Contents
Hypoventilation: all you need to know about this respiratory disorder
Hypoventilation is a decrease in breathing. With multiple causes, this respiratory disorder requires adequate medical management to limit the risk of complications, in particular the risk of respiratory failure.
Definition: what is hypoventilation?
Hypoventilation is a respiratory disorder characterized by less than normal breathing. It results in an insufficient quantity of inspired air.
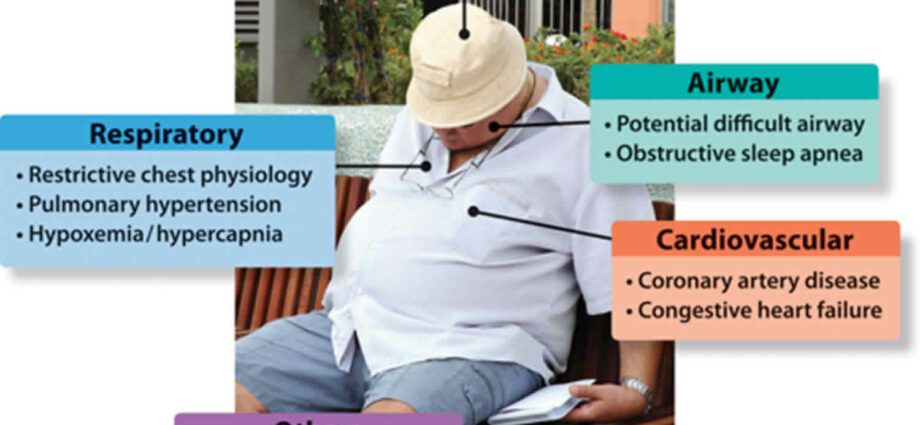
Special case: what is obesity-hypoventilation syndrome?
Formerly known as Pickwick’s syndrome, obesity-hypoventilation syndrome is characterized by the appearance of chronic hypoventilation in obese people without respiratory disease. This particular form of hypoventilation can have several explanations: mechanical constraints, dysfunction of the respiratory centers, and / or the repetition of obstructive apneas.
Explanation: what are the causes of hypoventilation?
Hypoventilation can have many causes, such as:
- primary neurological diseases, including certain forms of polyradiculoneuritis (nerve damage resulting in a depletion of the myelin sheath that surrounds the nerves) and certain forms of myasthenia gravis (neuromuscular disease causing muscle weakness);
- acute poisoning, such as intoxication with psychotropic drugs, morphines, or alcohol;
- fatigue of the respiratory muscles, which can appear during prolonged and / or intense muscular work;
- obstruction of the upper airways, which can especially occur during inhalation of foreign bodies, epiglottitis (inflammation of the epiglottis), laryngospasm (involuntary contraction of the muscles surrounding the larynx), angioedema (subcutaneous swelling), compressive goiter (increase in thyroid volume with local compression), tracheal stenosis (decrease in the diameter of the trachea), or glossoptosis (poor positioning of the tongue);
- bronchial obstruction, which may for example be due to severe acute asthma (inflammation of the airways), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (pulmonary disease the main cause of which is smoking), bronchial dilation, or bronchial congestion.
- chest deformity, which can be the result of kyphoscoliosis (double deformity of the spine), ankylosing spondylitis (chronic inflammatory disease of the joints of the spine and lower back) or thoracoplasty (rib surgery thoracic);
- extensive lung resection, a surgical operation which constitutes to remove part of the lung, in particular in the event of lung cancer;
- a pleurisy, which is an inflammation of the pleura, the membrane covering the lungs;
- a obesity, as in the context of obesity-hypoventilation syndrome.
Evolution: what is the risk of complications?
The consequences and the course of hypoventilation depend on many parameters including the origin of the respiratory disorder and the patient’s condition.
Hypoventilation can be accompanied by two other clinical phenomena:
- hypoxemia, that is, a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the blood;
- hypercapnia, that is, an excessive level of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Hypoventilation can also result in respiratory failure, damage to the pulmonary system. Acute respiratory failure requires prompt medical attention.
Treatment: how to treat hypoventilation?
The medical management of hypoventilation depends on its origin, its consequences and its evolution. Depending on the case, it can be performed by a general practitioner or a pulmonologist. Management by emergency medical services is necessary in the most serious cases, especially in cases of acute respiratory failure. During major hypoventilation, mechanical ventilation may be implemented.