Contents
- Where do roundworms come from in children?
- What happens after the eggs of the parasite enter the child’s body?
- Symptoms of ascariasis in children
- What do roundworms and their eggs look like?
- What to do if roundworm comes out?
- What is ascariasis?
- Consequences and complications of ascariasis
- Diagnosis of ascariasis in children
- Treatment of ascaris in children
- Can ascariasis recur after treatment?
- How to prevent ascariasis in a child?
Ascariasis is the defeat of the body of children and adults by a helminth (human roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides). Humans are both intermediate and definitive hosts of this parasite. The disease is seasonal, with the greatest prevalence in the warm season. Symptoms of ascariasis in children are associated with the migration of this parasite in the body. Most often, the symptoms of ascariasis appear in the gastrointestinal tract, less often in the respiratory system.
Where do roundworms come from in children?

Infection of children with ascariasis occurs by the fecal-oral route. A person in whose body sexually mature individuals produce fertilized eggs excretes them along with feces. Children become infected with such eggs through soil, contaminated water, food, and dirty hands.
Ways of infection:
Contact with infected children in the children’s team;
Toys;
Door handles in public places, in transport;
Banknotes and coins;
Vegetables and fruits with soil microparticles;
Transfer of Ascaris eggs by insects.
What happens after the eggs of the parasite enter the child’s body?

Once in the intestines, roundworm eggs from the duodenum 12 with blood flow are carried throughout the body. They penetrate into the lungs, into the liver, into the right parts of the heart. Once in the lungs through the pulmonary circulation, the larvae enter the alveoli. Then the larvae rise into the larynx, into the pharynx, are swallowed again and enter the intestine for the second time. Such a roundworm cycle takes 2-3 weeks.
In the small intestine, roundworms go through a stage of growth and maturation to sexually mature individuals. If a sexual partner is found for them, soon the female excretes about 200 thousand eggs with feces. These eggs need to mature in the soil within 1-2 weeks under favorable conditions (temperature from +16 to +32°C). Then they find a new host and the cycle of development repeats again.
Symptoms of ascariasis in children

In infants, ascariasis practically does not occur, since they are protected by specific antibodies of the mother through breast milk. Accidental entry of parasites into the body of children under one year old ends with their removal. From 2-3 to 10 years old, children become active, their diet expands, and they most often get helminthic invasion.
Symptoms of ascariasis in children:
Stunting, underweight,
Delayed physical development
Remaining in mental and mental development during mass invasion;
Weakness, lethargy, frequent headaches;
Manifestations of allergies;
With complications – pneumonia, hyperthermia, cough with sputum;
Occasionally, symptoms such as restless sleep, photophobia, and abdominal pain may occur.
What do roundworms and their eggs look like?
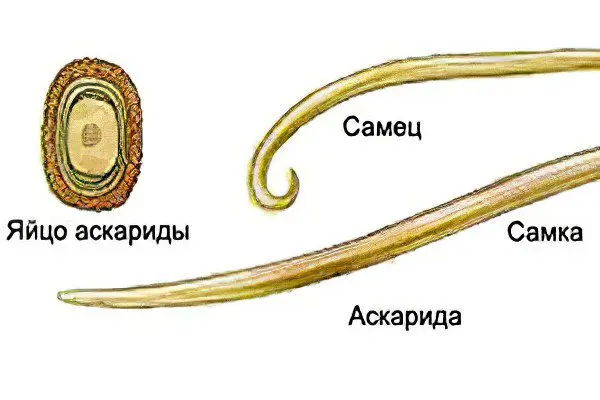
The human roundworm belongs to the roundworms. It has a pink color, up to 25 cm in males and 40 cm in females. The thickness of the roundworm is 3-5 mm, the mature individual is covered with a cuticle. This shell protects the helminth from gastric juice and enzymes that process protein. The main habitat of roundworm is the small intestine. The parasite does not attach itself to its walls, it does not have scolexes for fixing in the mucous membrane. In the intestinal lumen, the helminth is held by constant movement against the movement of food.
The life span of roundworm is 2 years, then the parasite dies. If re-infection does not occur, ascariasis in rare cases ends spontaneously. Eggs of sexually mature individuals are yellow or yellow-brown in color, 50 to 70 microns in size. They can only be seen under microscopic examination.
What to do if roundworm comes out?
The released copy of the helminth should be placed in a container with a lid and shown to a specialist. If it is impossible to transfer the roundworm, you need to photograph it. Accurate data on the presence of the parasite in the child’s body will help to make an emergency diagnosis and timely start of treatment.
What is ascariasis?

Classification of ascariasis according to its localization:
With intestinal complications;
With complications in other organs;
Ascariasis of unspecified etiology.
Classification of helminthiasis depending on the stage of development of the disease:
Acute stage;
intestinal stage;
stage of complications.
Consequences and complications of ascariasis

If for most adults this type of helminthiasis does not pose a threat to life or health, then the helminthic invasion of the children’s body has serious consequences.
Complications of ascariasis:
Intestinal obstruction. Accompanied by pain in the abdomen, constipation, bloating, vomiting with the smell of feces. It occurs due to the fact that the lumen of the small intestine is closed by a ball of ascaris, it can be complicated by perforation of the intestinal wall and peritonitis.
Appendicitis. Occurs with the accumulation of ascaris in the caecum, manifested by pain and fever.
Pneumonia. Appears after the larvae stay in the lungs for 10 days. Damaged capillaries and alveoli are affected by a secondary bacterial infection.
Asphyxia. Occurs when the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is irritated by larvae or during reflex spasm of smooth muscles.
Atypical location of roundworms. Occurs during the migration of larvae with blood flow into the sinuses, middle ear, lacrimal canal, genitals.
liver abscess. Occurs as a result of ingestion of larvae and adults with venous blood flow, damaging the mucous membrane.
Mechanical jaundice. Bile stasis appears when the bile ducts are blocked by large helminth specimens during migration from the duodenum.
The chronic course of the disease, which is not manifested by serious complications, exacerbates the course of bacterial infections in children, leads to growth retardation and mental development.
Diagnosis of ascariasis in children

It is possible to differentiate ascariasis in children from diseases similar in symptoms when conducting an accurate diagnosis. The doctor tries to collect a preliminary history, determine the stage of development of helminthiasis.
Methods for diagnosing ascariasis in children:
Complete blood count – when larvae migrate to the lungs, an increase in the concentration of leukocytes in the blood is noted;
Analysis of blood biochemistry – the fraction of eosinophils, which are the first to react to helminthic invasions, increases;
A blood test for antibodies to ascaris is an accurate serological diagnostic method; specific antibodies to the parasite Ascaris lumbricoides are formed almost immediately after ascaris larvae enter the body;
Sputum analysis – is carried out with a pulmonary form of ascariasis in children, with an intense cough, ascaris larvae and a large number of eosinophils are found in the sputum;
Fecal analysis – during microscopic examination, yellow-brown fertilized ascaris eggs are found in the excrement; at the larval stage of parasite development, fecal analysis may be false-negative;
Urine analysis – the release of volatile fatty acids can indirectly indicate the presence of ascaris, and even in the larval form.
Chest x-ray – within 10 days with a pulmonary form of invasion, it can show characteristic changes, a volatile infiltrate of the lung;
X-ray of the abdominal cavity – used in differential diagnosis with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, can reveal intestinal obstruction from a large number of roundworms in the intestinal lumen;
Anthropometry is used in children, since in the chronic form of ascariasis, especially with mass invasion, the parasite takes away nutrients and vitamins from the child’s body.
Treatment of ascaris in children

Treatment of ascaris in children is reduced to taking anthelmintic drugs. In no case should you independently select one or another remedy, only a doctor can do this.
First, not every drug can be used to treat children. Secondly, the dose for them is selected individually. Thirdly, all anthelmintic drugs have a toxic effect on the body, so self-medication can bring significant harm to health.
If roundworm is diagnosed in a child in the migration phase, then desensitizing drugs and anthelmintic drugs are shown to him. Most often, thiabendazole (Mintezol) or mebendazole (Vermox) is prescribed in childhood. They have a wide spectrum of activity and have a detrimental effect on roundworm larvae. If the child has severe pulmonary symptoms, then a dose of bronchodilators and corticosteroids is selected for him.
When roundworms in the intestinal stage are detected in children, the following drugs are prescribed for him to choose from:
Vermox (Mebendazole).
Decaris (Levamizole).
Pyrantel (Combantrin).
Piperazine.

These drugs are highly effective and often one course of treatment is enough to save the child from invasion. 30 days after treatment, a re-diagnosis of the disease is necessary.
If a child suffers from acute ascariasis, regardless of the purpose of the drug, antihistamines are an obligatory component of treatment. They stop allergic reactions resulting from the release of toxins by helminths. For sensitization, calcium gluconate, calcium chloride, ascorbic acid, glucocorticosteroids are used.
Drugs for the treatment of ascariasis:
Mintezol. The daily dose is 25 mg / kg / day, it is divided into 3 doses, the course of treatment is 5 days.
I think. The daily dose is 10 mg / kg / day, it is divided into 3 doses, taken during the day, with a massive invasion, the course takes 2-3 days.
Decaris (Levamisole). The daily dose is 2,5 mg / kg / day, it is divided into 2-3 doses, taken during the day.
Kombantrin. It is used in the form of tablets according to age and body weight.
Vermox (Mebendazole). The daily dose is 25-50-100 g / day, it is divided into 2 doses, the course of treatment is 3-4 days. It is not used in children under 2 years of age, as well as in case of mass invasion, as it can cause ascaris to enter the lungs, into the pharynx, stop intestinal motility, vomiting, and acute pain.
During the treatment of the child, it is desirable to transfer to a dietary diet, with food rich in vitamins and proteins of animal origin. You need to give up simple carbohydrates (sweets, flour and confectionery), fatty foods.
To correct the intestinal microflora, patients are recommended to take Bifiform, Linex and other prebiotics and probiotics. Enterosorbents prescribed after a course of anthelmintic therapy. They are aimed at reducing the desensitization of the body. These can be drugs such as Polyphepan, White activated carbon, Polysorb, etc. In addition to specific drugs, enzymes, multivitamins, and iron preparations are prescribed (if anemia is present).
Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment is carried out 3 weeks after its completion. In laboratory conditions, feces are examined three times. The prognosis for the treatment of ascariasis is favorable, special care should be taken in the treatment of helminthic invasion of infants. Asphyxia after ascaris migration into the respiratory tract can be fatal, it is stopped during urgent surgical intervention. As a rule, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Complications are rare, but in emergency cases, surgery may be required.
Can ascariasis recur after treatment?
Ascariasis once transferred in children cannot serve as a guarantee against re-infection. When eggs enter the gastrointestinal tract, a new cycle of development of the parasite and the appearance of symptoms of the disease begin. Specific immunity to ascariasis is not formed either in children or in adults.
How to prevent ascariasis in a child?

It is very important to carry out the prevention of ascariasis in children, since after treatment it is easy to get a helminthic invasion again. In the habitat of the child, even after thorough disinfection, parasite eggs could remain. Therefore, in order to protect family members and the child himself, eggs and roundworm larvae should not be allowed to enter the body.
Preventive measures against ascariasis:
Early diagnosis and treatment of patients. At the slightest suspicion of helminthiasis, you should take a stool test, make a test sample to detect antibodies to ascaris in the blood, undergo treatment under the guidance of a helminthologist or infectious disease specialist.
Thorough hand washing after contact with sand and earth, before eating, after using the toilet. This route of infection is most common among children.
Eating only carefully processed foods: fruits, vegetables, berries, herbs, or appropriate heat treatment of dishes for baby food (at least 50 ° C), drinking exclusively boiled water.
Change of sand in children’s sandboxes, its processing, regular digging and loosening for solar sanitation.
Engineering soil protection from faecal contamination during the construction of childcare facilities, filtration and neutralization of sewage, cleaning of cesspools.
Composting of faeces for 4 years prior to use as fertilizer.
Fight against insects – carriers of roundworm eggs.
The doctor notes:

The main source of ascariasis is contact with soil contaminated with helminth eggs. Contact with pets, eating fish or meat cannot cause this infestation.
When expelling ascaris, it is necessary to monitor the condition of children after taking the medicine. Dead parasites can accumulate in the intestinal lumen in large balls, cause intestinal obstruction, accompanied by pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Spontaneous death of roundworm in a child’s body after 2 years of stay does not guarantee a complete cure. The constant ingestion of parasite eggs constantly renews the helminth colony.
Pathologies of the intestines, skin, lungs, the appearance of an allergic reaction in children are a reason for examination for ascariasis and other helminthiases. The clinical picture of these pathologies does not have its own specifics, it can be disguised as other diseases. The sooner an accurate diagnosis is made, the sooner recovery will come.









