyngitis : transient and frequent, it is most often of infectious origin, by bacteria or local viruses. It can also correspond to the beginning of a general infectious disease such as measles, scarlet fever, rubella, mononucleosis … There are also accidental pharyngitis by heat or acid burns.
Chronic pharyngitis : it can be due to many factors that are generally non-infectious.
Causes of pharyngitis
Un virus or a bacterium can be responsible for acute pharyngitis. Pharyngitis can also be secondary to a non-infectious cause, especially when it comes to chronic pharyngitis: iron deficiency, exposure to a allergen such as pollen, Pollution, To thealcohol, has a spray or the smoke of cigarette, vitamin A deficiency, exposure to poorly ventilated or conditioned dry air, chronic exposure to dust, overuse of nasal drops, irradiation (radiotherapy). It can also be linked to mouth breathing, nasal obstruction, chronic sinusitis, or enlarged adenoids. Menopause, diabetes or hypothyroidism can also be the cause of pharyngitis, as can respiratory failure, chronic bronchitis or poorly managed use of the voice (singers, speakers, lecturers, etc.)
Possible complications
Rheumatic fever: it is a serious and feared complication of physicians during infectious pharyngitis. It occurs during infection with a bacteria called group A ß-hemolytic streptococcus, which can lead to dangerous heart and joint complications. These tonsillitis are most common between 5 and 18 years old and require antibiotic treatment to prevent these complications.
Glomerulonephritis : it is a kidney damage that can occur after the same type of pharyngitis due to group A ß-hemolytic streptococcus.
Peripharyngeal abscess : this is a collared area containing pus which must then be surgically drained.
The spread of infection can cause sinusitis, rhinitis, otitis media, pneumonia …
How to diagnose it?
THEclinical observation is enough for the doctor to establish his diagnosis. He examines the patient’s throat and notices the inflammation (red throat). On palpating the patient’s neck, he may sometimes find that the lymph nodes have increased in size. In some cases, a sample of the fluid that covers the tonsils will be taken using a small cotton swab-shaped utensil called swab, in order to detect ß-hemolytic streptococci of group A, potential sources of serious complications.