Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
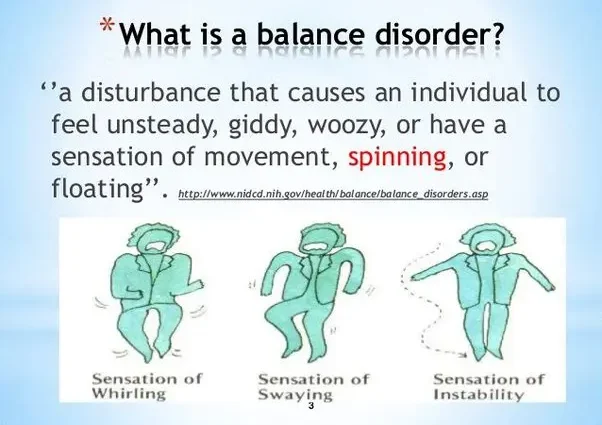
Imbalance is the trouble with balance, dizziness and the floor ‘spinning’. Dizziness may occur as a result of, for example, a sudden change of position from sitting or lying down to standing, but it can also be a sign of more serious discomfort. They often appear in patients with brain cancer.
What are imbalances?
Balance disorders and accompanying dizziness is a very common condition that occurs mainly in adults. It is a feeling of instability and ill-positioning in space, usually accompanied by dizziness. The equilibrium system consists of, among others, the organ of vision, the labyrinth system and the sense of deep feeling, which allows us to assess the position of our limbs at present, even when we have closed eyes or are in the dark. All information from these various systems is transported to the central nervous system. Then, excitatory impulses are sent to the skeletal and oculomotor muscles, which stabilizes the eyesight and maintains balance when standing or lying down.
Types of dizziness
The following division of vertigo results from the fact that it is a consequence of disorders of the labyrinthine system, which is divided into the central and peripheral parts. The labyrinth is a peripheral part, while the central part consists of the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem, the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum and their connections.
We can distinguish:
1. Classic vertigo – otherwise known as systemic. Dizziness can be defined as two different complaints. On the one hand, they can create the illusion that we are spinning and floating in relation to the world around us, without an external stimulus to move. They come on suddenly and carry with them other symptoms such as nausea and even vomiting. The patient describes his symptoms without any problems;
2. Non-systemic dizziness – the sick person feels unstable, he lacks balance and confidence in walking, he is still afraid that he will fall down. This type of dizziness is difficult for the patient to describe.
Balance disorders – causes
Balance disturbance is accompanied by dizziness, which occurs suddenly when changing position and looking to one side. The patient has a spinning sensation. Such disorders are one of the symptoms accompanying the damage to the labyrinth. Dizziness may be caused by fainting, then patients also complain about scotomas in front of their eyes and ringing in the ears. Also, drinking too much alcohol and nicotine or inhaling exhaust fumes can make you feel dizzy. In addition, balance disorders may result from low visual acuity (especially in the elderly) and as a result of damage to deep sensation, paresis or motor slowdown.
According to epidemiological studies, the most common causes of vertigo are:
- disorders in the inner ear,
- arterial hypotension,
- neurological ailments,
- side effects of medications taken.
Other causes of disorders may be psychological or psychiatric abnormalities. Among all the factors that cause dizziness and imbalance, only a few percent of symptoms pose a threat to health and life.
The most common diseases that cause vertigo and dizziness are listed below.
1. Ear diseases:
- external: foreign body, wax;
- middle: cholesteatoma and Eustachian tube inflammation;
- internal: all kinds of injuries, noise, labyrinthitis, motion sickness, toxic effects of drugs, Menier’s syndrome.
2. Diseases of the nervous system:
- inflammation of the vestibular nerve,
- multiple sclerosis,
- migraine,
- epilepsy,
- depression,
- anxiety syndromes,
- injuries,
- tumor attacking the XNUMXth nerve,
- cerebral vascular diseases: infarction or hemorrhage of the brain stem / cerebellum, insufficiency of vertebrobasilar circulation, transient ischemic attacks.
3. Systemic disorders:
- menopause,
- arterial hypertension,
- hypertension,
- low sugar level,
- aging.
Symptoms of imbalance
Physiological dizziness should not cause anxiety in the patient. The situation is different when the vertigo occurred for the first time and was not influenced by any external factor. A doctor should be consulted if there is additional pain, numbness in one half of the body or weakness in the limbs.
Other symptoms of Imbalance Syndrome are nausea, sometimes vomiting, weakness or tinnitus. The neurasthenics complain of constant dizziness.
Diagnostics of imbalances
It happens that balance disorders and dizziness are difficult to describe by the patient. On the other hand, during a medical interview, the doctor asks about the frequency of dizziness recurrences and their duration. It is also important whether tinnitus, nausea and vomiting co-exist. The specialist should also determine whether the symptoms worsen during movement and decrease when motionless. It is also important to know if the dizziness decreases when the patient closes their eyes? It is the doctor’s responsibility to gather information from you about the medications you are taking, as some of them can make you feel dizzy.
The medical history makes it possible to distinguish between systemic and non-systemic dizziness, which in turn helps in selecting further diagnostic tests.
During the examination, the doctor measures the patient’s arterial pressure and checks if there is nystagmus, if so: is it bilateral or unilateral? This is important because the type of nystagmus may suggest damage to the cerebellum, brain stem, or labyrinth. In addition, the assessment is made of the patient’s balance (Romberg’s test) as well as his gait and staggering. If a patient is suspected of having mild paroxysmal positional dizziness – an examination is carried out, which consists in placing the patient on a couch with the head hanging beyond it and turned to the side.
An ENT consultation is needed in patients with vertigo. The laryngologist will assess any changes in the external ear and perform (if necessary) a test of the labyrinth excitability and hearing assessment. A visit to a neurologist is necessary when the basis of imbalance disorders are neurological ailments.
Imaging tests are also performed in diagnostics, especially if there are signs of focal brain damage. The doctor then orders MRI and computed tomography, thanks to which it is possible to reveal:
- MS (multiple sclerosis)
- vascular causes of dizziness,
- tumor of the VIII nerve,
- post-traumatic changes and other ailments of the nervous system.
Some patients undergo an EEG or electroencephalographic test – if there are suspicions that epilepsy is the cause of vertigo.
Balance disorders – treatment
Treatment of imbalances is established after a specialist examination, which should be performed as soon as possible. Dizziness also occurs in patients with vascular disorders, tumors of the brain and cerebellum, therefore balance disorders require consultation and diagnosis of a doctor who excludes possible risks.
Treatment of balance disorders is symptomatic and temporary. It is important to alleviate or remove discomfort. Causal treatment is possible depending on the factor that caused the ailment.
You can also exercise your balance, e.g. with the Airex Balance Pad for training, which you can buy at an attractive price at Medonet Market.