Deer cobweb (Cortinarius hinnuleus)
- Division: Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes)
- Subdivision: Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes)
- Class: Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes)
- Subclass: Agaricomycetidae (Agaricomycetes)
- Order: Agaricales (Agaric or Lamellar)
- Family: Cortinariaceae (Spiderwebs)
- Genus: Cortinarius (Spiderweb)
- Type: Cortinarius hinnuleus (Deer webweed)
- Cobweb red-brown
- Deer cobweb
- Agaricus hennuleus Sowerby (1798)
- Telamonia hennulea (Frieze) Wishes (1877)
- Gomphos hinnuleus (Fries) Kuntze (1891)
- Hydrocybe hinnulea (Fries) M. M. Moser (1953)

Deer cobweb is an agaric, belongs to the genus Cortinarius, subspecies Telamonia and section Hinnulei.
Current title – Curtain Fries (1838) [1836–38], Epicrisis systematis mycologici, p. 296.
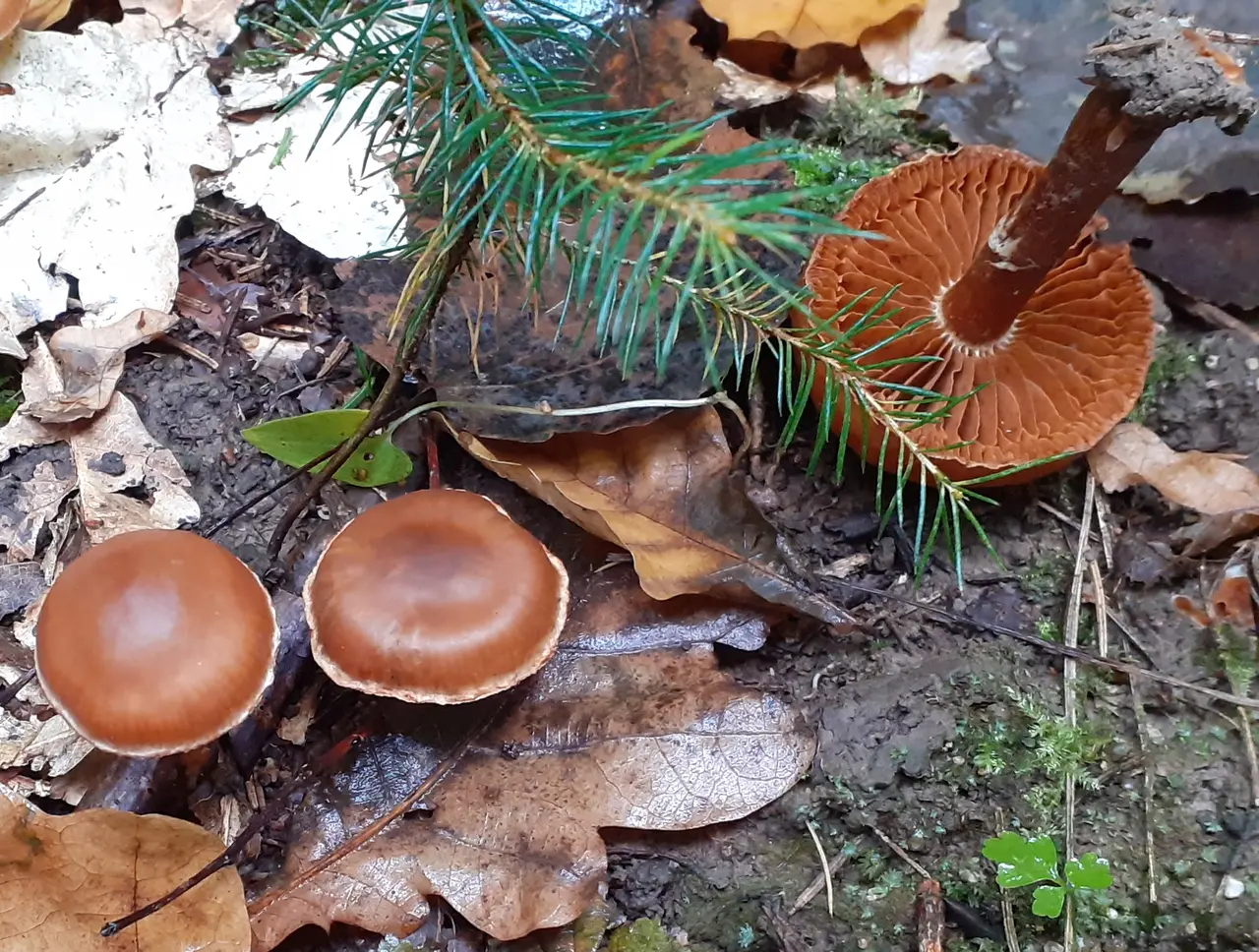
Deer cobweb is one of the most common and at the same time variable species. The mushroom got its name for its characteristic reddish-brown hue, reminiscent of the color of the skin of a young deer. But it should be borne in mind that the color is highly dependent on the humidity of the environment.
Inside the Genus Cortinarius (Spiderweb) has its own classification. In it, Cortinarius hinnuleus is located in
- Subspecies: Telamonia
- Section: Hinnulei
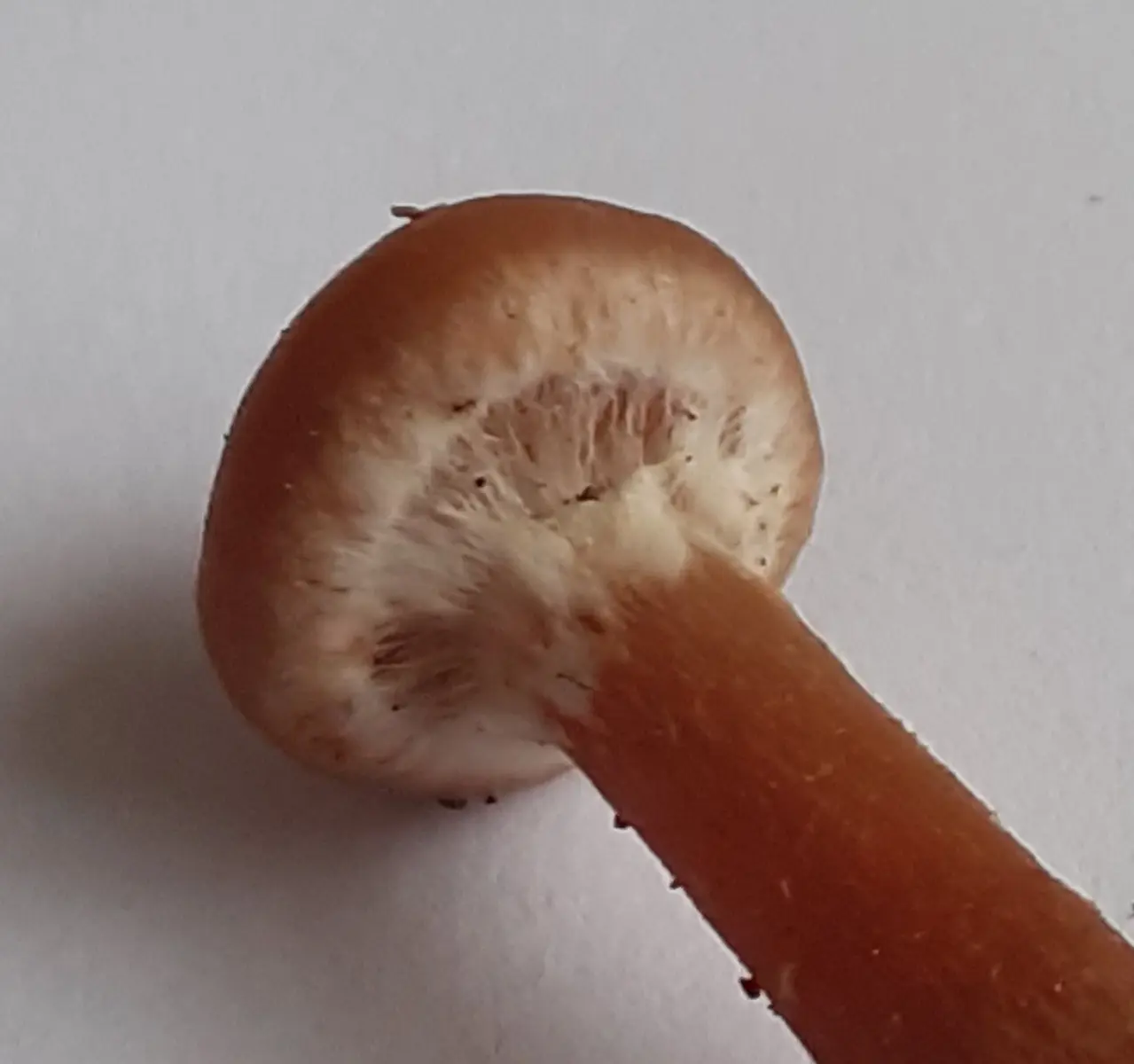
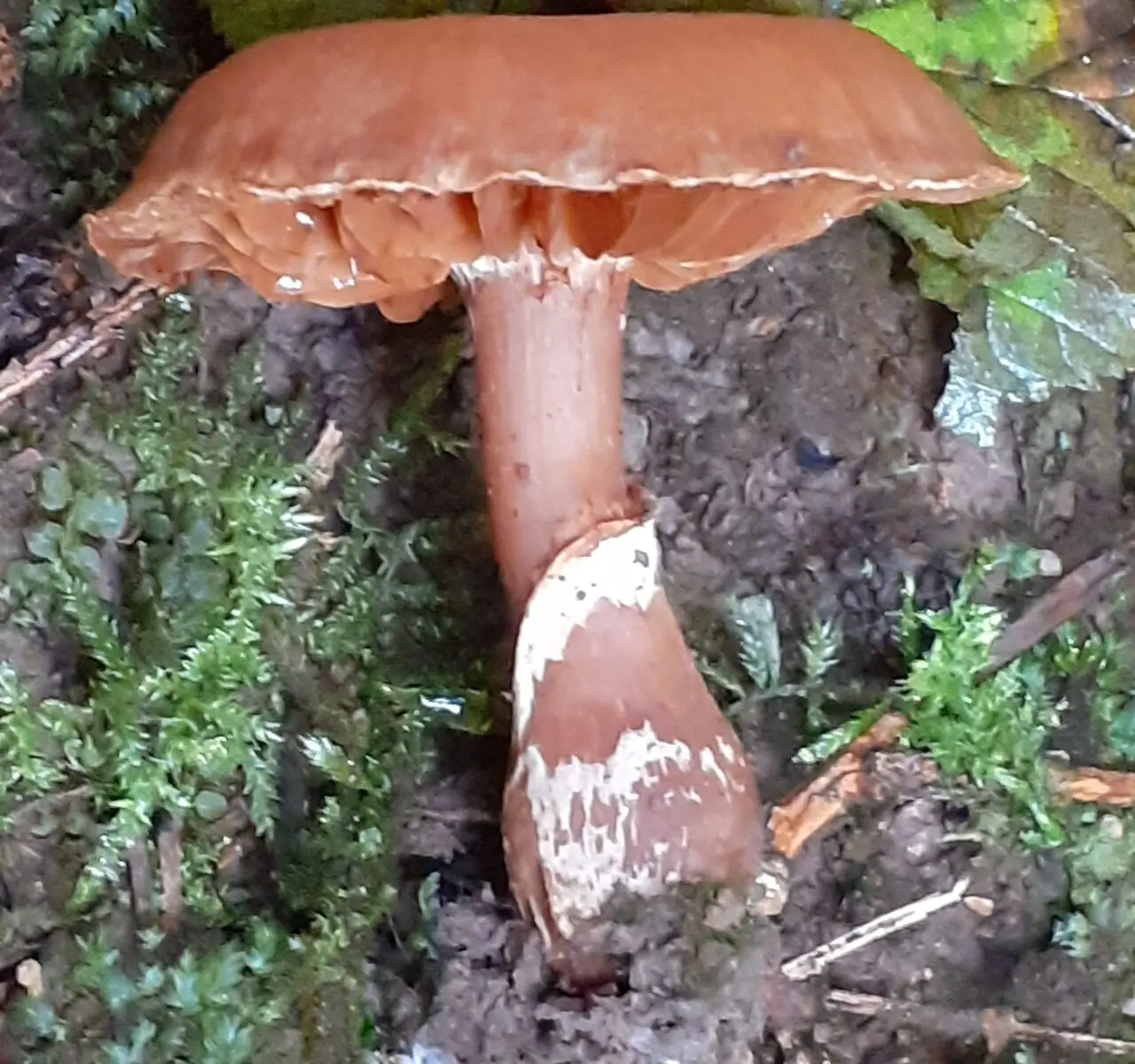
head initially bell-shaped, convex, with a folded edge, later convex-prostrate, with a flat lowered edge, smooth, moist in wet weather, hygrophanous, usually with a tubercle in the center, 2–6 (9) cm in diameter.
The color of the cap is yellow, ocher yellow, orange, cream or tan to reddish brown, especially in the center. The cap is lighter in dry weather, darker when wet, yellow-dark brown, shiny, turns red when dry and forms radial stripes in the form of rays.
The surface of the cap may crack, often showing the remains of a white cobweb along the edge, sometimes zonal; in older specimens, the edge is wavy or uneven. The skin of the cap slightly extends beyond the edge of the plates; on its surface, longitudinal dark spots may be noticeable in places of bites or insect damage, sometimes the hat becomes completely spotted.

The cobweb cover is white, later brownish, abundant, at first forming a thick shell, then remaining in the form of a clearly visible ring.
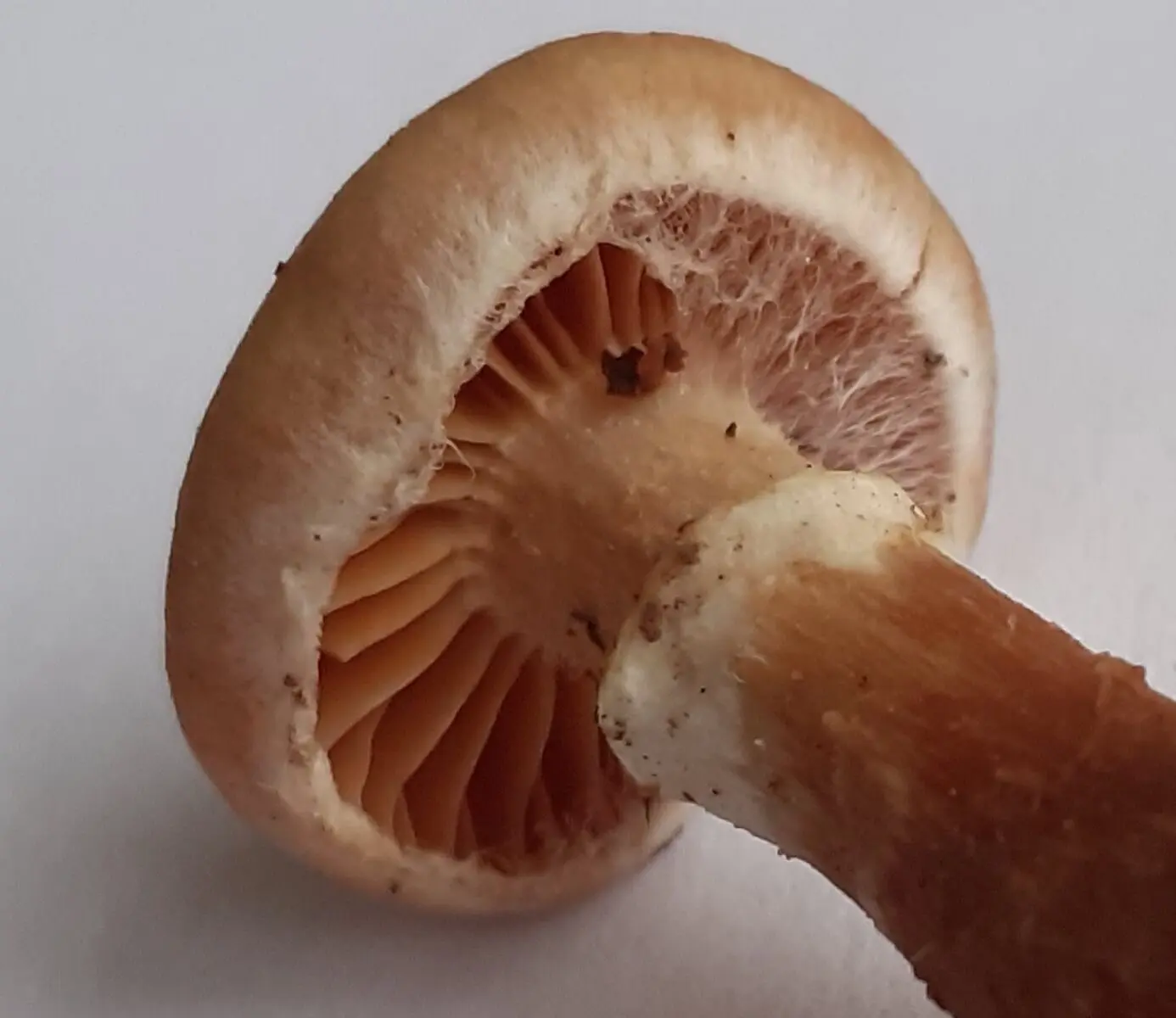

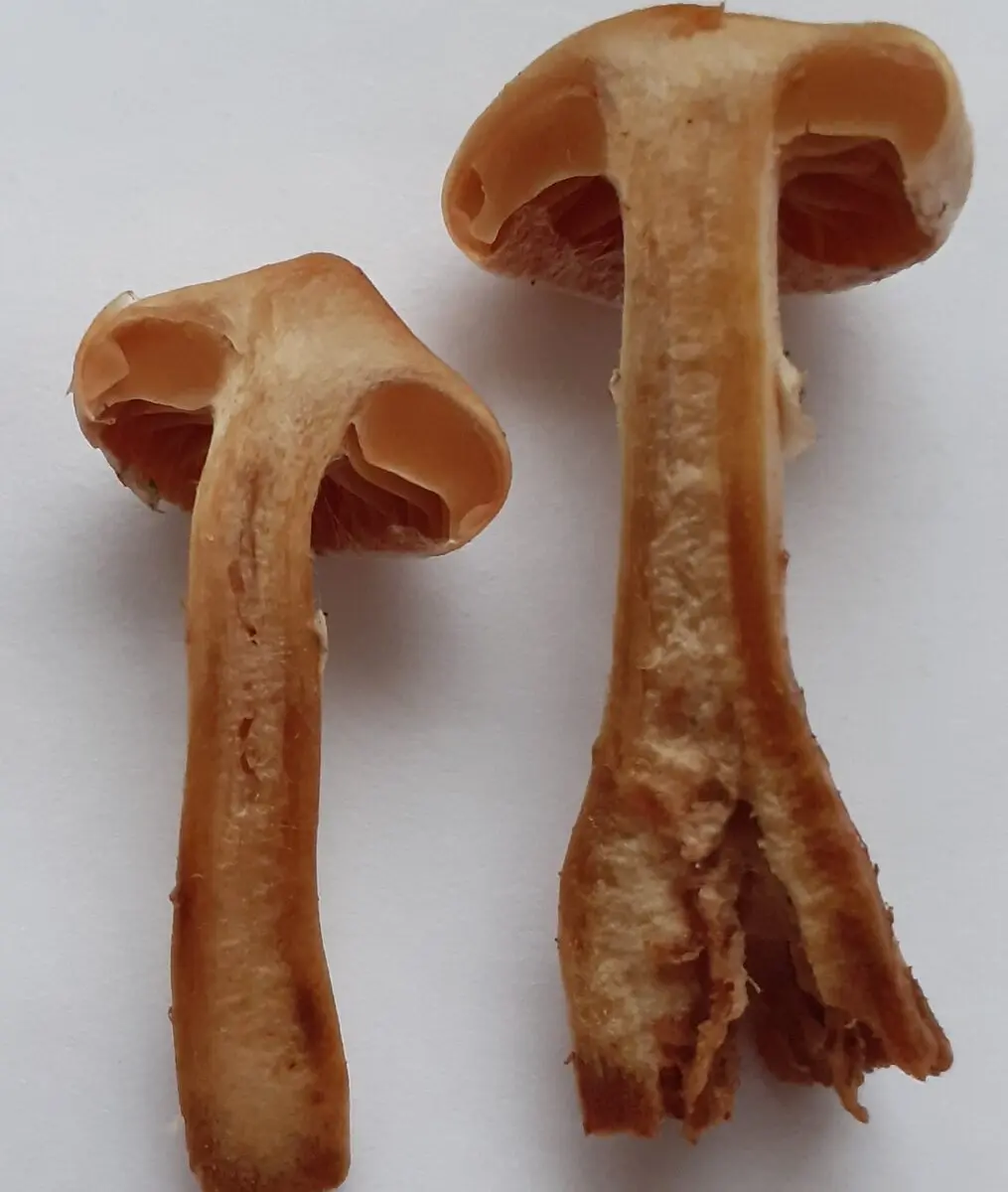
Records sparse, thick, wide, deeply arched, adnate with a tooth or slightly descending on a stalk, the color of a cap, with an uneven edge, in young mushrooms with a lighter edge. The color of the plates varies from pale ocher, light ocher brown, orange, brownish apricot, yellow-brown in youth to brown and dark brown in mature specimens. Some authors mention a violet (pale lilac) shade of plates in young mushrooms.
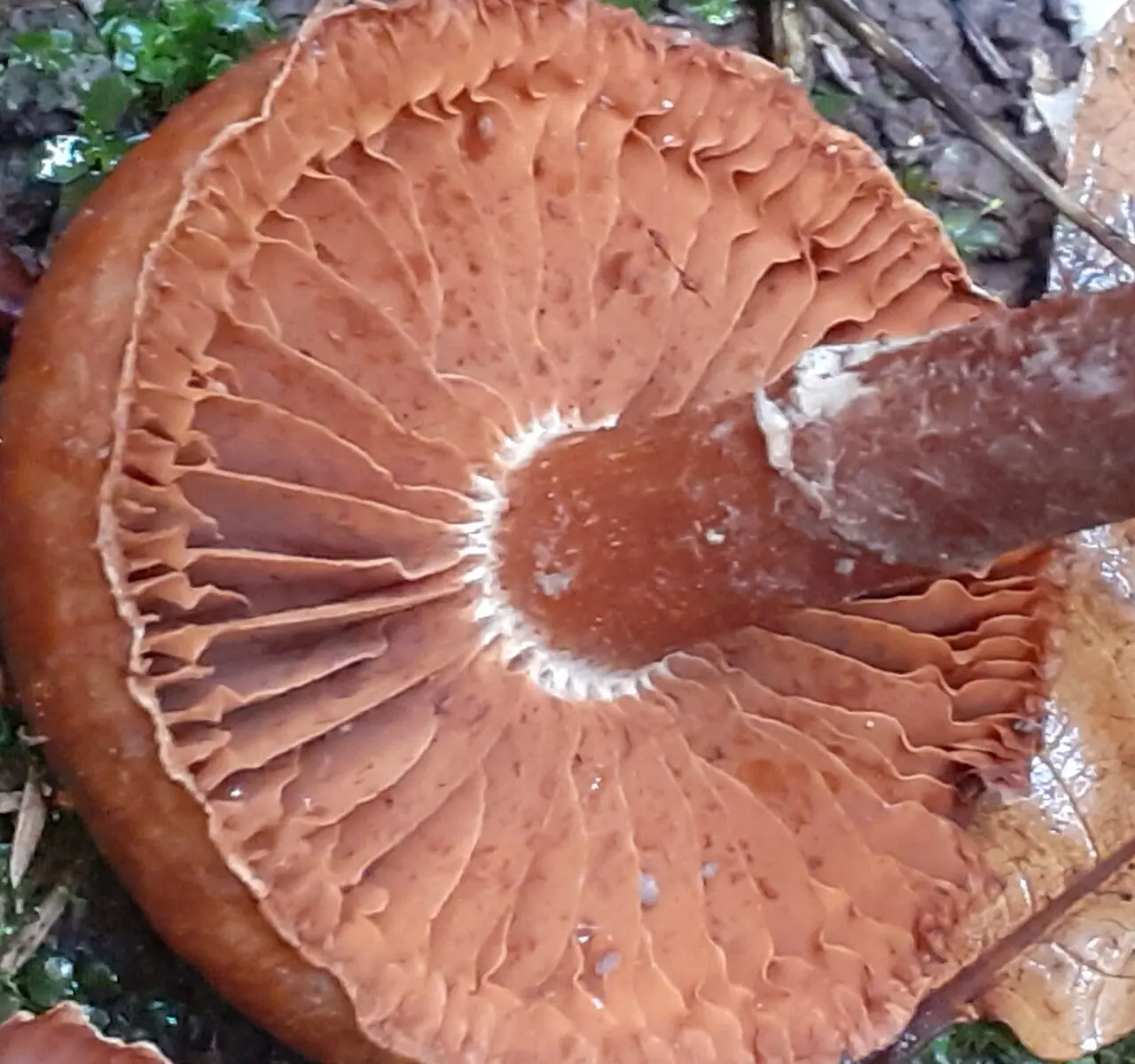

Leg mushroom 3–10 cm high, 0,5–1,2 cm thick, fibrous, cylindrical or club-shaped (i.e., slightly expanded towards the base), made, may be with a small nodule, partially immersed in the substrate, white, whitish brown, yellowish or reddish brown, ocher-red, brown, later with a reddish tinge, whitish at the base.
In young mushrooms, the stalk has a characteristic white membranous ring, below which (or along the entire length) it is covered with the remains of a white silky coverlet, subsequently usually with or without a distinct annular zone, with one or more white cobweb belts.

Pulp creamy, yellowish-brown (especially in the cap) and reddish, pale brownish (especially in the stalk), in young mushrooms the flesh at the top of the stalk may be with a purple tint.

The fungus has a distinct, unpleasant earthy smell, dusty or musty, with a hint of radish or raw beets.
The taste is unexpressed or at first soft, then slightly bitter.
Споры 8–10 x 5–6 µm, elliptical, rusty-brown, strongly warty. Spore powder is rusty brown.
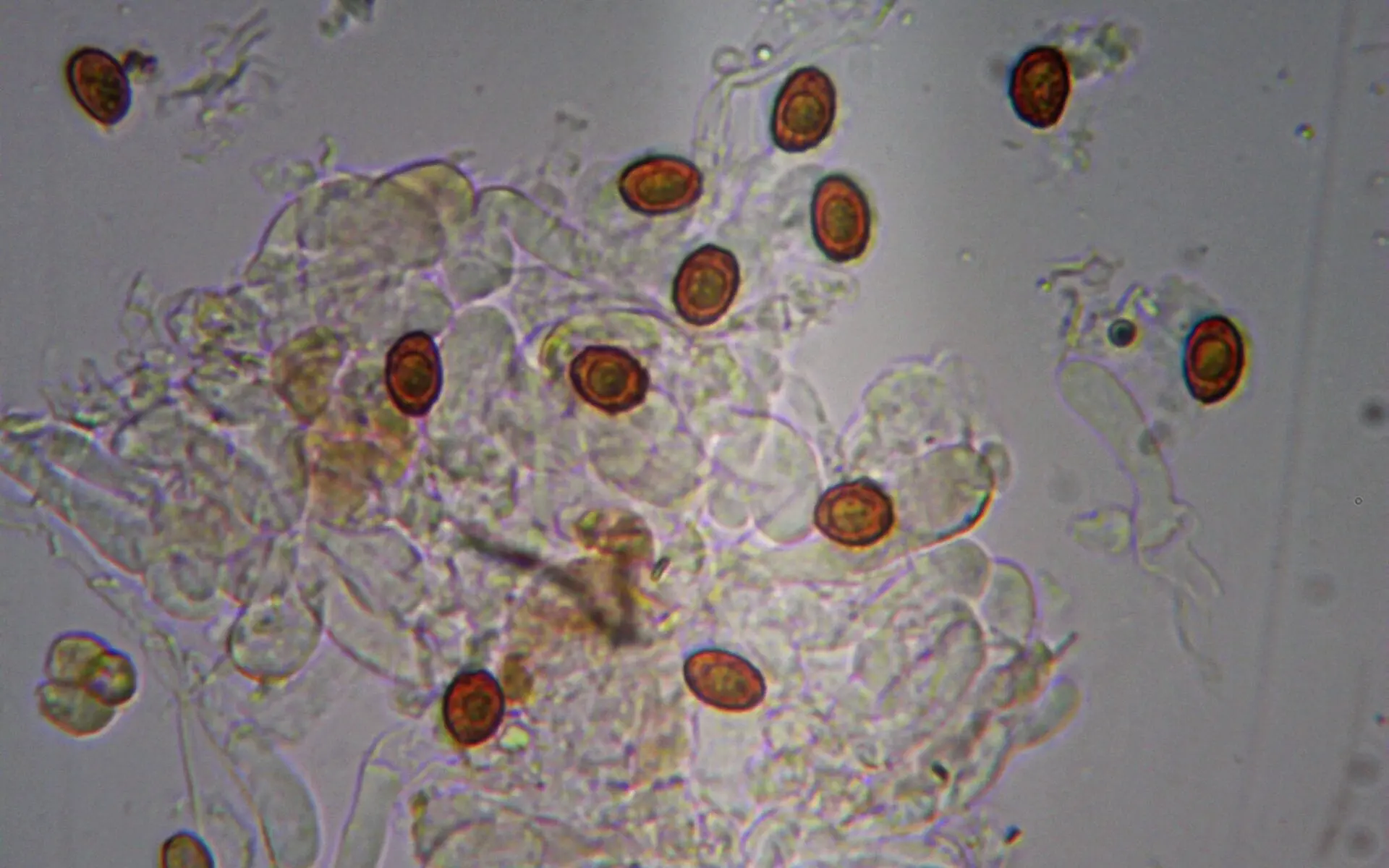
Chemical reactions: KOH on the surface of the cap and flesh is brown.
It grows mainly in deciduous, sometimes in coniferous forests, found under beech, oak, hazel, aspen, poplar, birch, hornbeam, chestnut, willow, linden, as well as under larch, pine, spruce.
It bears fruit quite abundantly, in groups, sometimes growing together with legs. Season – late summer and autumn (August – October).
Inedible; poisonous according to some sources.
Characteristic distinguishing features – removed plates, a highly hygrofan cap and a persistent earthy smell – make it possible to distinguish this fungus from many other cobwebs. However, there are several outwardly similar species.
Conical curtain – a little smaller.
Cortinarius safranopes – also a little smaller, the flesh at the base of the leg becomes purple-black when reacting to alkali.
Other representatives of the section Hinnulei and the subgenus Telamonia may also be similar to the deer cobweb.









