Contents
If there is a decrease in milk yield in the herd, cows lose weight for no apparent reason, cases of death become more frequent, then most likely the cause is worms in cattle. Parasites in the body of an animal are diverse, the disease often occurs without symptoms, so it is important to remember about prevention methods and know how to treat cows. Most often, helminthic invasion affects calves, the treatment of which is difficult.
Cattle parasites
Various types of worms cause helminthiases in cattle, they settle in the intestines, heart, kidneys, liver or lungs of the animal. Most often found in cows and calves:
- gastrointestinal nematodes;
- respiratory roundworms;
- subcutaneous, heart and other nematodes;
- trematodes;
- cestodes.
All worms are similar in morphological features, but outwardly different. The methods of defeat are also different.
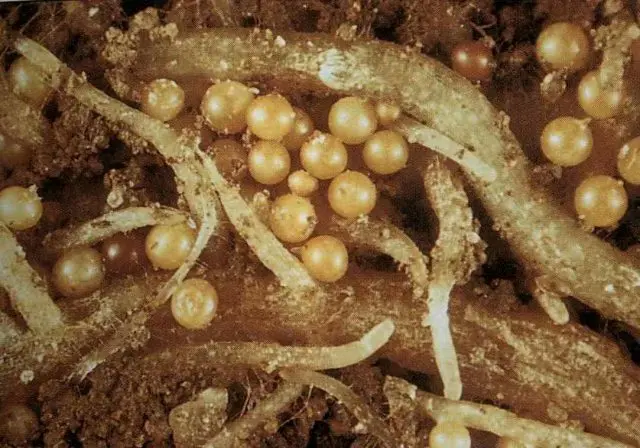
Gastrointestinal worms in cattle are of several types.
View name | Description |
Bunostomum | The parasite is grayish in color, no more than 3 cm long. It occurs in regions with a humid and warm climate. Worms settle under the skin, can affect the lungs |
Сooperia | Red worms up to 10 mm, ubiquitous |
Gongylonema | Yellow-brown worm, up to 14 cm long. Males – no more than 6 cm. Worms affect the esophagus and stomach walls |
Haemonchus | The parasites are red in color, the body is up to 3 cm in length. They live everywhere in pastures. Worms settle in the stomach and liver of cattle |
Nematodirus | White worms – up to 2,5 cm. Found in temperate regions |
Radiate oesophagostomy | They live in regions with a hot and humid climate. The body of the parasite is up to 25 mm. Live in the small intestine |
Ostertagia | Worms are common in the Northern regions. Thin brown worms – up to 12 mm long. Strike the young |
Strongyloides | They are found in farms with violations of sanitary standards. Parasites are almost transparent in color, no more than 6 mm long. Settle in the lungs and intestines |
Toxocara calves | Worms live everywhere. They look like boiled spaghetti. Worms live in the small intestine and stomach of cattle |
Trichostrongylus | Parasites are everywhere. These are red-brown worms – from 5 to 10 mm long |
Respiratory roundworms infect young cattle in regions with cold and humid climates where it often rains. These are medium-sized parasites, up to 8 cm long, white or gray in color. Most often, worms affect the respiratory tract and cause bouts of severe coughing. With advanced invasion, pulmonary edema or pneumonia occurs.
Of the subcutaneous worms in Our Country, the genus Parafilaria bovicola is most often found in cattle. These are white worms up to 6 cm long. They settle under the skin of calves in the back and abdomen.
Trematodes or flatworms are common throughout the world. These are oval-shaped parasites, the body of which does not exceed 30 mm in length. They have oral and ventral suckers. The color can be from white to dark red, depending on the species. Most often they parasitize in the stomach and small intestine.
Tapeworms or cestodes in the body of cattle are in the larval stage until they get into a suitable environment. In some cases, they do not pose a big threat to cows and calves. But there are exceptions, such as the Moniezia worm. It grows in the body of cattle and reaches a final size of 10 m.
How does the infection occur?
The defeat of cows with worms occurs through the larvae that enter the body of cattle along with food or water. Even compliance with all sanitary standards does not guarantee that there are no parasites in the herd. Animals can become infected with worms on the run, eating grass, beetles and other food.
The defeat by nematodes occurs mainly in the pasture, when young cattle are walking along with adult cows. The larvae of the worms enter the bloodstream of the animal, from where they reach all the organs of the calf. For more than 3 weeks, the parasite lives in the body, gradually maturing and laying new larvae. Ready for invasion worms, getting into the external environment, remain viable at temperatures up to 27°C. At higher rates, their development is inhibited, but does not stop. If a cow becomes infected with worms in autumn, then the larvae remain in her body until spring.
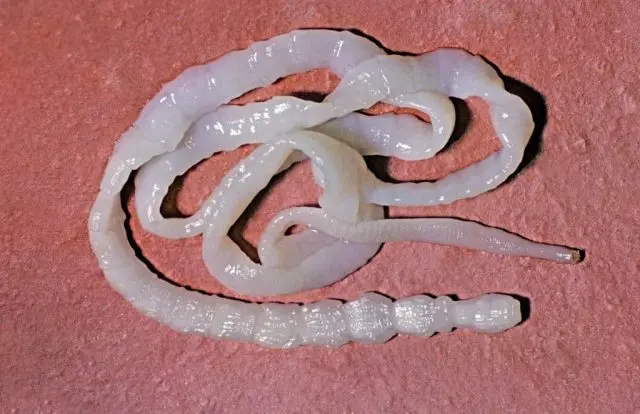
Tapeworms most often infect young animals. Cattle get into the body along with a pasture tick, which swallows up to 200 worm larvae. After 15-20 days, the worm becomes sexually mature and is ready for reproduction.
Symptoms of helminths in cattle
If the worms have settled in the liver or other organs of a cow, then only a veterinarian can determine the degree of invasion. The owner should pay attention to the external signs and symptoms of damage:
- the animal is oppressed, oppressed;
- disheveled wool;
- appetite is absent or weak;
- young cattle are lagging behind in development;
- diarrhea is observed;
- anemia occurs;
- when the respiratory tract is affected, coughing, wheezing occurs;
- purulent discharge appears from the nose;
- young cattle lose weight, exhaustion sets in.
If treatment for worms is not started in time, then the death of calves and cows occurs as a result of blockage of the intestines, suffocation with balls of helminths or exhaustion. Recovery is possible, but such an animal is not suitable for breeding.
In some cases, there are no obvious signs of helminths. However, the quantity and quality of milk is declining. A pregnant cow has a miscarriage or postpartum bedtime.
Deworming of cattle
Infection with helminths occurs quickly. The whole herd suffers from one sick animal, so the fight against worms begins immediately.
Therapeutic
In order to relieve worms of cattle calves with medication, you need to inject drugs into the throat of a sick animal. The process of destruction of helminths begins in the stomach, where the anthelminthic agent enters.
Before processing the animal, you need to correctly calculate the weight so as not to cause poisoning and overdose. The cow’s head is held obliquely, forcing her to drink the mixture.
All drugs for worms in cattle have severe side effects, so you cannot make a decision on treatment on your own. First you need to accurately establish the diagnosis, consult with a veterinarian.
Prophylactic
In order to prevent deworming, do 2 times a year. Usually in spring and autumn. Medications should be distributed to all animals, as time passes from the lesion to the first symptoms.
Preparations for cattle from parasites
There are a lot of drugs for the treatment of cows from worms. These are tablets, powders, injections. They are selected depending on the type of parasites.
The most common drug for various nematodes is Tetramizol. The granules of this remedy are mixed with drinking water and forcibly poured into the mouth of the cattle. The drug is distributed in the fall, when the animal is no longer on the run. For one adult, 45 g is calculated, while the calf is given 15 g for every 10 kg of weight. Under the action of Tetramisol, diarrhea stops on the second day.
Preparations from flatworms are very toxic to humans, therefore they require a long exposure to milk and meat. Most often for the treatment of CRS use:
- “Hexihol”;
- “Hexachloroethane”;
- “Acemidofen”;
- “Clozatrem”.
Medicines are administered orally or parenterally. From parasites in the liver, intramuscular preparations are used. Injections to cows are administered on the basis of Closanthine.
For the treatment of tapeworms in cattle and nematodes, veterinarians recommend the use of complex means:
- “Panakur”. A suspension is prepared from the powder, which is orally injected into the stomach of cattle. The dose is calculated at 3,3 g for every 100 kg of weight. After treatment, milk is not consumed for 3 days, and meat for about 10 days.
- “Albendazole”. The drug in the form of an emulsion is distributed to cows at the rate of 30 ml for every 100 kg of weight. The medicine is contraindicated for pregnant animals of the first trimester. The suspension is not used during the period of exacerbation of infectious diseases of cattle. Before drinking milk, you need to withstand 4 days, for meat the ban is up to 20-25 days.
Deworming of cattle with powders or other oral agents is repeated after 14 days. If injections were used, then the powders are re-introduced. Worms in cattle are completely eliminated from the body after 40-45 days, after which the tests must be repeated.
When choosing a drug for worms in cattle, you need to consider whether it can be given to pregnant cows, at what dose, and in what trimester. With special attention, you need to approach the treatment of a dairy cow. If it is not possible to take tests for helminths, then you need to choose broad-spectrum drugs.
One deworming of cattle is not enough, because drugs for worms only remove parasites, but the consequences of their activity must be treated differently. Be sure to pierce the cow with vitamins and immunostimulating drugs to support the liver, kidneys and lungs of the animal. After that, it is advisable to give drugs that are aimed at removing toxins from the body, since there is a general intoxication of cattle. The most popular among medicines are:
- Oligovit;
- “Catozal”;
- “Trivit”;
- “Introvit”.
In some cases, probiotics and prebiotics are added, which restore the intestinal and rumen microflora.
Prevention
To protect young cattle from parasites, feeding and watering are organized in special places equipped with everything necessary. Access to water must be dry. If this is not possible, then year-round stall maintenance is practiced.
For the purpose of prevention, the pasture is replaced with a clean one. Cultivate greens and destroy pests. After the parasites die in the grass, the cattle are returned to the old pasture.
In order for the animal’s body to independently fight against worm larvae, it is necessary to keep young cattle in clean rooms, feed the herd with balanced feed. That is why, in order to prevent worms in cattle, pumpkin, birch tar, wormwood grass, flax seeds or oil, specialized top dressing with an anthelmintic composition are introduced into the diet.
Conclusion

Worms in cattle is a serious and dangerous disease that should not be ignored, otherwise you can lose most of the herd. To protect young and adult cows, prevention is carried out twice a year. But drugs are not prescribed on their own, as they have strong side effects. Only a veterinarian can prescribe medicines after a detailed examination and analysis of cattle.










Nimependa elimu yako
SPRANGI YA NDAMAN