Contents
Acute purulent inflammation of the tissue of the tonsils is a paratonsillar abscess, the last and most severe stage of paratonsillitis. Most often this disease occurs in the age group of 15-35 years. Both women and men suffer from paratonsillar abscess with the same frequency. Synonyms of the disease – acute paratonsillitis, phlegmonous tonsillitis. The frequency of diseases increases during the off-season – in winter and autumn.
Causes of the disease

The formation of a paratonsillar abscess in most cases is provoked by the introduction of pathogenic microbes into the tissues of the palatine tonsils. The disease is almost always a secondary lesion, a complication of chronic tonsillitis.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess:
Bacterial infection of the pharynx – develops as a complication of chronic tonsillitis, acute tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
Dental diseases – caries, periostitis of the alveolar tissue, chronic inflammation of the gums and gingival papillae (gingivitis);
Injuries of the oral cavity, neck, pharynx, infected wounds, burns;
Penetration of infection through the middle ear;
Purulent process in the salivary glands.
All these reasons could not contribute to the development of paratonsillar abscess if the patient had not had a decrease in general and local immunity. In the high-risk group, patients with diabetes mellitus, and patients with a history of anemia, oncological pathologies, HIV. Obesity, smoking, anatomical anomalies of the pharynx and tonsils, hypothermia increase the risk of developing paratonsillar abscess.
Pathogenesis
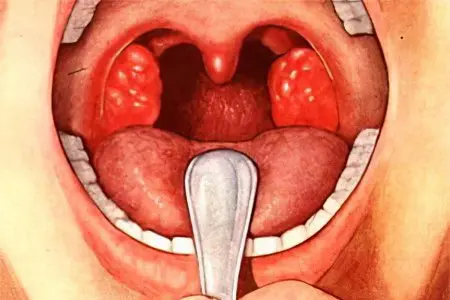
The causative agents of the disease are streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci, Echshieria and Klebsiella, a fungus of the genus Candida. The recesses of the tonsils (crypts) in chronic tonsillitis are filled with purulent discharge. They are deepest in the upper part of the tonsils – in the place of the most pronounced inflammation.
After several episodes of acute inflammation, the tonsil tissue is replaced by scar tissue. Due to scars, the outflow of pus from deep crypts is disturbed, they are not completely cleared. The infection, concentrated in the tonsils, penetrates deep into the tonsils, into the paratonsillar space around the tonsils.
Frequent localization of the abscess in the upper part of the tonsils contributes to the friability of its fiber. With reduced local immunity, the infection easily penetrates into the deeper layers of the tissue.
Classification
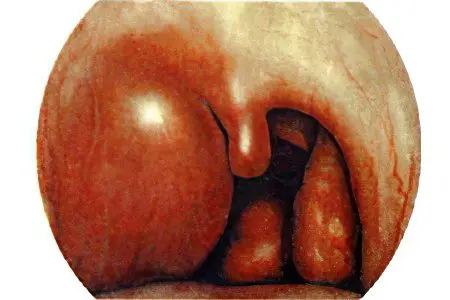
Forms of abscess depending on the stage of development:
Edema stage – the tissues around the tonsils swell, there is no inflammation, as well as the clinical symptoms of the disease.
Infiltration stage – the affected tonsil is hyperemic, there is pain, fever.
Abscessing stage – 4-7 days after the formation of an infiltrate, a fluctuating protrusion of a large size is formed.
Classification by location:
Anterior or anterior-upper abscess – diagnosed in 75% of cases, formed above the tonsil;
Posterior abscess – diagnosed in 10-15% of cases in the posterior arch or between the edge of the tonsil and the edge of the arch.
Inferior abscess – diagnosed in 5% of cases between the lower edge of the tonsil and the lateral wall of the pharynx.
symptoms
Lateral or external abscess – diagnosed in 5% of cases between the pharyngeal wall and the lateral edge of the tonsil, it is very difficult.
Symptoms
In all cases, the disease begins with a sharp pain when swallowing. Since a peritonsillar abscess most often occurs on one side, the pain is one-sided. Bilateral abscess occurs much less frequently – in only 10% of cases. The intensity of the pain increases rapidly, soon it becomes difficult for the patient to swallow not only food, but also saliva. Its quantity increases, hypersalivation is fixed, saliva flows from the corner of the mouth.
Visually, the abscess looks like a rounded formation of bright red color. Its surface is tense, white-yellow contents shine through it. Part of the abscess on palpation has a focus of fluctuation – a tissue area softened due to purulent fusion. The tongue of the pharynx is displaced to the side opposite to the pathology, the palatine tonsil is pushed aside.
The main symptoms of paratonsillar abscess:
Irradiation of pain in the ear, in the lower jaw;
There are symptoms of intoxication with the waste products of pathogenic bacteria – headache, hyperthermia up to 38,5 °, fever, weakness, insomnia:
Hypertrophied regional lymph nodes;
A putrid odor from the oral cavity is fixed;
With the development of the disease, trismus occurs – a spasm of the masticatory muscles;
Speech is disturbed, it acquires a nasal connotation;
Due to the ingress of liquid food into the larynx and nasopharynx, the patient chokes;
He assumes a forced posture with an inclination to the affected side or with the head tilted forward due to excessive salivation.
The patient is mentally overstrained due to insomnia, inability to eat, due to exhausting pain.
After 4-7 days, a spontaneous opening of the paratonsillar abscess occurs. The general well-being of the patient improves dramatically and significantly, the body temperature decreases and the symptoms of the disease decrease. Pus appears in the saliva, trismus is minimized.
With a complicated course of paratonsillar abscess, it breaks through in 2-2,5 weeks. If purulent masses penetrate deep into the tissues of the peripharyngeal space, the abscess may not open. With a similar course of the disease, the severity of the patient’s condition increases.
Complications of paratonsillar abscess
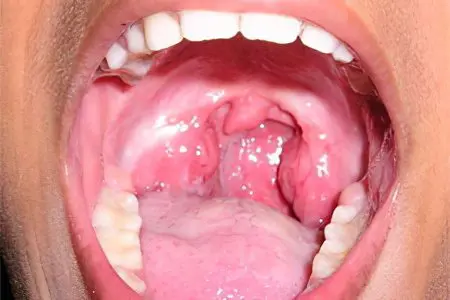
With adequate therapy, the disease ends in recovery. With unqualified therapy or no treatment, the purulent process spreads into the pharyngeal space. Such complications can provoke damage to the walls of the pharynx during an operation to open an abscess, a spontaneous breakthrough of the abscess into deeply located tissues.
Possible complications:
Phlegmon of the tissue of the neck, peripharyngeal tissue;
parapharyngeal abscess;
Sepsis;
Asphyxia due to stenosis of the larynx (compression of the pharynx from the inside);
Purulent mediastinitis, or inflammation of the mediastinum – a purulent lesion of the tissue of the heart, aorta, vena cava and pulmonary vein;
Thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus of the brain;
brain abscess;
Meningitis;
Encephalitis;
Arrosive bleeding due to purulent fusion of the arteries of the peripharyngeal space.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture of paratonsillar abscess is so vivid that the diagnosis by an otolaryngologist does not cause difficulties. For express diagnosis, there is enough data obtained as a result of pharyngoscopy, studying the patient’s history.
Advanced Diagnostic Program:
The study of anamnesis – the presence of injuries of the oral cavity and pharynx, infectious processes in them requires special attention;
Visual examination – the doctor pays attention to the tilt of the head, hypertrophied lymph nodes, bad breath, hyperthermia;
Pharyngoscopy – a rounded formation with a hyperemic surface and a zone of fluctuation is visually determined;
Studying the data of a general blood test (increased ESR, leukocytosis), bacterial culture of an abscess separated from the cavity to determine the pathogen;
Differential diagnosis of paratonsillar abscess using ultrasound and CT of the neck, X-ray of the neck and head from mediastinal abscess, parapharyngeal abscess, diphtheria, aneurysm, tumors of the pharynx and oral cavity, aortic aneurysm.
Treatment

Due to the high risk of complications, the treatment of paratonsillar abscess is carried out exclusively in stationary conditions. The surgeon performs an immediate opening of the formation under local anesthesia (Dikan, Lidocaine). On the protruding part of the abscess, an incision is made with a scalpel, the cavity of the abscess is expanded with pharyngeal forceps, cleaned of pus.
The surgical wound is thoroughly washed with an antiseptic solution, a drain is installed to remove the exudate.
With surgery performed against the background of frequent tonsillitis, it is possible to remove the tonsils. If sore throats rarely occur, the doctor recommends that such an operation be performed no earlier than 1,5-2 months from the moment the abscess is opened. In the recovery period, the patient is recommended medication.
Groups of drugs:
Intramuscular and intravenous administration of antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Ceftriaxone, Amikacin, Penicillin, Gentamicin, Cefuraxime), the choice of which depends on the causative agent of paratonsillar abscess;
Infusion administration of Hemodez for detoxification of the body;
Local treatment – gargling with antiseptic solutions (Miramistin, Furacillin);
Prevention of candidiasis with the introduction of antibacterial drugs (Intraconazole);
antihistamines;
NSAIDs to relieve pain and inflammation.
Since the patient experiences acute pain in the throat, the drugs are administered mainly in the form of injections, rectal suppositories.
If the treatment of the abscess is started on time, after 2-3 weeks there is a complete recovery. With the addition of complications, inflammatory processes affecting the brain and mediastinum, the prognosis of recovery is doubtful, a fatal outcome is possible.
Prevention of paratonsillar abscess
To prevent the occurrence of an abscess in the oral cavity, it is necessary to promptly treat tonsillitis, gingivitis, inflammation of the adenoids, sanitize carious cavities in the teeth. Strengthening the immune system through the use of physical education, adequate hardening, the use of a large amount of fresh fruits and vegetables will help to resist the disease.









