Contents

Worms is the name for a large group of lower worms that parasitize in the human body. They provoke diseases called helminthiases. There are three classes of worms: tapeworms, roundworms and flukes. Science knows 300 species of helminths that can exist in the human body, however, no more than 70 helminths are found on the territory of the Russian Federation. The breadth of the distribution of helminthic invasions depends on the climatic conditions in a particular country, on the level of its economic development. Therefore, helminthiases are more common in tropical and subtropical countries, as well as in developing countries.
Modern scientists significantly underestimate the importance of helminthic invasions for human health, although many of the leading doctors and researchers around the world have long sounded the alarm about this. In Russia alone, about 500 new cases of infection are registered every year. Most of these patients are children. They account for up to 000% of all helminthiases. Moreover, 80 is a very average figure, since there are data on an annual invasion of 500 million people. It has been established that people living outside the city are more likely to become infected, since the contamination of the soil and the possibility of contact with worm eggs are much higher there.
Worms can be transmitted to humans in three ways:
From animals to humans (biohelminthiasis);
From person to person (contagious helminthiases);
Geohelminthiases (the development of worms occurs in the soil).
The symptoms of worms depend on how massive the invasion is, how the worm entered the body, how well it adapted in the human body, etc.
Of particular danger to human health are the larvae of worms and those forms of worms that are in the process of growth and development. If a sexually mature adult worm occupies a certain place in the patient’s body, then the larvae are most often in the migration stage. They can damage various organs, settle in them, injure their membranes, disrupt their functioning. Most worms are intestinal worms. Depending on their type, the specific location of the worm will differ. For example, pinworms prefer the lower part of the small intestine and the upper parts of the large intestine, roundworms parasitize in the upper part of the small intestine, the whipworm stops at the beginning of the large intestine.
Depending on where exactly the worm parasitizes, experts distinguish between tissue and luminal helminthiases. In the first case, the worms stop in the thickness of the tissues, and in the second case, they live in the lumen of the organ. And it doesn’t have to be the gut.
What are worms?
There are several types, classes and groups of worms.
The criterion for classification is the features of the life cycle of worms and the source of the spread of helminths:
Geohelminths. The larvae of these worms mature in the soil.
Biohelminths. The larvae of these worms mature in the body of an animal or insect. They are the source of invasion.
contact worms. Humans are the sole host of worms. You can only get infected from it.
The criterion for classification is the biomorphological features of worms:
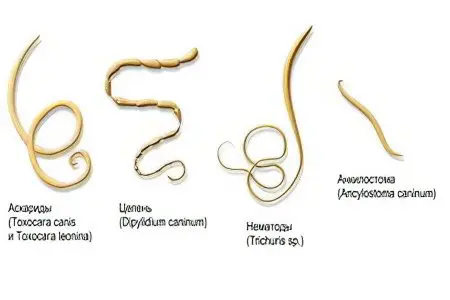
Nematodes or class of roundworms. Worms are always of different sexes, their body sizes vary. The most common worms in this class are pinworms and roundworms.
Flukes or a class of trematodes. These worms always need an animal in whose body they develop. All worms in this class are hermaphrodites. Worms are armed with suckers and hooks, which act as a device for fixing to the internal organs. In addition, suction cups can perform another function, for example, to be used as a mouth opening. Representatives of trematodes are schistosomes and opisthorchid.
Cestodes or a class of flatworms. The food of such worms is carried out with the help of a cover lining their long body. These parasites do not have an intestinal tube. The most common worms of this class are pork and bovine tapeworm, as well as echinococcus.
If all representatives of the trematode class and the cestode class are parasites, then the nematode class is not always parasitic worms. This class includes more than 20 worms, most of which do not need living organisms (animals and humans) to carry out their own life activities.
Human parasites also include protozoan microorganisms. They, contrary to popular belief, are not worms. Representatives of this class are Toxoplasma, Giardia and Amoeba.
The most common human worms:
What do worms look like and where do they parasitize? How many live? |
Echinoderms (enterobiosis)
The maximum pin size is 10 mm. The color is milky white. Worms of this species parasitize in the human intestine. The female lays her eggs on the perianal folds. The source of the spread of helminthic invasion is a person. The life expectancy of adult pinworms is 2 months. Their eggs are highly contagious, and the female can leave several thousand eggs in one clutch. |
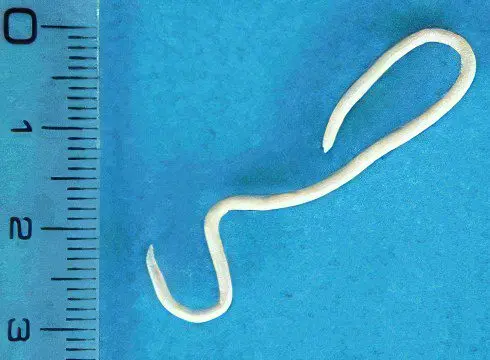
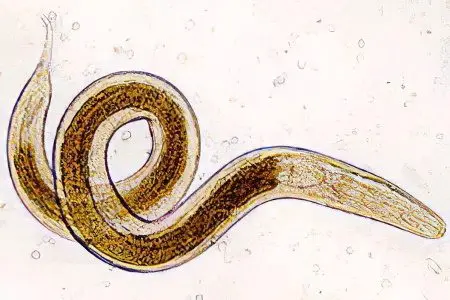
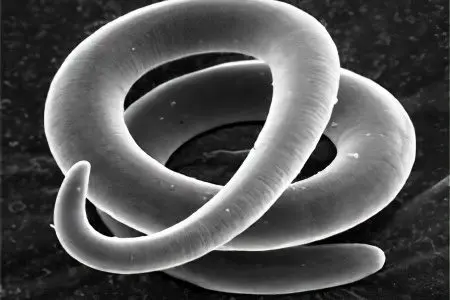
Ascariasis (ascariasis)
Ascaris in length can reach 40 cm (females) or 25 cm (males). The maximum width of the worms is 6 mm. The color of the parasites is pinkish-yellow, the shape is spindle-shaped. Ascaris larvae mature in the soil. From the soil, they enter the human intestine through the digestive tract, after which the larvae are carried through the body with the bloodstream. Classical migration is as follows: liver, lungs, bronchi, trachea, throat, oral cavity, intestines. After re-entering the intestine, the worm turns into an adult and begins to lay eggs, which, together with feces, go out into the external environment. Sometimes the larvae of these worms can settle on the internal organs, disrupting their work. They are able to penetrate the skin, the brain, the organs of vision, the heart. The life span of roundworm in the human body is 2 years. |
Vlasoglav (trichocephalosis)
The length of the worm is 50 mm, and the width is not more than 0,5 mm. The end of his body is pointed. It is with its help that the parasite is attached to human organs. Parasite eggs mature in the ground. After entering the intestines, their shell dissolves and larvae emerge from them. Vlasoglavy are frequent “inhabitants” of the caecum and appendix. In the human intestine, the parasite can survive for about 4 years. |
Toxocariasis
This worm belongs to the group of roundworms. It has a structure similar to roundworm, but it can reach 10 cm in length. Toksokara has a yellowish color A person becomes infected with toxocariasis from animals, mainly from dogs and cats. In just 24 hours, an adult female Toxocara is able to release about 250 eggs. They come out with the feces of an infected animal and enter the human intestine. There, the shell of the egg dissolves and the larva hatches from it. It migrates through the human circulatory system in his body. The larva passes through the liver, spleen, lungs, heart. It can settle in the skin and in the eyes. Toksokara is not able to become a sexually mature individual in the human body, since there are no conditions suitable for the worm in it. Therefore, the parasite is encapsulated. In this state, the worm can exist in the human body for about 10 years. |
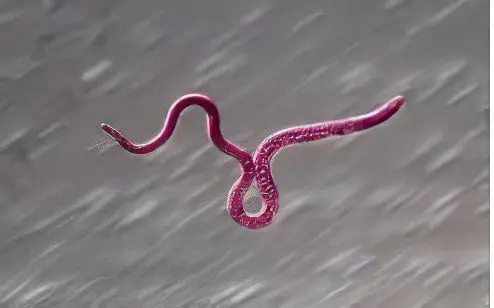
Trichinella (trichinellosis)
This is a small roundworm. Its length does not exceed 5 mm. The worm belongs to the class of biohelminths, which parasitizes mainly in the body of livestock and wild animals. A person becomes infected while eating poorly processed meat. In the human intestine, the female worm gives birth to larvae that migrate through the circulatory system. Most often they settle in skeletal muscles. The life of the worm is not more than 5 years. |
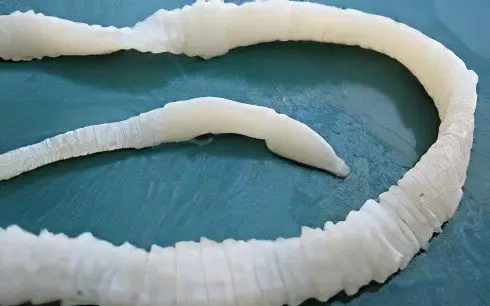
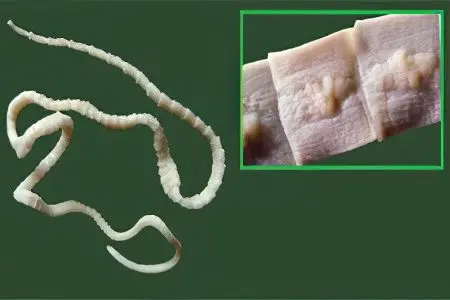
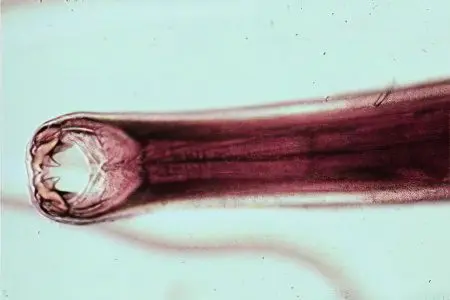
Bull tapeworm or tapeworm (taeniarinhoz)
Worm in length can reach 30 meters. His body is represented by a small head and segments, of which there are several thousand. The tapeworm is a biohelminth, since for the development of its larvae the worm needs an animal. A person becomes infected by eating infected beef. In the human small intestine, the worm begins to grow, which comes down to the constant formation of new segments with eggs. The lifespan of a bovine tapeworm in the human body can be up to 10 years. |
Pork tapeworm or tapeworm
The morphophysiological characteristics of the worm are similar to the morphophysiology of the bovine tapeworm. But the pork tapeworm is somewhat smaller. Its maximum length is 5 meters. You can also become infected with a tapeworm by eating infected pig meat and from a sick person. The danger is not only the larvae of the parasite, which provoke a disease called taeniasis, but also its eggs, which cause cysticercosis. The tapeworm larvae settle in the small intestine, where they begin their growth. The tapeworm eggs migrate throughout the human body and can settle in any organ. Eggs enter the external environment along with feces. They are contained in the segments of the worm. The lifespan of a tapeworm can be up to 30 years. |
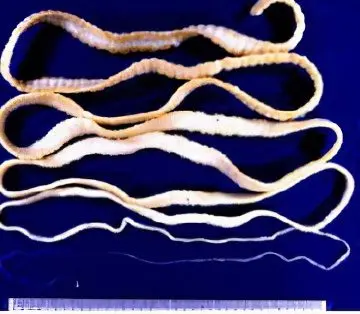
Wide ribbon
A flatworm that can grow up to 10 meters in length. The larvae of the tapeworm go through their development in the body of fish that live in freshwater reservoirs. A person becomes infected by eating such fish. The worm parasitizes in the human small intestine, releasing segments containing eggs into the external environment. Its life expectancy can be several decades. |
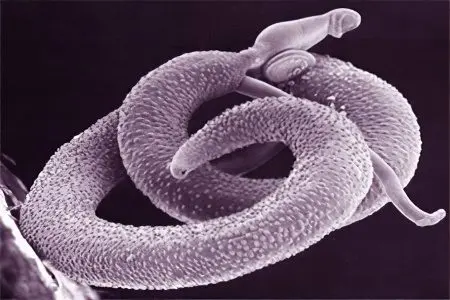
Echinococcus
The worm is small in size, on its head are hooks and suckers. The body consists of several segments. Worm larvae form cysts (bubbles containing both larvae and eggs). The diameter of the cysts can reach 10 cm. The larvae enter the human body from infected dogs and livestock. In the intestines, they begin to grow, lay eggs there. The larvae enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Settling in various organs, they form cysts that contain larvae and eggs. They are able to maintain their viability for many years. |
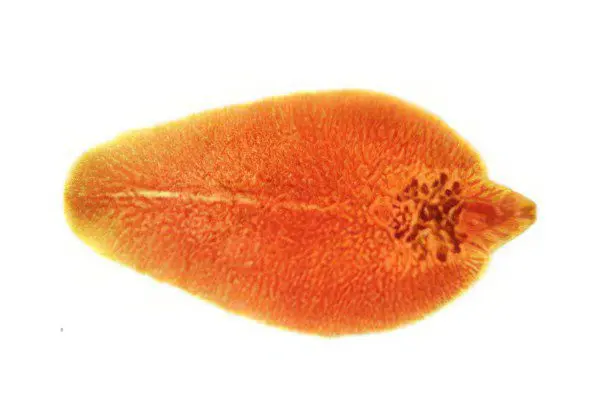
Siberian or cat fluke (opisthorchiasis)
A small worm that does not exceed 10 mm in length. It attaches to the internal organs with the help of an oral sucker. A person becomes infected by eating the meat of an infected fish. Worms settle in the lumen of the bile ducts, in the ducts of the pancreas, in the intestines. The worm can reproduce very quickly. It exists in the human body for about 20 years, and at the same time up to several thousand individuals can parasitize in the body. |
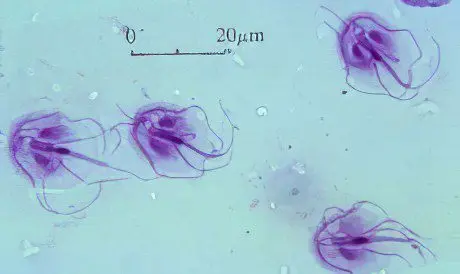
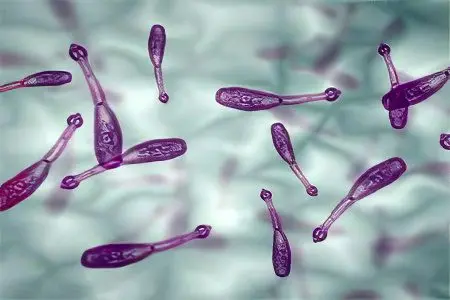
Giardia (giardiasis)
These are protozoan microorganisms that are very small in size. One individual in length does not exceed 12 microns. Some varieties of Giardia have flagella for movement, while others lack these flagella and are unable to move. The source of the invasion is a sick person. Giardia inhabit the small intestine, multiply by division. Cysts go into the external environment, and new Giardia remain in the human body. The life span of lamblia is about six months. Giardia quickly die when it enters the large intestine. |
The most common worms in the world are pinworms, roundworms and whipworms. In some countries, other types of worms are more common, which depends on their location relative to the equator, the sanitary and hygienic education of the population, and the predominance of one or another type of animal that is the carrier of worms.
Signs and symptoms of worms in humans

Different types of worms provoke different signs and symptoms, however, they will always be present in varying degrees of severity. Firstly, all worms secrete toxins that negatively affect the functioning of the body. Secondly, the infected always have an allergic reaction to the invasion. Thirdly, the functioning of the organ that has been attacked by worms worsens.
At first, people do not feel the presence of worms in the body. But over time, the symptoms and signs of worms in a person increase and begin to bother him more and more. Moreover, the clinical picture of helminthic invasion is constantly progressing. Often, the symptoms of a particular type of helminthiasis do not directly indicate the presence of worms in the body. However, a doctor may even suspect by indirect signs that a person has a parasitic invasion.
What are the very first signs of worms?
The first signs of worms can be considered:

Over a long period of time, a person retains an increase in body temperature to a mark of 38 ° C. At the same time, it is not possible to find other visible reasons for persistent subfebrile condition.
Abdominal syndrome, which is primarily manifested by pain in the navel, in the right hypochondrium.
Sometimes a person may experience vomiting, nausea is often disturbing.
The chair becomes unstable, constipation is replaced by diarrhea.
Appetite is disturbed. Most often, it first increases and then disappears.
The person begins to lose weight.
The skin becomes pale, bruises appear under the eyes.
The patient is worried about itching, a rash appears on the body. Allergic reactions proceed according to the type of urticaria, or according to the type of atopic dermatitis.
The patient gets tired faster, begins to experience weakness even in the morning hours, and performance deteriorates.
Characterized by emotional lability.
Often a person begins to pursue a dry cough, shortness of breath, noisy breathing appears.
Night rest is disturbed.
Bruxism is an indirect sign of a parasitic invasion.
Symptoms of long-term presence of worms in humans

Symptoms of prolonged helminthic invasions in humans (chronic helminthiases):
Deterioration of the immune system, as a result of which a person becomes more susceptible to bacterial and viral infections.
Strong weakness.
Pronounced signs of beriberi, including: increased fragility of the nail plates, alopecia, pallor and dry skin, destruction of tooth enamel, bleeding gums.
An unpleasant odor constantly emanates from the patient’s mouth, from which it is impossible to get rid of.
The patient’s weight continues to fall.
The risk of developing nervous disorders increases, including: apathy, depression, etc.
In addition, the symptoms of worms in humans largely depend on which organ has been affected. If the liver is damaged, it will be enlarged. Often these patients develop jaundice. If the worms have migrated to the lungs, then the patient complains of shortness of breath and cough, blood impurities may appear in the sputum.
However, there are also specific signs characteristic of a particular helminthic invasion. So, when the intestines are colonized with pinworms, the patient will experience severe anal itching. Sometimes he independently detects small worms in the feces. Frequent companions of enterobiasis are vaginitis and vulvovaginitis.
If there are a large number of worms in the intestine at the same time, then there is a risk of developing such complications as intestinal obstruction. This is due to the fact that the worms stray into a ball. At the same time, a person begins to suffer from severe pain in the abdomen, intestinal motility stops, and body temperature rises. In this case, only surgery can help.
The intestine is not the only organ in which obstruction develops. The pancreas, brain, liver ducts, heart and other internal human systems can suffer. As a result, the organs cease to function normally, which requires emergency medical care.
It is known that echinococcosis larvae form cysts. The rupture of such a formation is very dangerous for human health, since this process is always accompanied by the release of a huge amount of toxins. In this case, the larvae themselves enter the bloodstream. It is possible that toxic shock will develop and the person will die.
Biochemical indicators indicating the presence of worms in the body
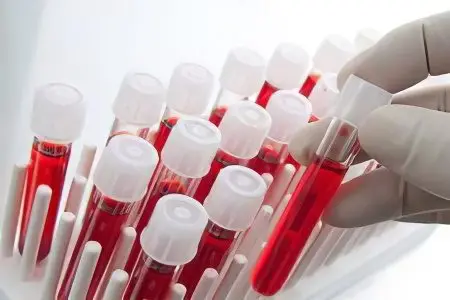
During the examination, a specialist can detect the following symptoms of worms in a patient:
Standard Inspection:
Lymph nodes are enlarged. Moreover, a similar reaction is observed immediately in several groups of lymph nodes.
Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, and pancreatic enlargement.
Symptoms of pneumonia on auscultation of the lungs.
Changes in the general blood test:
Anemia (hemoglobin below 100 g / l /), a decrease in the level of red blood cells (below 3 g / l).
The growth of ESR, exceeding 15 mm / h.
Eosinophilia with an increase in the number of eosinophils by 6% or more.
Leukocyte jump, the level of leukocytes exceeds 9 g / l.
Change in biochemical blood test:
The level of immunoglobulin E is high.
The level of total protein is low.
Symptoms of worms depending on their type
Type and symptoms of worms |
Pinworms
Pinworms parasitize the human small intestine. This helminthic invasion is the most common in the world. The disease they cause is called enterobiasis. Symptoms of pinworms in humans are as follows:
Children are more susceptible to enterobiasis, although the disease is often diagnosed in adults. |
Roundworm
Roundworm parasitizes the human intestine, causing a disease called ascariasis. This helminthic invasion is the second most common after enterobiasis. Symptoms depend on the age of the person, on the phase of the disease, on the number of worms in the body. Symptoms of the migration phase of Ascaris larvae:
Symptoms of the intestinal phase of ascariasis:
The more massive the invasion with roundworms, the stronger the symptoms of the disease will be. Invasion can be complicated by liver abscesses, appendicitis, peritonitis, cholangitis, pancreatitis. With obstruction of the lungs by roundworms, the development of suffocation is possible. |
Whitewash
Vlasoglav parasitizes in the human intestine and causes a disease called trichuriasis. Symptoms of whipworm parasitism in the body:
The severity of the invasion is largely determined not only by the age of the patient, but also by the presence of other worms in the body. So, severe forms of trichocephalosis are observed in those patients who are simultaneously infected with amoebas and roundworms. |
Wide ribbon
A wide tapeworm parasitizes in the human intestine and causes a disease called diphyllobothriasis. Symptoms of a wide tapeworm in the human body can be bright, or, on the contrary, blurred:
If the disease is very severe, then the patient’s liver and spleen increase in size, intestinal obstruction may develop. |
hookworms
Hookworms parasitize in the human intestine and cause a disease called hookworm. Symptoms indicating the presence of hookworm in the human body:
If children suffer from worms, then a delay in mental and physical development is likely. Adult patients become more irritable, aggressive. Women experience disruptions in the menstrual cycle. |
Trichinella
Trichinella in the mature stage parasitizes in the wall of the small intestine, and in the larval stage in the striated muscles (an exception is the heart muscle). Trichinella symptom:
Symptoms reach their maximum by the end of the 7th day after the invasion, and after 3-4 weeks the disease ends. |
liver fluke
The liver fluke is an extraintestinal worm that parasitizes in the liver parenchyma and in the biliary tract, causing a disease called fascioliasis. Symptoms of parasitism of the liver fluke in the human body, characteristic of the acute stage:
The acute phase of the disease passes after 3-6 months, after which the chronic phase of the disease begins. It is characterized by such symptoms as: pain in the right hypochondrium, jaundice, hepatomegaly. They are caused by damage to the liver and biliary tract. |
Pork and bovine tapeworm
Pork tapeworm is an intestinal parasite from the group of cestodosis. The worm causes a disease called taeniasis, and its larvae cause a disease called cysticercosis. Teniosis symptoms:
The extraintestinal form of taeniasis is cysticercosis. Very often, infection occurs during vomiting, when the vomit thrown into the stomach contains segments and invasive eggs. They migrate throughout the body and settle on various organs. Science knows cysticercosis of the brain, lungs, heart and skin. Symptoms of the disease depend on which organ is affected:
The bovine tapeworm is a close relative of the pork tapeworm. It also parasitizes the human intestine and causes a disease called taeniasis. A distinctive feature of this worm is its impressive size, which can reach 12 meters. Symptoms of teniarynchosis:
Both bovine and pork tapeworm can cause serious complications for human health. |
Echinococcus
In the human body, Echinococcus parasitizes in the oncosphere stage. The disease may not manifest itself in any way for several decades. This period is called the latent stage. The parasite invades human tissues and exists there until a certain point in time. Symptoms of echinococcus in the stage of clinical manifestations are as follows:
A person suffers from nausea and diarrhea at regular intervals if a cyst forms in the liver. In addition, the patient’s appetite is disturbed, weight is lost. If the oncosphere is located in the lungs, then the pains are localized in the chest, coughing and shortness of breath appear. Subfebrile condition persists for a long time. When the cyst is in the brain, the patient develops characteristic cerebral symptoms. It largely depends on where exactly the neoplasm is located. Possible paresis of the limbs, deterioration of sensitivity, epileptic seizures, etc. If the oncosphere develops in the heart, then the patient experiences pain behind the sternum, they are similar in nature to angina pectoris. When the formation is ruptured, the patient develops symptoms of intoxication, pleurisy, peritonitis, ascites, myocardial infarction, cardiac tamponade and other complications may develop. |
Alveococcus
Alveococcus is dangerous for humans in the larval stage. It settles in the human liver, after which it begins to spread metastases to various organs: the brain, lungs, etc. The disease is called alveococcosis. Symptoms that indicate the presence of a worm in the body may be absent for many years. In the preclinical period, a person will periodically be disturbed by pruritus and urticaria. It is also possible to develop an attack of hepatic colic and dyspeptic disorders. The remaining symptoms of the disease are not very specific for alveococcosis (periodic pain in the right hypochondrium, a feeling of heaviness, an increase in the liver in size, loss of appetite). When the disease clinically manifests, the patient develops severe complications, including:
Alveococcus sends metastases to other internal organs, which can lead to the rapid death of the patient. |
Flukes
Trematodes are flat worms that cause dangerous diseases in humans, which are called trematodes. About 40 species of trematodes are capable of parasitizing in the human body, among which the most common are: liver fluke, cat fluke and schistosome. The main symptoms that indicate the presence of trematodes in the body:
Perhaps some variety of symptoms, with the prevalence of certain clinical signs. It depends on what kind of worm from the trematode class lives in the human body. |
Symptoms of worms in children
The pediatrician of the highest category – Mikhailova Tatyana Mikhailovna will tell you about the symptoms of worms in children: