In this publication, we will consider what arithmetic (mathematical) equality is, and also list its main properties with examples.
Definition of Equality
A mathematical expression that contains numbers (and/or letters) and an equals sign that divides it into two parts is called arithmetic equality.
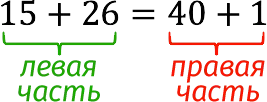
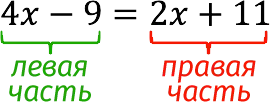
There are 2 types of equalities:
- Identity Both parts are identical. For example:
- 5 + 12 = 13 + 4
- 3x + 9 = 3 ⋅ (x + 3)
- The equation – equality is true for certain values of the letters contained in it. For example:
- 10x + 20 = 43 + 37
- 15x + 10 = 65 + 5
Equality properties
Property 1
Parts of the equality can be interchanged, while it remains true.
For example, if:
12x + 36 = 24 + 8x
Consequently:
24 + 8x = 12x + 36
Property 2
You can add or subtract the same number (or mathematical expression) to both sides of the equation. Equality will not be violated.
That is, if:
a=b
Hence:
- a + x = b + x
- a–y = b–y
examples:
16 – 4 = 10 + 2 ⇒16 – 4 + 5 = 10 + 2 + 5 13x + 30 = 7x + 6x + 30 ⇒13x + 30 – y = 7x + 6x + 30 – y
Property 3
If both sides of the equation are multiplied or divided by the same number (or mathematical expression), it will not be violated.
That is, if:
a=b
Hence:
- a ⋅ x = b ⋅ x
- a : y = b : y
examples:
29 + 11 = 32 + 8 ⇒(29 + 11) ⋅ 3 = (32 + 8) ⋅ 3 23x + 46 = 20 – 2 ⇒(23x + 46): y = (20 – 2): y









