Contents
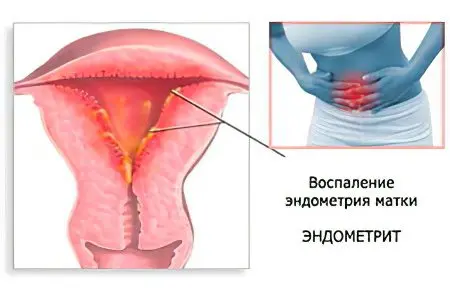
Women often face the diagnosis of “endometritis” after undergoing surgery on the genitals, after an abortion or other traumatic procedure. You should not despair, as you can get rid of endometritis.
Endometritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane that lines the uterus from the inside. This membrane is called the endometrium. It peels off every month. It happens during menstruation. During the next cycle, the endometrium grows again. This is necessary so that the egg has the opportunity to attach to it, and the woman managed to become pregnant. If renewal does not occur, then the fertilized egg will be rejected.
The endometrium performs a barrier function. It protects the uterus from various infections. When these functions are reduced, the pathogenic flora penetrates inside and begins to multiply there. This leads to inflammation, which will be characterized by the doctor as endometritis.
The disease can be acute or go into a chronic phase. Inflammation can spread to the uterine appendages, to the ovaries and cause serious health problems. Endometriosis is more common in young women of childbearing age.
Differences between endometritis and endometriosis. With endometritis, inflammation captures the membrane lining the uterus from the inside. With endometriosis, the inflammatory process extends beyond the uterus. Connecting strands grow on adjacent organs.
Causes of endometritis
Most often, various manipulations that are carried out on the uterus lead to endometritis. They may have a therapeutic or diagnostic purpose.
Normally, the endometrium has sufficient protection against pathogenic flora. It has 2 layers: basal and functional. When the next menstrual cycle ends, the functional membrane begins to move away. The new endometrium is formed from the basal layer. This process causes menstruation. If the uterine mucosa is damaged, then bacteria and viruses can easily penetrate inside.
Factors such as:
Postponed abortions.
Childbirth.
Setting up the probe.
Scraping.
Hysteroscopy.
Douching, if it is not carried out according to the rules.
There are additional risk factors that can lead to the development of endometritis:
Deterioration of human immunity.
Chronic diseases
Setting the intrauterine device.
Injury to the uterus.
Vitamin deficiency.
Low level of hygiene skills.
Intimacy during menstruation.
Sexual infections.
Violation of the hormonal background.
Carrying out diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations on the uterine cavity.
First of all, women who have weakened immunity suffer from endometritis. Defense mechanisms are unable to resist infection. Therefore, bacteria freely penetrate the mucous layer of the uterus and multiply there.
causative agents of endometritis
Endometritis of the uterus does not develop on its own. It is caused by pathogenic flora:
Conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that are activated when the body’s defenses are reduced.
Germs that cause sexually transmitted infections.
Trichomonas and gonococci.
Most often, the disease develops when several representatives of the pathogenic flora are exposed to the uterine mucosa at once. These can be colonies of staphylococci, streptococci, viruses, fungi, etc.
Harmful microbes enter the uterus along its cervix from the vagina. They can also spread their fallopian tubes, from the intestines. Sometimes they get inside the uterus with a blood or lymph flow.
Causes of acute endometritis
Acute endometritis can develop in the following cases:
Conducted diagnostic curettage of the uterus.
Performing operations on the uterine cavity.
Postponed abortion.
Accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity.
Postponed operations for the removal of the placenta and the remains of the fetal egg.
Complications after childbirth.
Performed caesarean section.
Therapeutic and diagnostic procedures performed on the uterine cavity can cause a violation of the integrity of the endometrium. In this regard, probing, hysteroscopy, and biopsy are dangerous. As a result of such procedures, damage remains on the uterine mucosa, which are the entrance gate for infection.
If a woman undergoes an abortion or curettage, then the endometrium is completely cleaned. After that, the uterus is a large bleeding wound surface. Any infection will be able to freely penetrate into its basal layer.
Causes of endometritis in the postpartum period

A woman after the birth of a child may develop endometritis. It occurs in 5% of all women in labor. If a caesarean section was performed, then the likelihood of developing inflammation rises to 30%.
Causes of endometritis in the postpartum period:
Hormonal changes in the body.
Weak immune system.
Infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites.
Equally important is the proper functioning of the nervous, endocrine and immune systems of a woman. If they fail, then the disease will have a severe course.
Reasons for the development of chronic endometritis

The chronic form of the disease develops when an acute infection has not been fully treated.
The following factors can provoke the development of the disease:
Sex during menstruation.
Injury to the uterus or cervix.
Stress.
Lack of vitamins in the body.
Chronic diseases that negatively affect the state of immunity.
Errors in intimate hygiene.
Chronic diseases of the genital organs.
If a woman has an intrauterine device installed, this can lead to the development of endometritis. It is easier for infectious agents to climb into the uterus along the threads of this device. Less often, microbes enter the uterine cavity during the installation of the spiral. This happens when the antiseptic rules of the procedure are not followed. The longer a woman uses a spiral, the higher the likelihood of chronic endometritis.
Doctors point out that endometritis in 80% of cases develops in women of childbearing age who use spirals, or often have abortions.
Other causes of endometritis
Other causes of endometritis include:
Injuries received during childbirth with ruptures of the cervix or vagina. Bacteria easily enter the uterus through existing damage and begin to multiply there.
Chemical damage to the endometrium of the uterus.
Frequent douching.
Use of contraceptives that contain chemicals and are inserted into the vagina. Spermicides disrupt its natural microflora.
Prolonged wearing of tampons. In this case, bacteria begin to multiply actively, which leads to inflammation.
Sometimes endometritis is limited to the uterus, and sometimes extends beyond it. It must be understood that for a long time inflammation will not be concentrated in the superficial uterine layer. The infection will certainly penetrate deeper if it is not eliminated in time. Therefore, endometritis leads to infertility. The more damaged the uterus, the lower the chance that a woman will be able to become pregnant.
Endometritis symptoms
Symptoms of endometritis develop quickly, 3 days after the defeat of the uterus by pathogenic flora. The more massive the focus of inflammation, the more intense the symptoms of the disease.
General symptoms

Once in the uterine cavity, bacteria or other microorganisms cause inflammation. First, it is localized in the surface layer of the organ. If a small area of the epithelium is affected, then the symptoms of endometritis will be mild. Sometimes a woman decides to heal herself. After taking the drugs, the symptoms of the disease disappear. The patient thinks that recovery has come. In fact, the disease just subsided. If at this stage competent therapy is not started, then the endometritis will turn into a chronic form.
Changes that occur in the uterus:
The blood vessels supplying the organ dilate.
The endometrium becomes thick.
A purulent plaque appears on the mucous membranes of the organ. This leads to the fact that the cells of the body begin to die.
The uterus has many glands. Due to the disease, they are pinched and begin to produce inflammatory exudate. As a result, the amount of vaginal discharge sharply increases in a woman.
In some patients, the symptoms of the disease have a latent course, while in others the inflammation develops acutely. However, this process cannot go unnoticed.
Patients make the following complaints to the doctor:
Mucus and pus are secreted from the vagina.
An unpleasant odor emanates from the discharge. It occurs when the cause of inflammation is Escherichia coli.
Blood is visible in the discharge. This symptom indicates that there is a rejection of the endometrium of the uterus.
Lower abdomen hurts. The pain may be mild or intense. She often gives in the groin, in the coccyx, in the intestines.
When the doctor begins to palpate the uterus, the patient indicates an increase in pain. The pain will be more intense, the stronger the inflammation.
Symptoms of acute endometritis

Acute endometritis manifests itself on the 4th day from the entry of pathogenic flora into the uterine cavity.
The following symptoms will indicate the beginning of the inflammatory process:
Rise in temperature to high levels. Sometimes it reaches 40 °C.
A sharp deterioration in well-being.
Severe pain in the lower abdomen that radiates to the intestines, to the groin, to the sacrum.
When the myometrium is involved in the inflammatory process, the patient cannot say exactly where her stomach hurts.
In addition to high body temperature, patients experience symptoms such as:
Headache.
Nausea, which may result in vomiting.
Increased weakness.
An increase in heart rate.
In the discharge from the vagina, pus and mucus are visible. Sometimes streaks of blood are visible. They appear due to the fact that the inner layer of the uterus does not have time to recover, and the existing defects on it bleed.
The menstrual cycle is disrupted. Women complain of prolonged bleeding.
If endometritis develops after an abortion and particles of the fetal egg remain in the uterine cavity, then it will not be able to contract normally. This leads to the fact that the woman develops massive bleeding. Blood clots are visible in the discharge.
The acute stage of the disease lasts no more than 10 days. If the treatment was chosen correctly, then the woman recovers. When there is no therapy, the symptoms of endometritis also gradually fade away, but this does not mean that the disease goes away. It’s just that it transforms into a chronic form and will remind you of itself from time to time.
Symptoms of chronic endometritis

Chronic endometritis has a sluggish course. In this case, the mucous layer of the uterus is gradually destroyed and replaced by connective tissue. This leads to the fact that the uterus loses its natural functions.
Symptoms of the chronic form of endometritis:
Irregular menstruation. In this case, the work of the ovaries will not be disturbed.
Pain in the lower abdomen. It is not intense, but worries a woman for a long time.
Changes in the structure of the endometrium with the formation of deep lesions on it.
The menstrual cycle lengthens and exceeds 7 days. Menses become profuse.
The woman cannot get pregnant.
In this case, the patient complains of discharge, which has a cloudy consistency. The chronic form of the disease is difficult to treat and causes the development of serious health problems.
Symptoms of endometritis after childbirth

If the disease develops after childbirth, then the woman will experience symptoms such as:
Immediately after childbirth, a woman develops vaginal discharge that has an unpleasant odor. Their number is increasing sharply.
Body temperature rises, can reach 39 ° C. This happens on the second day after the birth of the child.
The woman begins to worry about severe pain in the lower abdomen.
The patient’s state of health worsens, there is no appetite, severe chills, headaches appear.
The pulse quickens.
ESR is greatly increased.
During the examination, the doctor detects signs of inflammation such as:
The uterus is slightly reduced.
A woman complains of pain when the doctor palpates the organ.
Discharges are brown in color. They may contain impurities of pus.
In some women, endometritis has an erased form. Symptoms are blurred, so it is difficult to identify them. Inflammation develops 3-4 days after birth, and sometimes a few days later. In this case, the body temperature will not exceed 38 ° C, there is no chill, and the level of leukocytes noticeably increases in the blood test. The secretions may contain a small amount of blood, they have an unpleasant odor. The erased form is dangerous because it is diagnosed late. In this case, the infection spreads with the bloodstream throughout the body and the patient develops sepsis.
These symptoms require emergency treatment.
Symptoms of endometritis after caesarean section

After a caesarean section, a severe form of the disease often develops. Infection may be introduced during the first incision. In this case, the seam will not tighten, the wound on the uterus does not heal.
Recovery is complicated by the fact that the uterus loses its ability to normal contraction. Exudate begins to accumulate in it. Symptoms of inflammation may appear 1-5 days after surgery. At this time, the woman is in the hospital, so doctors can provide her with adequate assistance to the situation.
Other signs of endometritis that develops after a caesarean section include:
An increase in body temperature to high levels.
Chills.
Headache.
Nausea.
Pain in the pubic region.
Increased heart rate.
Features of vaginal discharge with endometritis against the background of caesarean section:
The discharge has an unpleasant odor, they are not transparent, watery. They may contain pus.
A brown fluid is secreted from the genitals. Its volume is increasing all the time.
The seam becomes edematous.
The woman has increased bloating, constipation may develop.
Painful urination.
Air accumulates in the seam area, and the scar will be deformed.
The muscles of the uterus contract weakly.
During palpation of the uterus, the woman complains of pain.
The uterus is greatly enlarged.
In the blood, the ESR and the level of leukocytes increase.
Sometimes the symptoms of endometritis after caesarean section develop a few weeks after the operation. Therefore, after discharge from the hospital, a woman should carefully monitor her well-being. If signs of inflammation are found, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Endometritis diagnostics

If a woman finds signs of endometritis in herself, she needs to contact a gynecologist. The doctor will examine the patient on the chair, assess the nature of the discharge and take a smear. He will be sent for cytology bacteriological examination. Sometimes PCR is required. This allows you to identify such microorganisms as: chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma. For the study, you will need to donate blood from a vein. Another way to diagnose endometriosis is an ultrasound.
During the examination on the gynecological chair, the doctor will be able to notice signs of the disease, such as:
Puffiness of the uterus, its inelasticity and large size.
Touching the body causes pain.
Pain when trying to move the cervix indicates inflammation of the peritoneum.
In a clinical blood test, an increase in ESR and a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left will be noticeable.
US
You can suspect endometritis in a woman during an ultrasound scan.
The specialist will be able to notice signs such as:
The uterus will be larger than normal.
The endometrium thickens.
Adhesions are visible in the uterus.
Ultrasound does not give a complete clinical picture of the disease. With its help, it will not be possible to determine the severity of the pathology. To get more information, you need to perform a biopsy. However, this study is prescribed only for a severe form of the disease. At the same time, a small piece of the mucous layer of the uterus is taken from the patient.
Differential diagnostics

Symptoms characteristic of endometritis can also develop with other gynecological diseases.
Therefore, it is important to carry out differential diagnosis with pathologies such as:
Parametritis that develops after childbirth.
Thrombophlebitis of the veins of the small pelvis.
Metrothrombophlebitis.
Pelvioperitonitis.
Ectopic pregnancy.
Acute appendicitis.
Functional pain in the pelvic area.
Diagnosis of the acute form
Diagnosis begins with the collection of anamnesis, after which the doctor proceeds to a gynecological examination, palpates the uterus. Then the doctor directs the patient to donate blood. She will need to undergo an ultrasound and diagnostic laparoscopy. If the diagnosis cannot be established, then a biopsy of the endometrium of the uterus is performed.
Diagnostics of the chronic form
During the diagnosis, you need to find out the following points:
Find out if the woman had an ectopic operation.
Find out if a woman has an ectopic device.
Has the patient had a miscarriage?
Has she suffered from acute endometritis before?
Does she have other diseases that can lead to infertility.
Then a smear is taken from the woman for examination. It is possible to perform a scraping of the mucous membrane of the uterus with its further histological examination. The patient is given a referral for ultrasound, hysteroscopy and biopsy. The main advantage of hysteroscopy is that this method is highly informative, but it is traumatic and is equivalent to surgical intervention.
A comprehensive study of the mucous layer of the uterus is called immunohistochemical diagnostics. During its implementation, they study the biopsy, aspirate and scrapings that are taken from the woman. This will allow you to make the most accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis after childbirth
To make a diagnosis, you will need to take blood and urine for analysis, perform a LHC sowing a smear. Sometimes a CT or MRI is required. These studies are prescribed when there is a suspicion of pelvic thrombophlebitis or abscess.
Postpartum endometriosis is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. A similar situation is observed with atelectasis, stagnation of breast milk and infections of the genitourinary organs.
Endometritis treatment
Treatment of endometritis is complex. It is based on the appointment of antibiotics, antioxidants and immunomodulators.
If a woman is diagnosed with acute endometritis, then she should be hospitalized. She was shown bed rest. She should eat right and drink enough water.
The main directions of therapy:
The appointment of antibiotics, which are aimed at the destruction of pathogens of inflammation. In severe cases, several antibacterial agents are prescribed at once. If the cause of inflammation is anaerobic bacteria, then the patient is prescribed Metronidazole.
To prevent the development of complications caused by taking antibacterial drugs, a woman is prescribed antifungal agents and probiotics.
To remove intoxication from the body, the introduction of protein and saline solutions, antihistamines is indicated.
Immunomodulators and vitamin-mineral complexes are designed to increase the body’s own defenses.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce body temperature.
When the acute stage of the disease is behind, the woman is prescribed physiotherapy.
In acute endometritis that occurs after childbirth, antibacterial drugs from the group of cephalosporins or aminoglycosides are prescribed. The average course of treatment is 5-10 days. Drugs can be administered intravenously, but sometimes injections are placed directly into the uterine cavity. For high-quality treatment, it is important to establish the causative agent of the inflammatory process. This will allow targeted therapy. While the results are unknown, the patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Oral contraceptives are used to speed up the restoration of uterine tissues, and also prepare the body for conception.
Surgery for endometritis
Often, with purulent endometritis, surgical intervention is required, since pus blocks the cervical canal of the uterus. This leads to the fact that blood, mucus and pus remain in its cavity. To free the organ, you need to remove the cork.
For this purpose, such methods of surgical intervention are used as:
Hysteroscopy.
Sounding.
Cervical dilation.
Active emptying of the uterus is used if endometritis develops after childbirth or abortion and particles of the fetal egg remain inside. After emptying, the uterus is washed with antiseptic solutions.
If there is a lot of pus, the inflammation is severe and cannot be eliminated, the uterus is completely removed.
Treatment of endometritis that develops after childbirth

If a woman develops postpartum endometritis, then the woman is shown hospitalization. Antibacterial drugs form the basis of therapy. Be sure to prescribe drugs aimed at increasing immunity. In order for the uterus to carry out a normal outflow of exudate, antispasmodics are required.
Treatment with antibiotics requires not breastfeeding. A woman should remember that after the treatment of endometritis, she will need to refrain from intimacy for a month.
If particles of the placenta remain in the uterine cavity, then cleaning is required. In this case, vacuum aspiration, hysteroscopy and washing of the uterus with antiseptics are used. When washing, all the pathological contents come out, it ceases to be absorbed into the blood, so the woman’s well-being improves. After natural childbirth, washing is performed no earlier than 4-5 days, and after cesarean section – on 6-7 days.
It is imperative to treat endometritis that develops after childbirth, as this is a serious pathology that poses a threat to life.
Prevention of endometritis

To prevent the development of endometritis, the following recommendations must be observed:
Compliance with hygiene rules. A woman should wash herself every day.
Use of condoms during intimacy. This allows not only to protect against infection, but also to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
Timely treatment of diseases that are sexually transmitted. Therapy should take place under medical supervision.
Passing the study and passing tests before any intervention in the gynecological field. If a pathogenic flora is detected, then first you need to get rid of it, only after that proceed with the operation.
Prophylactic course of antibiotics after an abortion and diagnostic procedures associated with the risk of infection. The drugs are most often taken once.
Planned visit to the gynecologist. All women should undergo an examination by a gynecologist once every six months, take tests, and perform an ultrasound scan. This will allow time to identify endometritis and prescribe treatment.
Control over the genitals during the setting of the spiral. Often, endometritis develops in the first year after the placement of the intrauterine device. Therefore, if unusual symptoms appear, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination. No less dangerous in terms of the development of endometritis is the long-term use of an intrauterine device.
Is pregnancy possible after endometritis?

It is possible to get pregnant after endometritis if the disease is treated qualitatively. Absolute infertility is observed only after a severe form of the disease, when the woman’s uterus is removed. There are many cases when patients who underwent purulent endometritis became happy mothers.
In order to increase the chances of a successful conception, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first sign of inflammation of the uterus.
You can reduce the threat of miscarriage if you follow the recommendations of specialists:
Even at the planning stage of pregnancy, you need to treat the disease. This applies not only to acute, but also to the chronic form of endometritis.
After the onset of pregnancy, you need to go to an appointment with a gynecologist. A woman should visit a doctor throughout the entire period of bearing a baby.
Chronic endometritis is often asymptomatic. It can only be identified through analysis. Therefore, sometimes it happens that a woman learns about her diagnosis only after conception. In fact, chronic endometritis allows you to become pregnant, although it significantly reduces the risk of becoming a mother. Moreover, the likelihood of miscarriage and other complications increases. Therefore, often pregnant women with endometriosis are hospitalized. This allows you to maintain the health of the expectant mother and child.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to take vitamins recommended by the doctor. It is important to observe moderate physical activity and avoid stress.
Endometritis therapy is carried out in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. The doctor selects the woman the safest antibacterial drugs. If the infection is not treated, then the fetus will be more harmed than from drugs. In parallel, the pregnant woman will have to take eubiotics, antiplatelet agents, hormones that increase the level of estrogen in the blood.
During pregnancy, physiotherapeutic methods can be prescribed, including: acupuncture, plasmapheresis, treatment with leeches, etc.
If necessary, a woman artificially compensates for the deficiency of hormones.
Against the background of endometritis, the likelihood of miscarriage increases. Most often this happens at 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. Therefore, you need to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, take medicines, and minimize physical activity. These activities will help save the child.









