Contents
Rhombus is a geometric figure; parallelogram with 4 equal sides.
Area formula
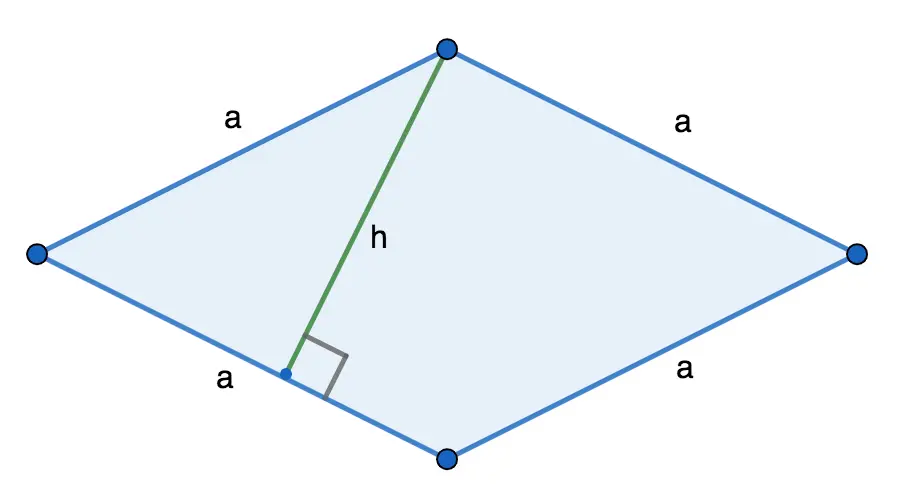
Side length and height
The area of a rhombus (S) is equal to the product of the length of its side and the height drawn to it:
S = a ⋅ h
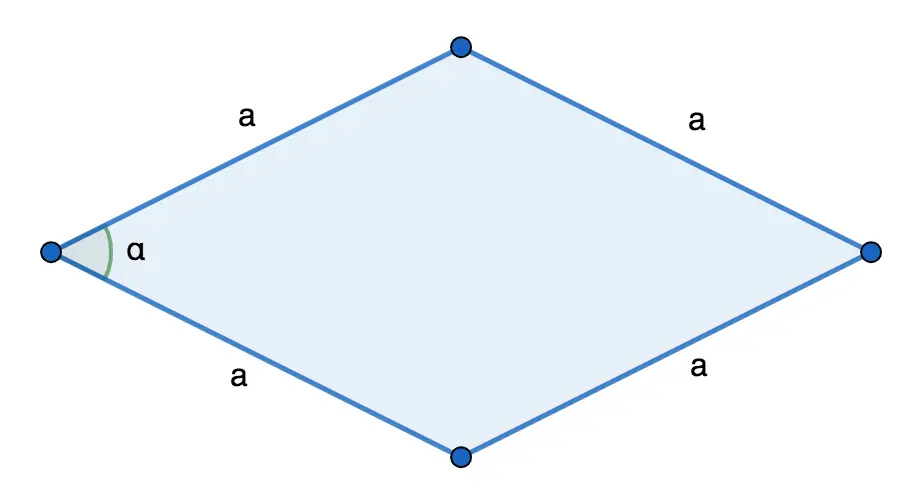
By side length and angle
The area of a rhombus is equal to the product of the square of the length of its side and the sine of the angle between the sides:
S = a 2 ⋅ without α
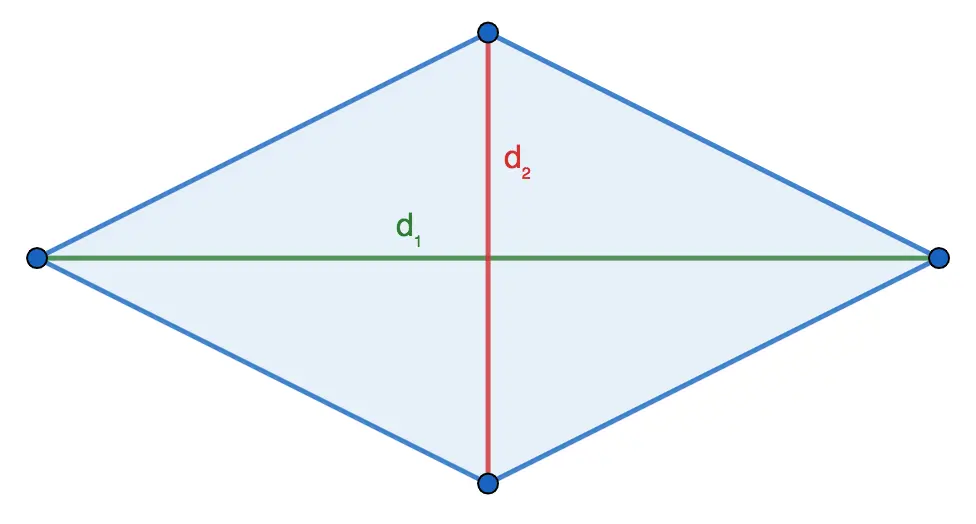
By the length of the diagonals
The area of a rhombus is one-half the product of its diagonals.
S = 1/2 ⋅ d1 ⋅ d2
Examples of tasks
Task 1
Find the area of a rhombus if the length of its side is 10 cm and the height drawn to it is 8 cm.
Decision:
We use the first formula discussed above: S u10d 8 cm ⋅ 80 cm uXNUMXd XNUMX cm2.
Task 2
Find the area of a rhombus whose side is 6 cm and whose acute angle is 30°.
Decision:
We apply the second formula, which uses the quantities known by the conditions of setting: S = (6 cm)2 ⋅ sin 30° = 36 cm2 ⋅ 1/2 = 18 cm2.
Task 3
Find the area of a rhombus if its diagonals are 4 and 8 cm, respectively.
Decision:
Let’s use the third formula, which uses the lengths of the diagonals: S = 1/2 ⋅ 4 cm ⋅ 8 cm = 16 cm2.









