Medical treatments for legionellosis (Legionnaire’s disease)
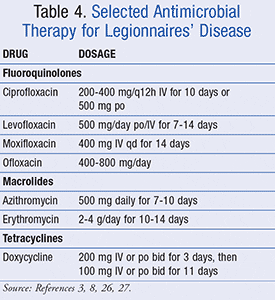
antibiotics. The bacteria Legionella pneumophila is naturally resistant to the penicillin usually used in the treatment of pneumonia. Erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin, levofloxacin, and ciprofloxacin are commonly used to treat legionellosis. Treatments generally last 7 to 10 days, sometimes several weeks, especially in the case of more vulnerable people.
The earlier treatment is started, the better the chances of recovery and the lower the risk of complications. Usually, improvement in symptoms occurs within 3 to 5 days.
In immunosuppressed patients or in patients with very severe pneumonia from the start, many may experience fatigue and neurological symptoms 18 months after infection.