Contents
Throat abscess is a purulent inflammation of the pharyngeal, paratonsillar or peripharyngeal tissue, with the involvement of regional lymph nodes in the process. Delay in diagnosis and treatment can lead to asphyxia due to suffocation. It can be a complication of tonsillitis, pharyngitis, purulent otitis, a consequence of a trauma to the larynx. The disease is fixed in each age category, more often affecting children of early and preschool age.
Classification
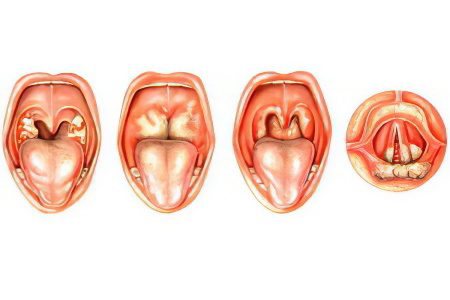
There are the following types of throat abscess:
Paratonsillar abscess – purulent inflammation occurs in the tissue of the tonsils;
Retropharyngeal abscess – more common in adults, affects the tissue around the retropharyngeal lymph node;
Peripharyngeal abscess – inflammation forms in the peripharyngeal part of the throat.
Classification by abscess localization:
Anterior abscess – formed in the upper part of the tonsils;
Posterior abscess – formed between the palatine arch and tonsils;
Lower abscess – a variety difficult to diagnose and treat, located under the palatine tonsil;
Lateral abscess – is severe, with complications, is formed on the side of the tonsil.
Types of pharyngeal abscess at the place of its localization:
Epipharyngeal – is formed above the palatine curtain;
Mesopharyngeal – formed between the edge of the palatal curtain and the root of the tongue;
Hypopharyngeal – formed below the root of the tongue;
Mixed – occupies 2-3 zones at the same time.
Causes of a throat abscess

In children, the most common cause of abscess development is an infection caused by streptococcus, staphylococcus, less often E. coli. The disease is almost always secondary to the pathology that provoked it. The infection enters the throat space through the lymphatic pathways, so nearby lymph nodes are always affected and inflamed.
Primary foci of infection in childhood:
Purulent otitis;
Mastoiditis;
Parotitis occurring with complications;
Rhinitis;
Pharyngitis;
Complications of acute infectious diseases (flu, SARS, measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria);
Complications after the operation (adenotomy, tonsillectomy).
The rapid development of the inflammatory process is facilitated by reduced immunity, rickets and diathesis in the history of the child.
In adults, the formation of a pharyngeal abscess most often occurs due to tissue trauma.
Causes of a throat abscess in adults:
Damage to the throat with rough food, bone, foreign object;
Injury of the throat mucosa after gastroscopy, bronchoscopy, endotracheal anesthesia;
Complication after angina;
A consequence of tuberculosis, syphilis;
The presence of caries.
The rapid spread of the infection is facilitated by a history of HIV infection in an adult, diabetes mellitus, a malignant tumor, somatic diseases, and any process that reduces immunity. The causes of a purulent inflammatory process in the throat cannot be strictly limited to age categories. Predisposing factors from each group can occur at any age.
Throat abscess symptoms

Any form of throat abscess begins with a sharp increase in body temperature to critical values - 39-40 ° C. A feverish state is accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition.
Symptoms and manifestations of a throat abscess:
In children, tearfulness and anxiety, loss of appetite, restless sleep;
In infants – violation of sucking;
Increased pain when swallowing food and saliva;
Violation of nasal breathing with damage to the upper pharynx;
nasality of voice;
Attacks of suffocation with the localization of an abscess in the middle and lower parts of the pharynx;
Violation of breathing in an upright position due to the flow of pus along the wall of the larynx, closing the lumen of the trachea;
Hoarseness of voice;
Rumbling in the throat during sleep;
Swelling and soreness of the occipital and upper cervical occipital lymph nodes;
Swelling of the neck in the region of the lower jaw.
Due to severe pain, the patient takes a forced position when his head is turned in the direction of the lesion and slightly thrown back.
Complications
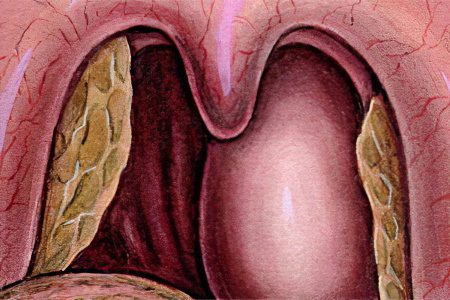
The development of a purulent inflammatory process leads to the appearance of severe complications:
Bronchopneumonia as a result of the spread of infection through the upper respiratory tract;
Congestive pneumonia due to respiratory failure;
Brain abscess, purulent meningitis due to the spread of infection into the cranial cavity through the circulatory system;
Cardiac arrest;
Asphyxia (suffocation) due to the overlap of the trachea with an abscess, swelling of the larynx, outpouring of purulent masses into the larynx during self-opening of the formation;
Purulent mediastinitis – the spread of infection in the mediastinum;
Phlebitis;
Thrombosis of the jugular vein;
Arrosive bleeding due to purulent fusion of blood vessels;
Sepsis (blood poisoning).
Diagnostics
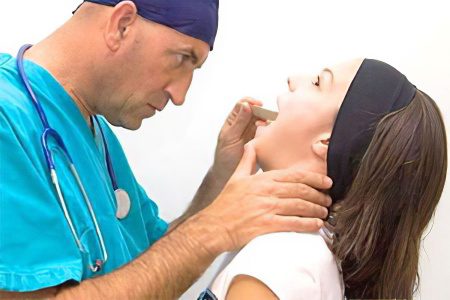
A vivid clinical picture of the disease will allow the otolaryngologist to make an accurate diagnosis. During a visual examination of the patient, he draws attention to the swelling of the neck, forced adoption of a fixed position, hypertrophied lymph nodes. Examination of the throat with a pharyngoscope will reveal an infiltrate in the throat, tissue hyperemia, and a spherical formation.
On palpation, the doctor notes the soreness of the lymph nodes. A more detailed examination can fix the area of fluctuation on one of the walls of the abscess – the accumulation of pus under the strained tissue.
Laboratory research:
Complete blood count – leukocytosis is detected, an increase in ESR;
Microscopic examination of a throat swab – reveals the type of pathogen (streptococcus, staphylococcus, E. coli, Klebsiella);
Bacteriological examination of a smear – determines the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics;
PCR test for tuberculosis, syphilis;
Sputum analysis for the detection of mycobacteria;
Anticardiolipin test for syphilis.
Instrumental studies to find the cause of throat infection:
Ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses;
Otoscopy;
Rhinoscopy;
X-ray of the maxillary sinuses;
X-ray of the cervical spine.
Throat abscess treatment

Throat abscess is treated exclusively surgically in a hospital setting. Before opening the abscess, local anesthesia is performed with Lidocaine, Procaine.
Operation procedure:
An incision of the abscess with a scalpel at the site of fluctuation by 2 cm or a preliminary puncture of the abscess to prevent the flow of pus into the respiratory tract.
Insertion of an electric pump into the incision for suction of pus.
Dilution of the edges of the abscess with Hartmann forceps or probe.
Installing a drain into the abscess cavity.
Monitoring within 3-4 days of the condition of the drainage.
With a low-lying abscess, the abscess is opened outside the neck along its anterior-lateral surface.
In case of respiratory failure, the breathing tube is not installed in the trachea, that is, the patient is not intubated. Instead, an incision is made in the laryngeal cartilage (cricotomy) to facilitate breathing. If, due to respiratory failure, the patient suffers from hypoxia, oxygen therapy is carried out – the installation of an oxygen mask, pillows, artificial ventilation of the lungs.
If the abscess of the throat resulted from syphilis or tuberculosis, it is not opened, preferring the puncture of the abscess because of the risk of infection of the surrounding tissues. Specific drugs for the treatment of syphilis and tuberculosis are injected into the abscess, general therapy for these diseases is prescribed.
Drug therapy accompanying surgical treatment and sanitation of foci of infection:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics (Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Amoxil, Roamycin, Josamycin, Ceftriaxone) to eliminate the pathogen;
NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Nimesulide), antipyretics (Nurofen, Paracetamol) to relieve inflammation, pain relief and lower temperature;
Hyposensitizers (Loratadine, Fenspiride, Desloratadine, Zyrtec, Tavegil) to reduce swelling and prevent autoimmune complications;
Antiseptics (Miramistin, Furozolidone, Chlorgesidine, Hexoral) for local treatment, gargling;
Multivitamins;
Immunostimulants (Imudon).
With timely medical care, the patient recovers. Severe complications at the current level of development of medicine are rare. To prevent the development of a throat abscess, timely treatment of foci of infection of the ear, throat, nose, and dental procedures is required. The doctor is required to strictly observe the technique of performing manipulations on the tissues of the throat – the introduction of probes, breathing tubes, operations to remove tonsils and tumors, to extract foreign bodies.









