Contents
Logarithm of a number is the power to which one number must be raised to obtain another.
If the number b to the extent y equals x:
by = x
So the logarithm of the number x by reason b is y:
y = logb(X)
For example:
24 = 16
log2(16) = 4
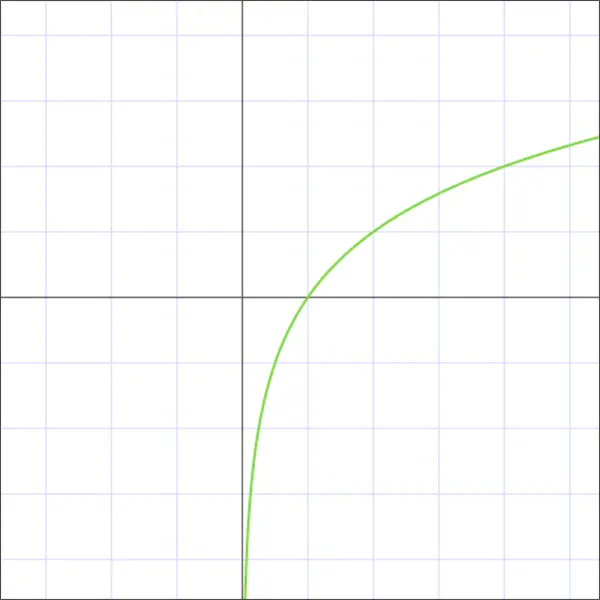
Logarithm as inverse function to exponential
logarithmic function y = logb(x) is the inverse function of the exponential x=b y.
So if we calculate the exponential function of the logarithm x (x > 0), it will turn out:
f (f -1(x)) = blogb(x) = x
Or if we calculate the logarithm of the exponential function х:
f -1(f (x)) = logb(bx) = x
Natural logarithm (ln)
The natural logarithm is the base logarithm е.
ln (x) = loge(x)
Number e is a constant that can be defined as a limit:
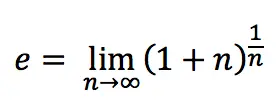
Or so:
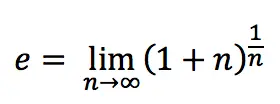
Inverse logarithm
Inverse logarithm (or antilogarithm) of a number n is a number whose base logarithm is a is equal to the number n.
ant logan = an
Table of properties of logarithms
Below are the main properties of logarithms in tabular form.
» data-order=»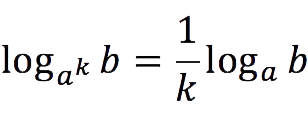 «>
«>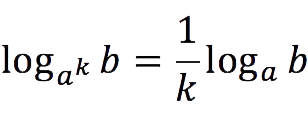
» data-order=»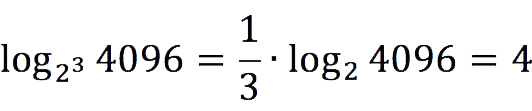 «>
«>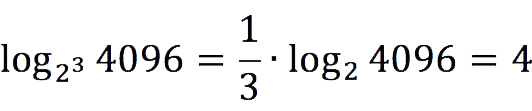
» data-order=»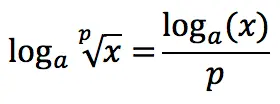 «>
«>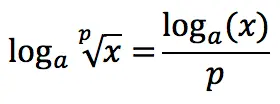
» data-order=»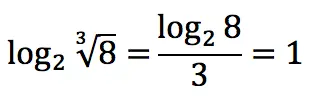 «>
«>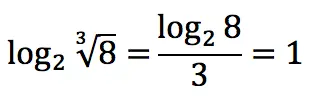
| Property | Formula | Example | |||||
| Basic logarithmic identity | Logarithm of the product | Division/quotient logarithm | Logarithmic degrees | Logarithm of a number to the base in the degree | |||
| root logarithm | |||||||
| Rearranging the base of the logarithm | Transition to a new foundation | Derivative of the logarithm | Integral logarithm | Logarithm of a negative number | Logarithm of a number equal to the base | Logarithm of infinity | Логарифмическая функция Функция, которая определена формулой f(x)=loga(x) – это логарифмическая функция с основанием a. При этом a>0, a≠1. График функции логарифмаГрафик логарифмической функции (логарифмика) может быть двух типов, в зависимости от значения основания a:
Leave a commentОтменить ответ |