Contents
Hypokinesia is defined as a decrease in the ability to move or muscle. It is mainly found in cardiac or neurological problems, with decreased movements of the heart ventricles and muscles linked to the decrease in brain activity. Find out about its causes and the different possible treatments.
Hypokinesia (Greek “from below” + “movement”) is a state of the body in which there is insufficient motor activity, causing a limitation in the pace and range of movements. Motor activity worsens against the background of mental and neurological disorders – Parkinson’s disease and other extrapyramidal syndromes.
What is hypokinesia?
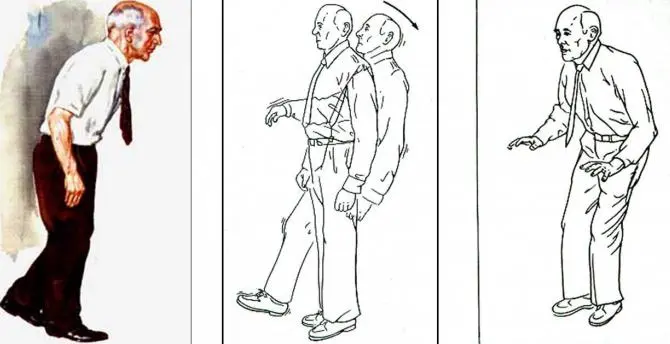
Hypokinesia is a movement disorder, corresponding to a motor decrease in certain parts of the body or organs. A person with hypokinesis has an inability to perform certain muscle movements. Hypokinesia is different from akinesia or dyskinesia, which correspond to muscle movement disorder and abnormal muscle movement, respectively. Bradykinesia combines the two elements: hypokinesia and akinesia.
Ventricular hypokinesia, or heart failure: causes and treatments
Ventricular hypokinesia is a decrease in the range of motion of the heart ventricles. It is therefore linked to heart failure.
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a decrease in the efficiency of the heart’s ventricles (the chambers surrounded by heart muscle, the myocardium, which are responsible for pumping blood). This is therefore a hypokinesia of the cardiac ventricles. The ventricles (left and right) are responsible for circulating oxygenated blood in the body and venous blood in the lungs. Concretely, heart failure is expressed by the heart’s inability to pump enough blood to oxygenate all of the body’s organs. The symptoms are therefore fatigue and rapid shortness of breath on exertion. These symptoms can vary and decrease or increase in intensity depending on the severity of the ventricular hypokinesia.
Heart failure is a serious complication of certain cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, which mainly affects people over the age of 75.
Public at risk
More and more frequent due to the general aging of the population, we find heart failure more often in elderly patients also because the cardiovascular and respiratory disorders at the origin of this disease are better treated. For example, myocardial infarctions cause fewer deaths in the short term, but their sequelae are leading to new cases of CHF.
Support and treatment
A medical care is possible by a better hygiene of life, a prescription of drugs in order to support the heart muscle and decrease the arterial hypertension. It is usually a treatment to be followed for life, once the diagnosis has been determined.
Hypokinesia in Parkinson’s disease: causes and treatments
Hypokinesia is a sign of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the progressive destruction of neurons in the brain. This disease is manifested by three characteristic symptoms:
- stiffness;
- tremors;
- and disturbances and decreased movement.
Parkinson’s disease is the most common cause of Parkinson’s syndrome, defined by the association of bradykinesia (slowing down in the execution of a movement and decrement of speed) potentially associated with a reduction in amplitude (hypokinesia) and a lack of initiation (akinesia).
Several difficulties in daily life can then arise: difficulties in performing simple actions, precise gestures, coordinated and repetitive movements. A person with hypokinesis may experience an inability to move certain movements, and / or a great feeling of fatigue, blockage, and sometimes stillness. Difficulties in writing and impaired speech may also occur.
Treatments
Several therapeutic avenues can be considered to limit the progression of the disease and relieve the symptoms. In particular, the following elements can be used to limit the harmful effects:
- maintaining moderate physical activity;
- relaxation (yoga, meditation);
- rehabilitation, thanks to various specialists (physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists);
- taking medicines such as L-dopa, dopamine agonists or anticholinergics;
- psychological follow-up, in the event of a feeling of unease or withdrawal.
Hypokinesia in vascular dementia
As with Parkinson’s disease, there are cases of hypokinesia in people with vascular dementia. It can be caused by a massive stroke or multiple heart attack, for example.
Vascular dementia includes all dementia syndromes having in common vascular insufficiency. This degeneration is the second most common dementia after Alzheimer’s disease, ie about 10-20% of dementias.
We find similar symptoms and therapeutic avenues as in Parkinson’s disease.
Hypokinesia of the ventricles
A decrease in the amplitude of movement of the left ventricle is also classified as hypokinesia. Zones of hypokinesia during echocardiography indicate either acute or past myocardial infarction (postinfarction cardiosclerosis), myocardial ischemia, thickening of the myocardial walls. Violations of local contractility of the segments of the left ventricle in patients with coronary heart disease are assessed on a five-point scale:
- Normal contraction.
- Moderate hypokinesia.
- Severe hypokinesia.
- Akinesia (lack of movement).
- Dyskinesia (a segment of the myocardium does not move in the right direction, but in the opposite direction).
Hypokinesia of the right ventricle is detected in patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). Studies have shown that the presence of hypokinesia of the right ventricle in patients with acute PE doubles the risk of mortality within the next month. This fact makes it possible to identify high-risk patients who appear to be stable.
Treatment of hypokinesia
How to treat hypokinesia depends on the underlying disease, a symptom of which is a decrease in motor activity. In the early stages of Parkinson’s disease, dopaminergic drugs are indicated. The doctor should prescribe medications and judge their effectiveness. With the progression of the disease and the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, surgical treatment (neurostimulation or destructive surgery) may be required.









