Contents
The immune system protects the human body from harmful bacteria and viruses. Allergy leads to the fact that the body begins to fight even with absolutely harmless substances. This happens due to a failure in the production of immunoglobulin. Its level in the blood rises, and, consequently, sensitivity to allergens increases due to the production of histamine.
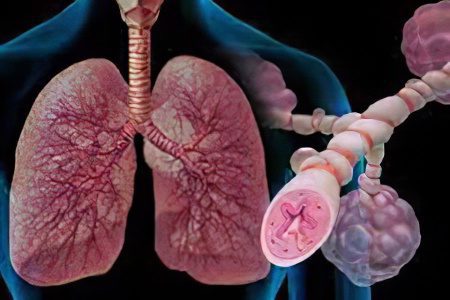
allergic asthma – this is the most common form of asthma, expressed by hypersensitivity of the respiratory organs to certain allergens. Inhaling the allergen, the body receives a signal about the irritant, the reaction of the immune system is triggered, which is expressed by a sharp contraction of the muscles located around the respiratory tract. This process is called bronchospasm. As a result, the muscles become inflamed and the body begins to secrete mucus, thick and quite viscous.
Each person suffering from allergic asthma experiences approximately the same conditions as in other types: deterioration of health due to physical exertion in cold air, after inhalation of tobacco smoke, dust or strong odors.
Allergens are quite common in the environment, so it is so important to identify the range of main irritants in time, thereby preventing the exacerbation of symptoms and the development of the disease into a more severe form.
Allergic Asthma Symptoms
Symptoms of manifestation of allergic asthma are associated primarily with the work of the respiratory tract, and represent the following features:
the appearance of a cough;
breathing is accompanied by a whistle;
there is severe shortness of breath;
inhalations and exhalations become more frequent;
pain in the chest area;
chest feels tight.
These are the main symptoms that any of the common allergens can cause:
flower pollen (or pollen from trees and plants, for example, common poplar fluff);
mold spore particles;
wool or saliva of animals (particles of skin and feathers of birds belong to the same category);
the presence of dust mite excrement in the environment.
Any contact with an irritant can cause an allergic reaction. For example, a scratch will immediately cause local itching and redness of the skin. In extreme cases, if such a substance enters the human body, a real danger may arise, because. possible rapid onset of anaphylactic shock, which is a serious asthmatic attack.
The mechanism of development of atopic asthma can be triggered not only by allergens. They can cause an attack, and not the allergic reaction itself.
Then the cause of the attack becomes nothing more than irritant particles in the inhaled air:
tobacco smoke;
smoke from a candle (including aromatic), fireplace or fireworks;
contaminated air;
cold air (including during physical activities in the fresh air);
smells of chemicals and their fumes;
perfume aromas;
dust.
The severity of the course of atopic asthma depends on the severity of the symptoms: mild, moderate or severe.
Allergic asthma in children

The manifestation of allergic asthma in a child can be at different age periods, but most often the disease affects the child’s body after a year of life. Allergic reactions of various etiologies are the main risk factor.
Atopic asthma in childhood has an unpleasant feature – it can hide under the symptoms of obstructive bronchitis. It is possible to identify asthma by the number of manifestations of the disease during the year. If bronchial obstruction appears more than four times a year, this is a serious reason to consult an allergist or immunologist.
The specificity of the treatment of atopic asthma in children lies in the paramount importance of inhalations as the main remedy. Such procedures not only help to eliminate the allergen that triggered the mechanism of the disease, but also increase the body’s defenses.
Allergic asthma attack
An attack of allergic asthma should be understood as such a reaction from the human immune system, in which bronchospasm appears in response to exposure to an allergen. It is he who represents an attack as such, accompanied by a contraction of the muscle tissue surrounding the airways. Due to this pathological condition, the muscles become inflamed and filled with viscous thick mucus. At the same time, the supply of oxygen to the lungs is sharply limited.
To eliminate an attack of atopic allergies, a whole range of measures is required. First of all, they are directed to the removal of the symptoms of the disease. A calm and relaxed state during an attack is a necessary component, if a person begins to worry and worry, then his situation only gets worse. Slow inhalations and exhalations, a stream of fresh air (not cold), a horizontal position of the body will help to cope with an attack of atopic asthma in a matter of minutes.
Ideally, you need to have an inhaler with a drug. Its use will quickly relieve a suffocating attack and restore the smooth muscles of the respiratory system.
Asthmatic status. Extremely life-threatening is a form of manifestation of atopic asthma, which develops an asthmatic condition called status asthmaticus. It is a long-term, not amenable to traditional drug treatment, suffocation, in which a person is simply unable to exhale air. Such a state develops from some clouding of consciousness to its complete loss. At the same time, the general well-being of a person is extremely difficult. Lack of proper treatment can lead to disability and even death.
Treatment of allergic asthma

Treatment of atopic asthma should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Self-medication therapy can aggravate the disease. This type of asthma is treated with the same means as other forms of asthma, but it is important to take into account the allergic nature of the disease.
Timely intake of antihistamines can reduce the manifestation of symptoms and the severity of atopic asthma. The modern pharmaceutical market offers a wide selection of such products, so choosing the right drug is not so difficult. The antihistamine effect is achieved by blocking receptors, as a result of which the release of histamine into the blood is either completely absent, or its dose is so small that it does not cause any response.
If a situation arises when it is impossible to avoid meeting with an irritant, it is necessary to take an antihistamine in advance, then the likelihood of an acute response is significantly reduced.
In medicine, there is a technique in which an allergen substance is introduced into the human body. Gradually the dosage increases. Thus, susceptibility to a certain stimulus is formed, thereby reducing the likelihood of allergy attacks.
The most common method of combating atopic asthma is the use of inhaled glucocorticoids and long-acting α2-adrenergic blockers. This is the basic therapy that helps to control the course of the disease for a long time.
Antibodies-antagonists of immunoglobulin E serve to eliminate the hypersensitivity of the bronchi and prevent a possible exacerbation for a sufficiently long period.
A group of drugs called cromones is actively used in the treatment of childhood allergic asthma. However, in adults, treatment with these drugs does not bring the desired result.
Methylxanthines are used in exacerbation of atopic asthma. They act very quickly by blocking adrenoreceptors. The main substances of this group of drugs are adrenaline and oral glucocorticoid.
Against the background of all medications, inhalation drugs are the priority, which, using a special device, penetrate directly into the respiratory tract of a person suffering from atopic asthma. In this case, an instant therapeutic effect occurs. In addition, inhalations are devoid of side effects that drugs often have.
Allergic asthma can and should be treated, but therapy should be structured in such a way as to take into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease. This can be done by a qualified doctor, based on the data of the clinical picture of the disease and diagnostic tools. Untimely treatment or improperly constructed therapy leads to a huge risk of developing pathological conditions in the body, as a result of which atopic asthma can become more severe, even death or disability.
In general, the prognosis for life with proper treatment is quite favorable. The main complications of atopic asthma include developing pulmonary emphysema, pulmonary and heart failure.
To date, there are no effective preventive measures that could completely eliminate the possibility of allergic asthma. The problem is solved only when a disease occurs and is reduced to the elimination of allergens and adequate treatment, the main task of which is to stabilize the course of the disease and reduce possible exacerbations.









